![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In fluid mosaic model,why is it called that? |
Fluid cause the phospholipids are never static and keep moving.they move in the membrane Mosaic because the proteins scattered make it look like a mosaic(small pieces make large picec |
|
|
Feature of fluid mosaic model? |
1.membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. 2.phospholipids move around,also separating the layer between from water out and inside(giving cell membrane flexibility) 3.have unsaturated hydrocarbons,the more unsaturated the more fluid phospholipids are. Because they are loosely packed. 5.fluidity is also affected by tail length ,longer the tail lesser the fluidity. 6.two protein types Intrinsic/integral: embedded in the membrane When they are fully through spanning it is known as transmembrane Extrinsic/peripheral :found on the outer and inner surface of the membrane.these are help on the surface by the intrinsic protein or molecule in and out of the cell
|
|
|
Roles of components of the cell membrane? |
E |
|
|
Phospholipids |

|
|
|
Cholesterol |

Small molecule Also has hydro phillic and phobic head ,fits easily in lipids Increase the fluidity at low temp. In membrane bcz it prevents close psckingof phospholipids meaning the cell can survive in cold temp |
|
|
Glycolipid, glycoproteins,and protein |

|
|
|
Glycolipid glycoproteins and protein |

|
|
|
Glycolipid Glycoproteins and protein |

|
|
|
Glycolipid Glycoproteins and protein |

|
|
|
Signalling |

|
|
|
Signalling |

|
|
|
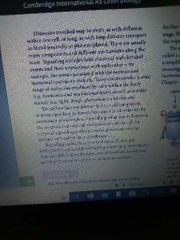
Signalling |
|
|
|
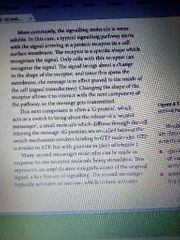
Signalling |
|
|
|
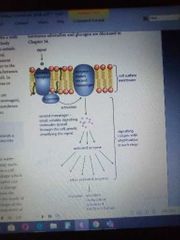
Signalling |
|
|
|
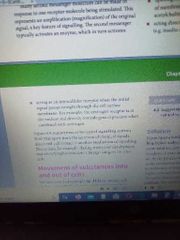
Signalling |
|
|
|
Carrier proteins flip and use energy so have acitve transport |
I |
|
|
Steroid hormones (lipid soluble ) and non polar molecules can easily cross the cell membrane |
F |
|
|
Steps of cell signalling
|
Signalling molecule:hormone Receptor:present in on,cytoplasm, nucleus Cellular activators:2 messenger Transcription factor Cellular affects:effect of signalling molecule on the cell
|
|
|
Commons pathway ? |
Signalling molecule Receptor Cellular response/effect Exp insulin |
|
|
Different pathways |
Cellular activator:2 messenger Transcription factor |
|
|
Pathways of signalling molecule? |

|
|
|
Most commons pathway exp insulin |

|
|

2 pthaway involves cellular activators(2 messenger) |

|
|
|
Ion channel patge way signalling |

|
|

Transcription factor pathways |

|
|
|
Diffusion |

|
|
|
Diffusion |

|
|
|
Diffusion and also facilitated diffusion |

|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |

|
|
|
Active transport |

|
|
|
Active transport |

|
|
|
Bulk tansport |
Large material move into or out of cell Endocytosis Exocytosis |
|
|
What happens in a neurone propagation |
Stimulus comes ,na v channel and k v channel open allowing na to enter in larger amount and k to leave the cell,after a while this causes the voltage potential to get really low and that's when the k channel open out flow of kLeak Chanel's cause k and na to go out and in the cell respectively,causing the voltage potantial to go down,than the na and pumps cash atp,to maintain it than.when the v approaches -55 mv it opens the gated sodium channel(sensitive to voltage)allowing. Huge amount of sodium to come in.wventually when we move away from the voltage is becomes inactive and close,there is also a k v gated channel which will open when the voltage becomes 30mv,allows passage of k which will go out of cell.In a action graph,the small dent or threshold is reached,so when -55 all sodium goes in and depolarizes the neurone.at 30 mv the k v gated channel become activated causing repolarization ,this causes later the k v gated channel to close causing undershoot which means the voltage is really low but permeability is restored and the leak channels will activate and allow permeability to establish the resting potential . Na and k pumps and leakage channel help to keep the RESTING ACTION stable ,when a impluse or stimulus comes the gated cell and leakage work |

