![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a major and common problem all terrestrial organism have in relation to water loss , give a particular example .
|
A major problem confronting all terrestrial organisms is how to avoid desiccation. Land plants in particular are continually losing water vapour to the atmosphere. In fact, above 99% of the water absorbed by the plant can be lost by evaporation through leaves.
|
|
|
What is transpiration?
|
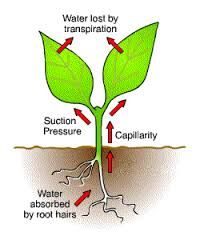
The evaporation of water from inside the leaves through the stomata to the atmosphere is know as transpiration and gives rise to the transpiration stream. A
|
|
|
'All plants have to balance water uptake with water loss' - why is this?
|
All plants have to balance water uptake with water loss. If a plant loses more water than it absorbs it wilts. If a plant loses an excessive amount of water it reaches a point where it cannot regain turgor and it dies.
|
|
|
'Plants face a dilemma' - why is this?
|
In plants the stomata need to be open during the day to allow the exchange of gases between the tissues of the leaf and the atmosphere . However, the presences of pore in the leaves means that valuable is lost from the plant. Most of the water is lost through the stomata although around 5% of the total water vapour loss can occur through the leaf epidermis. This loss is normally reduced due to the presences of the waxy cuticle on the surface of the leaves.
|
|
|
What is the name given to the rate at which water is lost from plants and name the external factors that this rate depends on
|
The rate at which water is lost from plants is called the transpiration rate and is dependent on external
factors such as temperature, humidity and air movement. |
|
|
What factor increases the rate of transpiration ?
|
Any factor that increases the water
potential gradient between the water vapour in the leaf and the surrounding atmosphere increases the rate of transpiration. |
|
|
Describe the effect of temperature on rate of transpiration
|
Temperature – a rise in temperature provides additional kinetic energy for the movement of water
molecules. This additional energy accelerates the rate of evaporation of water from the walls of the mesophyll cells and, if the stomata are open, speeds up the rate of diffusion of water vapour into the surrounding atmosphere. The water potential of the atmosphere becomes lower as its temperature is raised and it can hold more moisture. |
|
|
Describe the effect of humidity on the rate of transpiration
|
Humidity – the air inside a leaf is saturated with water vapour but the humidity of the atmosphere
surrounding a leaf varies, with values exceeding 70% being rare in Britain. Thus the water potential gradient between leaf and atmosphere is always great and when the stomata are open water vapour rapidly diffuses from the leaf. |
|
|
Describe the effect of air movement on the rate of transpiration
|
Air movement – transpiration in still air results in the accumulation of a layer of saturated air at the
surfaces of leaves. This offers considerable resistance to the diffusion of water vapour through stomata and thus reduces the rate of transpiration. Movement of the surrounding air reduces the thickness of the layer of saturated air and results in increased transpiration. |
|
|
Describe the effect of light intensity on the the rate of transpiration
|
Light intensity also affects transpiration by controlling the degree of stomatal opening.
|
|
|
'In reality, these factors do not act independently but interact with each other' - is this true? give an explain to explain why
|
Yes, In reality, these factors do not act independently but interact with each other, e.g. more water is lost on a dry, windy day than on a humid, still day. This is because the sub-stomatal chamber has a high water potential as the walls of the spongy mesophyll cells are saturated with water. The water evaporates from the walls and moves down a gradient of water potential from the plant to the atmosphere which has a low percentage relative humidity; the wind having reduced the thickness of the layer of saturated air at the leaf surface.
|
|
|
Draw , name, label and describe the device used to measure transpiration rate.
|
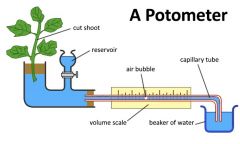
It actually measures the rate of water absorption but if the cells of the plant are fully turgid the rate of
water absorption and the rate of transpiration are the same. |
|
|
Draw graphs showing how environmental factors affect the rate of transpiration.
|
Ask Barrie
|

