![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Received Nobel prize in 1962 for discovering structure of DNA |
Watson, Crick, and Wilkins |
|
|
Allows for double helix to form |
Sugar phosphate backbone |
|
|
Type of macromolecule DNA is |
Nucleic acid |
|
|
The gene's sequence is copied from DNA to mRNA |
Transcription |
|
|
Gene's sequence is encoded in mRNA which directs the production of a protein |
Translation |
|
|
Enzyme used in transcription |
RNA polymerase |
|
|
Help to synthesize |
Ribosomes |
|
|
Multiple amino acids form |
Polypeptide |
|
|
Where does transcription occur |
Nucleus |
|
|
Needed for translation |
Free amino acids Ribosomal unit Transfer RNA |
|
|
Decoder ring works in multiples of 3 |
tRNA |
|
|
Universal starter |
Methionine (AUG) |
|
|
A sequence of bases in a DNA molecule that carries the info necessary for producing a functional product, usually a protein molecule or RNA |
Genes |
|
|
Different versions of a gene that code for the same trait |
Alleles |
|
|
A full set of DNA an organism carries |
Genome |
|
|
In eukaryotes, the genome is divided among smaller, linear strands of DNA |
Chromosomes |
|
|
Non coding regions of DNA May take the form of short (or long) sequences that are repeated thousands of times |
Introns |
|
|
Useful parts of DNA |
Exons |
|
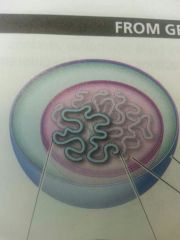
|
Genome |
|
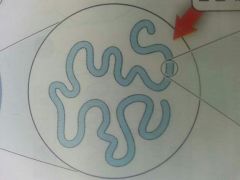
|
Chromosome |
|
|
Gene |
|
|
Three base sequence in mRNA |
Codon |
|
|
Three components of nucleotides |
A molecule of sugar A phosphate group A nitrogen containing molecule (base) |
|
|
Alteration in DNA bases |
Mutations |
|
|
Occur when one base pair in the DNA is substituted for another, or when a base pair is inserted or deleted |
Point mutation |
|
|
3 types of point mutation |
Nucleotide substitution Nucleotide insertion Nucleotide deletion |
|
|
Changes to the overall organization of the genes on a chromosome (gene moves) |
Chromosomal aberrations |
|
|
3 types of chromosomal aberrations |
Gene deletion Gene relocation Gene duplication |
|
|
Human genes for breast cancer |
BRCA1 & BRCA2 |
|
|
Increase risk of mutation |
Spontaneous mutation Radiation-induced mutations Chemical-induced mutations |
|
|
Generally exploits the use of cellular or cellular components to develop new technology |
Biotechnology |
|
|
How PCR works |
Small amount of DNA is collected Chopped up (restriction enzyme) Copied |
|
|
The study of genomes |
Genomics |
|
|
With your PCR amplified sample you can identify which genes are turned on in any individual |
Microarray |
|
|
Careful selection of genes/traits to alter the original state of an organism |
Genetic engineering |
|
|
You can genetically modify food to |
Make it larger Make it resistant to bacteria/viruses Longer shelf life More nutritious |
|
|
The complementary base pairs in a DNA molecule are stabilized by... |
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
DNA can be found in... |
Dead skin cells Saliva Blood |
|
|
The double helix model of DNA was exciting to the scientific community because... |
It explained how genetic material could be duplicated by means of the complementary strands |
|
|
Most genes come in alternative forms called |
Alleles |
|
|
DNA is a macromolecule that stores info. Which component of DNA is the source of this information? |
The base |
|
|
The highest percentage of non-coding DNA is found in |
Eukaryotes, except yeast |
|
|
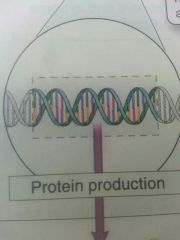
The central dogma of molecular biology states that |
DNA is transcribed into RNA which is translated into a protein |
|
|
The eukaryotic cell cycle consists of four phases. In this order |
Mitosis, gap 1, DNA synthesis, and gap 2 |
|
|
The majority of a eukaryotic cell's life is spent in |
Interphase |
|
|
Mitosis results in |
Daughter cells with the same number and composition of chromosomes |

