![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are senses?
|
structures that allow us to sense our environment
|
|
|
What do general senses give information about?
|
conditions within internal organs
|
|
|
What are the special senses?
|
the modalites of smell, taste, vision, hearing, and equilibrium
|
|
|
What are the three classifications of sensory receptors by structure?
|
free ending, encapsulated nerve endings, and separate sensory cells
|
|
|
What are the three classifications of sensory receptors by location?
|
exteroceptors, interoceptros, proprioceptors
|
|
|
How are sensory receptors classified?
|
by structure, stimuli detected, and location
|
|
|
What sensory receptor has bare dendrites and detects pain, temp, tickle, itch, and light touch?
|
Free nerve endings
|
|
|
What sensory receptor has dendrites enclosed in connective tissue capsule and detects pressure, vibration, and deep touch?
|
Encapsulated nerve endings
|
|
|
What sensory receptor has specialized cells that respond to stimuli and detects vision, taste, hearing, and balance?
|
Separate sensory cells
|
|
|
What do mechanoreceptors do?
|
detect pressure or stretch, touch , pressure, vibration, hearing, proprioception, equilibrium, and blood pressure
|
|
|
What do nociceptors detect?
|
damage to tissues
|
|
|
What receptos are near surface of body, receive external stimuli such a hearing, vision, smell, taste, touch, pressure, pain, vibration, and temp?
|
Exteroceptors
|
|
|
What receptors monitor internal environment and are not conscious except for pain and pressure?
|
Interoceptors
|
|
|
What receptors sense body position and movement such as muscle, tendon, joint and internal ear?
|
Proprioceptors
|
|
|
What kind of impulses do First-order neurons conduct?
|
from somatic receptors into the brain stem or spinal cord
|
|
|
What kind of impulses do second-order neurons conduct?
|
from the brain stem and spinal cord to the thalamus
|
|
|
What kind of impulses do third-order neurons conduct?
|
from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory area of the cortex on the same side
|
|
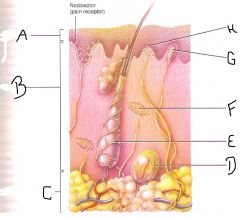
Label this figure
|
A) Epidermis
B) Dermis C) Sucutaneous layers D) Pacinian corpuscle E) Hair root plexus F) Ruffini corpuscle G) Meissner corpuscle H) Merkel disc |
|
|
What is fast pain?
|
perception of pain occurs very rapidly, use A type fibers
|
|
|
What is slow pain?
|
perception or pain occurs very slowly, pain increases over time, use C type fibers
|
|
|
What is visceral pain?
|
pain results from stimulation of nociceptors in visceral organs
|
|
|
What is referred pain?
|
instance of visceral pain where the pain is felt in or just deep to the skin that overlies the stimulated organ or in a surface area far from the stimulated organ
|
|
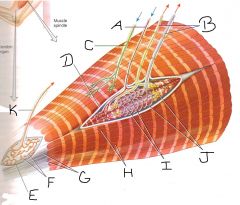
Label this figure
|
A) Gamma motor neuron to intrafusal muscle fibers
B) Sensory neurons C) Alpha motor neuron to extrafusal muscle fibers D) muscle spindle capsule E) Tendon organ capsule F) Sensory nerve endings G) Tendon fascicles H) Extrafusal muscle fibers I) Intrafusal muscle fibers J) Sensory nerve endings K) sensory axon |
|
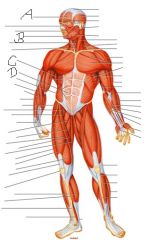
Label this man
|
A) Occipitofrantalis
B) Omohyoid C) Latissimus dorsi D) Rectus abdominis |
|
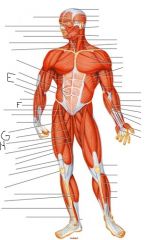
Label this man
|
E) Brachioradialis
F) Iliacus G) Pectineus H) Sartorius |
|
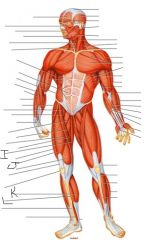
Label this man
|
I) Gracilis
J) Rectus femoris K) Gastrocnemius L) Soleus |
|
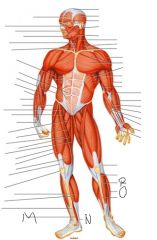
Label this man
|
M) Flexor digitorum longus
N) Calcaneal tendon O) Fibularis longus P) Tibialis anterior |
|
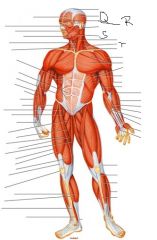
Label this man
|
Q) Temporalis
R) Orbicularis oculi S) Platysma T) Scalenes |
|
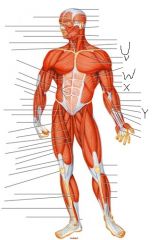
Label this man
|
U) Trapezius
V) Deltoid W) Biceps brachii X) Triceps brachii Y) Palmaris longus |
|
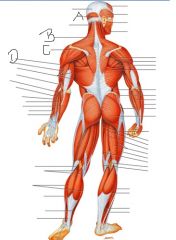
Label this man
|
A) Occipitofrontalis
B) Trapezius C) Deltoid D) Biceps brachii |
|
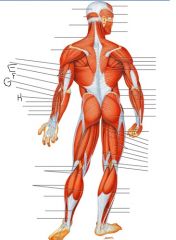
Label this man
|
E) Triceps brachii
F) Brachioradialis G) Extensor carpi radialis brevis H) Extensor digitorum |
|
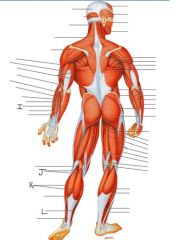
Label this man
|
I) Extensor carpi ulnaris
J) Gastrocnemius K) Soleus L) Flexor digitorum longus |
|
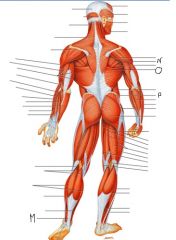
Label this man
|
M) Calcaneal tendon
N) Teres minor O) Latissimus dorsi P) Gluteus medius |
|
|
What is the point of origin?
|
point of attachment where muscle does not move
|
|
|
What is the point of insertion?
|
point of attachment where muscle moves
|
|
|
Why are skeletal muscles multi-nucleated?
|
composed of many myoblasts which all have one nucleus
|
|
|
What is so special about satellite cells in skeletal muscles?
|
they are underdeveloped muscle cells which can grow into a full blown muscle cell
|
|
|
True or False:
Skeletal muscles have a lot of satellite cells |
False
|
|
|
What happens when a muscle is damaged?
|
a scar forms on the muscle and that part cannot contract properly thus limiting it's ability
|
|
|
What is the protein that makes up thick filament?
|
myosin
|
|
|
What is the protein that makes up thin filament?
|
actin
|
|
|
What is the functional unite of a muscle fiber?
|
sarcomere
|
|
|
What is found in the I band?
|
Only actin
|
|
|
What is found in the A band?
|
the whole length of the myosin
|
|
|
What is found in the H zone?
|
only myosin
|
|
|
What are the three types of proteins that make up myofibrils?
|
contractile proteins, regulatory proteins, and structural proteins
|
|
|
What are contractile proteins?
|
myosin and actin
|
|
|
What are regulatory proteins?
|
troponin and tropomyosin
|
|
|
What protein holds the tropomysoin in place?
|
troponin
|
|
|
What protein will move tropomyosin when calcium is present?
|
troponin
|
|
|
What is titin?
|
elastic spring that helps stabilize and return the thick filament to its original length
|
|
|
What protein forms the m-line?
|
myomesin
|
|
|
What does the nebulin protein do?
|
strengthens the sarcomere
|
|
|
What does the dystrophin do?
|
integral protein that links filaments to the sarcolemma
|
|
|
What are the three filaments?
|
thick, thin, and titin
|
|
|
The force of the muscle contraction depends on ______.
|
the length of the sarcomere before contraction begins
|
|
|
What are the three ways a muscle can get ATP?
|
Creatine phosphate, anaerobic cellular respiration, aerobic cellular respiration
|
|
|
What are the three phases of a myogram?
|
latent, contraction, and relaxation
|
|
|
What is the latent period of a myogram?
|
the delay
|
|
|
What is the contraction period of a myogram?
|
the second phase. Ca+2 binds to troponin, forming crossbridges
|
|
|
What is the relaxation period of a myogram?
|
the third phase, Ca+2 is transported to the SR
|
|
|
What is the refractory period?
|
period of lost excitability
|
|
|
What is the wave summation?
|
time when stimuli arriving at different times cause larger contractions
|
|
|
Where does the Ca+2 come from?
|
SR
|
|
|
What happens during the relaxation period?
|
Ca+2 is returned to the SR
|
|
|
What are the two important factors of twitching/myograms?
|
number of stimuli and frequency
|
|
|
What is tetanus?
|
a sustained contraction, a muscle does not relax at all
|
|
|
What is concentric contraction?
|
moving weight from a lower position to a higher position (angle is decreasing), muscle shortens
|
|
|
What is eccentric contraction?
|
moving weight from a higher position to a lower position (angle is increasing), muscle lengthens
|
|
|
What is isotonic contraction?
|
sustained movement (not moving)
|
|
|
What are the three types of skeletal muscle fibers?
|
slow-oxidative, oxidative-glycolytic, and fast-glycolytic
|
|
|
Which muscle fiber is red/brown in color, and has prolonged and sustained contractions for posture?
|
Slow-oxidative
|
|
|
Which muscle fibers have a lot of mitochondria, myoglobin, and blood vessels?
|
Slow-oxidative and oxidative-glycolytic
|
|
|
Which muscle fiber is pink/light brown, splits ATP at a very fast rate
|
oxidative-glycolytic
|
|
|
What muscle fiber is used for walking and sprinting?
|
oxidative-glycolytic
|
|
|
Which muscle fiber is made of a fast twitch A?
|
oxidative-glycolytic
|
|
|
Which muscle fiber is white in color and is used for anaerobic movements and short duration such as weight-lifting?
|
fast glycolytic
|
|
|
Which muscle fiber is made of fast twitch B?
|
fast glycolytic
|
|
|
Which muscle fiber has a few mitochondria and blood vessels and low myoglobin?
|
fast glycolytic
|
|
|
Cardiac muscles contract when stimulated by their own __________ fibers.
|
autorhythmic
|
|
|
What are the 2 kinds of smooth muscle?
|
visceral (single unit) and multiunit
|
|
|
Where does the Ca+2 come from in the smooth muscle?
|
from outside
|
|
|
What activates the binding sites and allows for contraction to occur in smooth muscle?
|
calmodulin
|
|
|
Growth of muscle tissue is what kind?
|
enlargelment of existing cells - hypertrophy
|
|
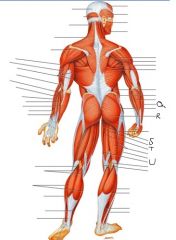
Label this man
|
Q) Brachioradialis
R) Gluteus maximus S) Gracilis T) Semitendinosus U) Semimembranosus |

