![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
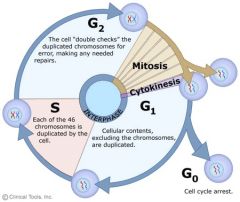
Cell cycle |
More complex series of stages |
Cell cycle is a more complex series of stages |
|
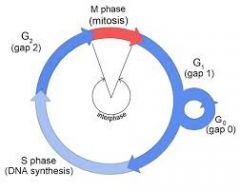
Interphase |
The period between divisions |
Period between divisions |
|
G1/G0 |
Cells pass in order through the phases |
G1 and G0 is called Gap1 or prereplication |
|
|
S |
DNA synthesis |
DNA S means Synthesis |
|
|
G2 |
Gap 2 or premitosis |
Gap 2 means G2 and it means premitosis |
|
|
M |
Mitosis |
M represents Mitosis |
|
Restriction Point |
When a cell in G0 or G1 receives these signals, it passes through this point |
Restriction point is a point where G0 and G1 receives the signals |
|
Cytokinesis |
Division of the whole cell |
Cytokinesis represents the division of the whole cell |
|
|
Daughter Cell |
Mitosis provides each daughter cell with a complete set of chromosome that are the same type and number as those of the parent cell. |
M provides eac |
|
|
Nucleotide base pairing |
Fors between specific nucleobases |
Also termed nitrogenous bases |
|
|
Hydrogen Bond |
Attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule |
Attractive forced are called hydrogen bond |
|
|
Antiparallel |
They run parallel to each other but with opposite alignments |
Have opposite alignments |
|
|
DNA polymerase |
the enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the new DNA strands |
Formation of the new DNA strands |
|
|
Semiconservative replication |
It would produce two copies that each contained one of the original strands and one new strands |
Produce new copies of each strands |
|
|
Histone |
Highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes |
Order the DNA into structural units |
|
|
Chromosome |
Thread- like structure located inside the nucleus |
Thread-like structure ( Nucleus ) |
|
|
Chromatin |
Complex of macromolecules found in cells |
Consisting of DNA, protein, and RNA |
|
|
Mutation |
Any change in the sequence of a cell's DNA |
Changing in the sequence of DNA |
|
|
Mutagen |
they need to detect and repair mutations introduced during replication or caused by environmental factors. |
Chemicals or radiation |
|
|
Excision repair |
The process by which these mutations are repaired |
Mutations are repaired are called excision repair |
|
|
Sister chromatids |
Two copies of each chromosome made during the S phase |
Two copies same copies |
|
|
Centromere |
Sister chromatids are still attached by proteins at a narrow point called the centromere |
Attached to the proteins are at a narrow point |
|
|
Aneuploid |
Such daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes |
Daughter cells at a number of chromosome |
|
|
Prophase |
First step of mitosis |
First step of the process |
|
|
Metaphase |
The second step of mitosis |
Middle of the process |
|
|
Anaphase |
The third step of mitosis |
Enzymes break down the protein holding the sister chromatids together |
|
|
Telophase |
The cells enter, begin to expand, and the nuclear envelope reforms around them |
Producing two new nuclei |
|
|
(Mitotic) spindle ( fibers) |
Demonstrate a simple type of cell division in which the DNA attaches to the plasma membrane |
simple type of cell division |
|
|
Spindle poles |
Microtubule organizing center in yeast cells |
Functionally equivalent to the centrosome |
|
|
Kinetochore |
Protein structure on chromatids |
Spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart |
|
|
Cyclins |
Proteins, Accumulate and the rapidly disappear as the cycle progresses |
Proteins |
|
|
Kinases |
In turn activate various enzymes needed for progress through the cell cycle |
activate various enzymes needed for progress |
|
|
Cell cycle arrest |
Checkpoint controls the consist of proteins tat detect mistakes and damage |
Quickly halt the cell cycle until repairs are made |
|
|
Cancer |
Important in the detection and prevention of the uncontrolled cell growth and reproduction |
Important in the detection |
|
|
Mitosis |
Process of sorting and distributin |
|

