![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the difference between prokaryotes & eukaryotes? |
Prokaryotes - no true nucleus. Eukaryotes - nuclear membrane around genetic material |
|
|
List an example of a prokaryote? |
Bacteria |
|
|
List an example of a eukaryote? |
Animal, plant, fungi, and protist |
|
|
What are the 3 basic principles involved in the cell theory? |
1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things 3. Cells come from other cells through cell division |
|
|
What is the function of the nucleus? |
Control cellular activities |
|
|
What structures are found inside the nucleus? |
Nucleolus |
|
|
Which organelle synthesizes proteins? |
Ribosomes |
|
|
What do chloroplasts do? |
Photosynthesis |
|
|
Which organelle provides the cell energy? |
Mitochondrion |
|
|
Which two organelles are only found in plant cells? |
Cell wall and chloroplasts |
|
|
Which two organelles are only found in animal cells? |
Lysosomes and centrioles |
|
|
What is the function of the cell wall? |
Support and protection |
|
|
Function: Lysosome |
Produce digestive enzymes to digest molecules. Break down dead organelles or harmful organisms. |
|
|
Function: Centriole |
Cell division |
|
|
Function: Cytoplasm |
Jelly like substance where most of the metabolic activity occurs |
|
|
Function: Endoplasmic reticulum |
Transports molecules throughout the cell |
|
|
Function: Cell membrane |
Regulates what may enter or leave the cell |
|
|
Fuction: Golgi apparatus |
Receive, process, and package materials to send to other parts of the cell |
|
|
Function: Cell wall |
Protect and support cell |
|
|
Function: Nuclear membrane |
Regulates what may enter and leave the nucleus |
|
|
Function: Cytoskeleton |
Maintains shape of cell |
|
|
Animal cell pic |
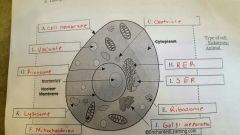
|
|
|
Plant cell |
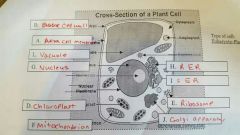
|
|
|
Microscope parts pic |

|
|
|
In the letter e lab, describe how the "e" looked under the microscope |
Upside down and backwards |
|
|
Using the microscope, what is the actual movement of a specimen if it appears to move up and to the left? |
Right |
|
|
What is the total magnification power using the scanning objective |
40x |
|
|
What is the total magnification power using the low power objective |
100x |
|
|
What is the total magnification power using the high power objective |
400x |
|

Use the picture to help you describe the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration- |
The reactants of photosynthesis are the products of cellular respiration. The reactants of cellular respiration are the products of photosynthesis |
|
|
What is the general chemical equation of photosynthesis |
Light energy + CO2 + H2O > C6H12O6 + O2 + H2O |
|
|
What is the general chemical equation of cellular respiration? |
C6H12O6 + O2 + H20 > Energy + CO2 + H20 |
|
|
Put the following in order in order: cell, organelle, organ, tissue, organism, organ system |
Organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organsim |
|
|
Hooke |
Discovered cells |
|
|
Van leewenhoek |
Created a single lens microscope. Discovered animalicules in pond water |
|
|
Schleiden |
Determined all plants are composed of cells |
|
|
Schwann |
Determined all animals are composed of cells. |
|
|
Virchow |
Stated that all living things cells come from cells |

