![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Classification Hierarchy
|
Domain,
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species, , , Dominic killed Phil cause Olivia faked good sex |
|
|
|
Two parts of a scientific name
|
1. Genus - capital first letter
2. species - all lower case italicized or underlined |
|
|
|
Element
|
a substance that cannot be broken down
|
|
|
|
Atom
|
smallest unit of matter that still retains properties of an element
|
|
|
|
Proton
|
positive (+) charged subatomic particle that makes up an atom
|
|
|
|
Neutron
|
subatomic particle with no electrical charge
|
|
|
|
Electron
|
negative (-) charged subatomic particle that makes up an atom
|
|
|
|
Ion
|
charged atom or molecule
|
|
|
|
cation
|
positive (+) charged ion
|
|
|
|
anion
|
negative (-) charged ion
|
|
|
|
isotope
|
two atoms of an element that differ in the number of neutrons
|
|
|
|
Molecule
|
two or more atoms held together by valence bonds
|
|
|
|
cohesion
|
hydrogen bonds that hold the substance together
|
|
|
|
adhesion
|
clinging of one substance to another
|
|
|
|
acid
|
a substance that reduces the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration of a solution. Has a lower pH.
|
|
|
|
base
|
a substance that reduces the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration of a solution. Lower pH.
|
|
|
|
buffer
|
a substance that minimizes changes in the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution.
|
|
|
|
Hydrogen ion
|
H+
single proton with a charge of 1+ |
|
|
|
Hydroxide ion
|
OH-
single proton with a charge of 1- |
|
|
|
Describe the shell model of atomic structure
|
an electronic can move from shell to sell only if the energy it gains or loses is exactly equal to the difference in energy between the energy levels of the shells.
|
|
|
|
Chemical symbols of important biological elements
|
O - Oxygen
C - Carbon H - Hydrogen N - Nitrogen Na - Sodium Fe - Iron Ca - Calcium |
|
|
|
Types of chemical bonds
|
1. Covalent Bonds
2. Ionic Bond 3. Hydrogen Bond |
|
|
|
Covalent Bond
|
sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms
|
|
|
|
Ionic Bond
|
attraction between anion and cation because of their opposite charges, which attract each other.
|
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bond
|
Noncovalent attraction between a hydrogen and electronegative atom.
|
|
|
|
Covalent Bond Structure
|
Single Bond
Single Solid Line H-H Pair of shared electrons Double Bond Double Solid Lines O=O Two pairs of shared electrons |
|
|
|
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
|
when two atoms with the same electronegativity, the electrons are shared equally. Considered hydrophobic.
|
|
|
|
Polar Covalent Bond
|
when an atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom, the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Considered hydrophilic.
|
|
|
|
Ionic Bond represented as...
|
if a compound is made up of a metal and a non-metal, its bonding is ionic. Bases (+) and Acids (-). Example, Magnet.
|
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bond represented as...
|
sharing of hydrogen atoms. shown as a dotted line between elements. (H......O)
|
|
|
|
Vander Waals Interaction
|
Sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds, or the electrostatic interactions of ions with one another.
|
|
|
|
Hydrophobic Interaction
|
interaction of nonpolar substances.
|
|
|
|
Four Emergent Properties of Water
|
1 Cohesive Behavior
2 Ability to moderate temperature 3 Expansion upon freezing 4 Versatility as a solvent |
|
|
|
Cohesive Behavior (Water)
|
Water molecules are linked by multiple hydrogen bonds. Water is attracted to different surfaces.
|
|
|
|
Surface Tension
|
a measure of how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid.
|
|
|
|
Ability to Moderate Temperature (Water)
|
Water absorbs heat from warm air and releases stored heat to cooler air. Water can absorb or release a large amount of heat with only a slight change in its own temperature.
|
|
|
|
Expansion upon Freezing (water)
|
Ice floats in liquid water because the hydrogen bonds in ice are more ordered, making ice less dense. Water reaches its greatest density at 4 degrees Celcius.
|
|
|
|
Versatility as a Solvent (Water)
|
Solution
Solvent Solute Aqueous Solution |
|
|
|
Solution
|
a liquid that is a mixture of substances
|
|
|
|
Solvent
|
dissolving agent
|
|
|
|
Solute
|
substances that is dissolved
|
|
|
|
Aqueous Solution
|
solution where water is the solvent
|
|
|
|
Hydrophilic
|
substances that has an affinity to water. Polar.
|
|
|
|
Hydrophobic
|
substance that does not have affinity to water. Nonpolar.
|
|
|
|
Colloid
|
stable suspension of fine particles in a liquid
|
|
|
|
Molecular Mass
|
mass of a molecule. Sum of each atom multiplied by the number of atoms of that element.
C12 H22 O11 (12.01 g/mol x 12) + (1.01 g/mol x 22) + (15.994 g/mol x 11) = Molecular Mass (daltons) |
|
|
|
Hydrogen Ion
|
(H+)
single proton with charge of 1+ |
|
|
|
Hydroxide Ion
|
(OH-)
single proton with charge of 1- |
|
|
|
Hydronium Ion
|
when proton binds with a water molecule
|
|
|
|
pH calculation
|
pH =-log [H+]
|
|
|
|
pH
|
the pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydrogen ion concentration. pH declines as H+ concentration increases. pH of a neutral solution is 7 at 25 deg C.
|
|
|
|
Less than 7 pH
|
Acidic
|
|
|
|
More than 7 pH
|
Basic
|
|
|
|
Organic Compound
|
compound containing carbon
|
|
|
|
polymer
|
a long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
|
|
|
|
monomer
|
small building-block molecules
|
|
|
|
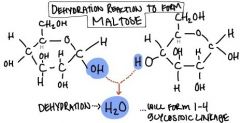
dehydration reaction
|
occurs when two monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule. Also known as condensation reaction.
|
|
|
|
Hydrolosis Reaction
|
polymers are disassembled to monomers by hydrolosis, a reaction that is essential the reverse of dehydration reaction.
|
|
|
|
Hydroxyl Group
|
-OH
Polar |
|
|
|
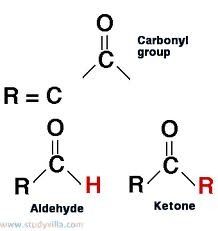
Carbonyl Group
|
>C=O
Polar |
|
|
|
Carboxyl Group
|
-COOH
Charged, ionizes to relase H+ Acidic |
|
|
|
Amino Group
|
-NH2
Charged, accepts H+ to form NH3 Basic |
|
|
|
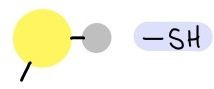
Sulfhydryl Group
|
-SH
Polar |
|
|
|
Phosphate Group
|
-OPO3 -2
Charged, ionizes to release H+ Acidic |
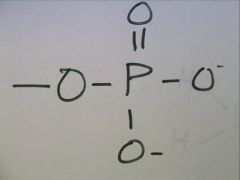
|
|
|
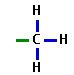
Methyl Group
|
-CH3
Nonpolar |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
building materials and source of energy
|
|
|
|
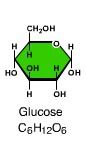
monosaccharide
|
simplest carbohydrate (simple sugar). Monomers from which more complex carbohydrates are constructed.
Glucose |
|
|
|
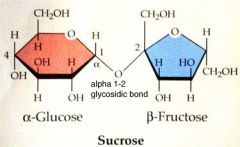
Disaccharide
|
two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage
Sucrose made from Glucose and Fructose |
|
|
|
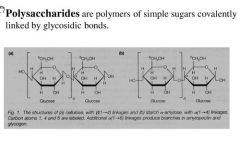
Polysaccharide
|
macromolecules, polymers with few hundred to a few thousand monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages.
Cellulose |
|
|
|
Glycosidic Linkage
|
covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction
|
|
|
|
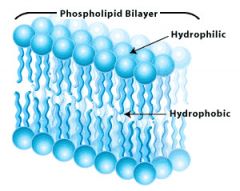
Lipids
|
Stored energy. Hydrophobic tail, hydrophilic head. Nonpolar.
|
|
|
|
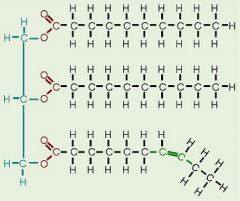
Triglyceride
|
a fat. Three fatty acids molecules are each joined to glyceral by an ester linkage.
|
|
|
|
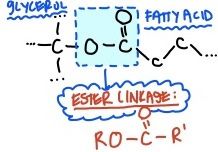
Ester Linkage
|
bond between a hydroxyl group and carboxyl group
|
|
|
|
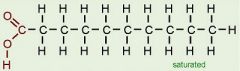
Saturated Fatty Acid
|
a fatty acid in which all carbon in the hydrocarbon tail are connected by single bonds, maximizing the number of hydrogen atoms that can attach to the carbon skeleton.
SOLID Butter Lard Leads to heart disease |
|
|
|
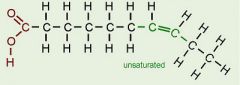
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
|
a fatty acid possessing one or more double bonds between the carbon in the hydrocarbon tail. Reduces the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton.
LIQUID Vegetable Oil Safer than saturated fats |
|
|
|
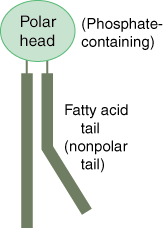
Phospholipid
|
a molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.
|
|
|
|
Steroid
|
a type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four rings with various functional groups attached.
Cholesterol |

|
|
|
Proteins
|
a biologically functional molecule that consists of one or more polypeptides folded and coiled into a specific three dimensional shape.
|
|
|
|
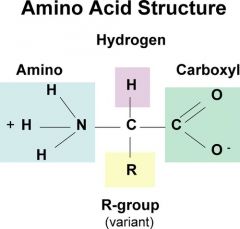
Amino Acid
|
organic molecule with both an amino group and carboxyl group
|
|
|
|
Classes of Amino Acids
|
Nonpolar side chains; hyrophobicPolar side chains; hydrophilicElectrically charged side chains; hydrophilic
|
|
|
|
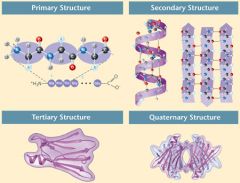
4 Levels of Protein Structure
|
1. Primary Structure
2. Secondary Structure 3. Tertiary Structure 4. Quaternary Structure |
|
|
|
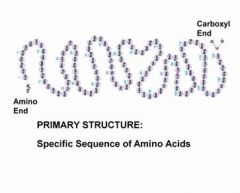
Primary Structure
|
level of protein structure referring to the specific sequence of amino acids. like the order of letters in a very long chain.
|
|
|
|
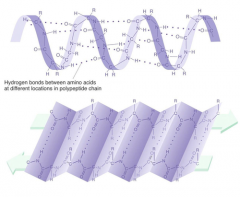
Secondary Structure
|
the localized, repetitive coiling or folding of the polypeptide backbone of a protein due to hydrogen bond formation between peptide linkages. like a coil or pleated sheet.
|
|
|
|
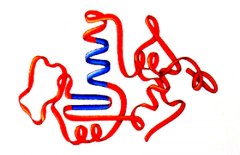
Tertiary Structure
|
Irregular contortions of a protein molecule due to interactions of side chains involved in hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, an disulfied bridges. like irregular loops and folds, 3-D
|
|
|
|
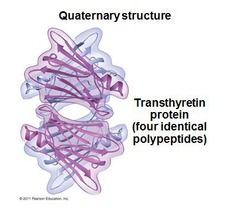
Quaternary Structure
|
shape of a complex, aggregate protein, defined by the characteristics 3D arrangement of its constituent subunits, each a polypeptide. two or more polypeptide units.
|
|
|
|
Functions proteins perform in a cell
|
Even a slight change in primary structure can affect a protein's shape and ability to function.
|
|
|
|
Neucleic Acid
|
polymers made up of monomers called nucleotides
|
|
|
|
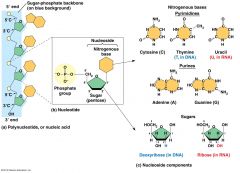
3 Parts of Neucleic Acid
|
1. Nitrogen containing base (nitrogenous)
2. 5-Carbon sugar (pentose) 3. One or more phosphate groups |
|
|
|
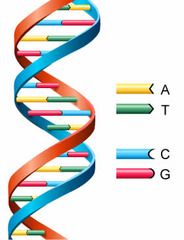
Nucleotides in DNA
|
two strands of neucleotides that twist around one another, forming a double helix held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of nitrogenous bases.
A -> T C -> G |
|
|
|
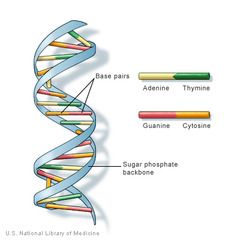
DNA
|
stores hereditary information
Sugar - deoxyribose Nitrogenous base - C, G, A, T Usually Double Stranded |
|
|
|
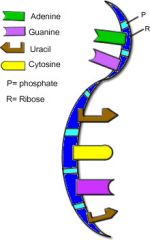
RNA
|
various functions in gene expression, including carrying instructions from DNA to ribosomes.
Sugar - ribose Nitrogenous base - C, G, A, U Usually Single Bonded |
|
|
|
Components of Nucleic Acids
|
|
|

