![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Levels of organization |
Biosphere, ecosystem, communities, populations, organisms, organs, tissues, cell, organelles, molecules. |
|
|
What is reductionism? |
Analyzing the most basic physical mechanics ism that are in operation during this phenomenon. |
|
|
What is emergent properties? |
The result from interactions among components at lower levels. |
|
|
What is an example of structure and function? |
Your finger are able to move to help you pick things up and eat. |
|
|
What is the basic unit of structure and function? |
Cells |
|
|
What is the difference in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? |
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled, no true nucleus. Eukaryotes cells are multi-celled and have a nucleus with DNA and RNA. |
|
|
Information on DNA is stored as four nucleotides that are called? |
A, T, C & G |
|
|
What is a gene? |
A discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of specific nucleotide sequences in DNA or RNA. |
|
|
What is a chromosome? |
A cellular structure consisting of one DNA molecule and associated protein molecules |
|
|
What does DNA stand for? |
Deoxyribonucleic acid |
|
|
What does RNA stand for? |
Ribonucleic acid |
|
|
What is transcription? |
.process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA |
|
|
What is translation? |
information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA |
|
|
The study of all info on whole set of genes is called? |
Genomics |
|
|
Study of protein and their properties? |
Proteomics |
|
|
What is negative feedback, what is positive feedback? |
Negative feedback a loop in which the response reduces the initial stimulus as seen in the example of insulin signaling after a meal the level of sugar glucose in your blood Rises, which stimulates the cell of the pancreas to secrete insulin. Positive feedback is when the products speeds up its own production for example the clotting of your blood in response to the injury is an example. |
|
|
What is unity and diversity? |
The process of evolution explained next illuminates both similarities and differences in the world of life. |
|
|
Are organisms living on the earth modified descendants of common ancestors? |
Yes |
|
|
Dr. King Paul came over for good spaghetti, what does this do you know? |
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species |
|
|
What is taxonomy? |
A scientific discipline concerned with naming and classifying the diverse forms of life . |
|
|
What are the three domains in life? |
Archaea , bacteria, and Eukarya |
|
|
Which three kingdoms are multicellular under domain Eukarya? |
Animalia, plantae, and fungi |
|
|
Which kingdom is single-celled eukaryote? |
Protist |
|
|
Explain descent with modification |
Has Charles Darwin's always said, if he was talking about the finches if there was more seeds that were smaller than the birds would need smaller beaks but if the birds were after bigger seeds than they would need bigger beaks so, we are all arising from our ancestors but we differ from Evolution to what would better our species. |
|
|
What is natural selection? |
Natural selection is an evolutionary mechanicsism for descent with modification. |
|
|
What are the three theories of natural selection? |
Populations vary in trait Population can produce more offspring that can survive. Species adapt to environment. |
|
|
What is a hypothesis? |
Is an explanation, based on observations and assumptions, that lead to a testable prediction. |
|
|
What is an experiment? |
Is it a scientific test, carried out under controlled conditions. |
|
|
What is a null hypothesis? What is a alternative hypothesis? Give examples (plants ) |
Null hypothesis: says there is no statistical significance between the two variables. Alternative hypothesis: there is a statistically significant relationship between two variables. Example : Null: If one plant is fed club soda for one month and another plant is fed plain water, there will be no difference in growth between the two plants. Alternative: If one plant is fed club soda for one month and another plant is fed plain water, the plant that is fed club soda will grow better than the plant that is fed plain water. |
|
|
How can you test hypothesis? |
Making additional observations. |
|
|
What is deductive reasoning? What is inductive reasoning? |
Deductive reasoning involves logic that flows in the opposite directions, from of General to specific. Inductive reasoning used to reach a logical true conclusion. All men are mortal therefore Herald is mortal. |
|
|
What kind of phenomenon cannot be tested by science? |
Science only deals with natural, testable explanation for a natural phenomena, it can either support nor contradict the invisible ghost hypothesis, nor whether Spirits or elves cause storms, rainbows or illnesses. Anything Supernatural simply can't be proven by science. |
|
|
What is an experimental variable? |
A feature or quantity that varies in an experiment. |
|
|
What is a controlled experiment? |
One that is designed to compare an experimental group with a control group. |
|
|
What is an independent variable? |
The factor being manipulated by researchers |
|
|
What is the dependent variable? |
The factor being measured that is predicted to be affected by the independent variable. |
|
|
What is a control group? |
group in an experiment or study that does not receive treatment |
|
|
Is Theory the same as speculation? |
Yes |
|
|
Theory vs. hypothesis, which has a greater body of evidence? |
Theory has a greater body of evidence because it has been proven where as a hypothesis you were trying to prove. |
|
|
Which one has a broad scope Theory or hypothesis? |
Hypothesis |
|
|
What type of data includes measurements? |
Quantitative |
|
|
In an experiment measuring the effects of temperature on solubility which is the dependent and which is the independent variable? |
The dependent variable is solubility. The independent variable is temperature. |
|
|
Can an element be broken down into another substance? |
It cannot be broken down into another substance. |
|
|
Define a compound and give two examples? |
Compound is a substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio. NaCl is an example in H2O is another example. |
|
|
What is the meaning of trace elements? |
Required by organisms in only minute quantities. |
|
|
What is the smallest unit of matter called? |
Atoms |
|
|
What are the three subatomic particles and what is their charge and Mass? |
Neutrons equal no charge Protons are positive charge Electrons or negative charge. |
|
|
What is a unit of mass? |
Amu |
|
|
Which particle for the atomic nucleus? |
Protons and neutrons |
|
|
What is the atomic number? |
Is the number of protons. |
|
|
What is the mass number? |
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom. |
|
|
What is an isotope? |
Different Atomic forms of the same element. |
|
|
How does potential energy of electrons differ compared to the first in the third shell? |
In the first shell you are only able to carry two electrons. In the second shell and third shell you are able to carry eight electrons. |
|
|
What are valence electrons? |
Valence electrons are the outermost electron shell. |
|
|
What are inert elements? Give an example. |
substance is one that is not generally reactive. Inert elements are typically on the far right of the periodic table. Some examples of inert elements are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). |
|
|
What is an orbital? |
The three dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time. |
|
|
The second shell has how many P orbitals? |
The second shell has 6 P orbitals |
|
|
How are reactivity and unpaired electrons related? |
unpaired electrons are relatively uncommon in chemistry, because an entity that carries an unpaired electron is usually rather reactive. |
|
|
What is a covalent bond and give an example? |
A covalent bond is sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms. Two hydrogen atoms come close enough for the first orbital to overlapped, and they can share electrons. |
|
|
What is a polar covalent and nonpolar covalent bond. Give examples |
A polar covalent bond is when an atom is bonded to more electronegative atom, the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. A nonpolar covalent bond is when the electrons are shared equally because the two atoms have the same electronegativity, the tug-of-war is a standoff. |
|
|
What is the difference between molecular and structural formula? |
molecular formulas show the correct number of each type of atom in the molecule. structural formulas show the arrangement of the atoms and the covalent bonds between them. |
|
|
What is electronegativity give an example? |
The attraction of that particular atom for the electrons of the covalent bond. |
|
|
Cation is Anion is |
Cation is positive Anion is negative |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
Cations and anions attract each other this attraction is called ionic bonds |
|
|
What are two examples of weak bonds? |
Hydrogen bonds and Van Der waals interactions |
|
|
The bond that enables atoms and molecules to stick to each other are? |
Van Der waals interactions |
|
|
Why does CH4 have a tetrahedron shape? |
A methane molecule consists of Four Bond pairs (electrons participating in bonding) which repel each other. |
|
|
What happens to reactants and products during chemical equilibrium? |
When reactions offset one another. |
|
|
Orbital formula |
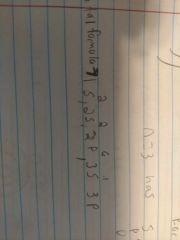
|

