![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dry Mount |
Specimens are placed on slide and cover slip over it |
|
|
Wet Mount |
Specimens suspended in liquid or oil and cover slip over |
|
|
Squash Slides |
Wet mount prepared and cover slip is pressed down on |
|
|
Smear Slides |
Edge of slide used to smear sample over slide |
|
|
Objective Lens |
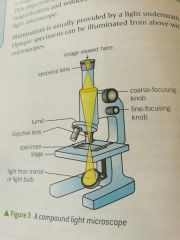
Lens near specimen |
|
|
Eyepiece Lens |
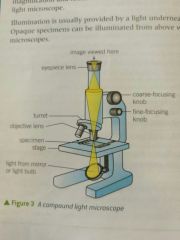
Lens used to view specimen |
|
|
Gram Stain Technique Target |
Stains gram positive bacteria (thick cell walls) as blue or violet |
|
|
Gram Stain Technique Method |
Crystal Violet to stain, Iodine to fix and washed with alcohol |
|
|
Gram Stain Technique Counterstain |
Safranin dye for gram negative bacteria, appearing red |
|
|
Counterstain |
Second stain used for contrasting colour e.g. safranin dye in gram staining |
|
|
Fixing Slides |
Chemicals used to preserve specimens e.g. formaldehyde |
|
|
Sectioning Slides |
Specimens dehydrated with alcohol and placed in mould to form a block, then sliced |
|
|
Staining |
Treated with stains to show structures |
|
|
Mounting |
Specimens secured to a slide |
|
|
Magnification |
How many times larger the image is than the actual size |
|
|
Resolution |
The ability to see individual objects as separate entities |
|
|
Magnification calculation |

Magnification=size of image/actual size |
|
|
Eyepiece graticule |
Used to measure size of sample under microscope, used with stage micrometer |
|
|
1000 Micrometres |
Um, 1mm |
|
|
1000 nanometres |
nm, 1 micrometer (um) |
|
|
Compound light microscope |
Regular microscope, used with light |
|
|
Artefacts |
Objects created through specimen processing |
|
|
Transmission Electron Microscope |
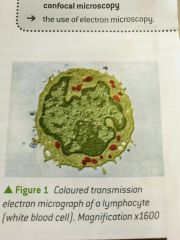
Beam of electrons passed through specimen, focused to produce image (r power 0.5 nm) |
|
|
Scanning Electron Microscope |
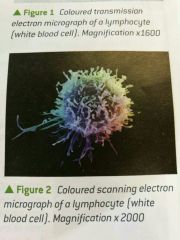
Beam of electrons reflected from specimen (r power 3-10 nm) |
|
|
Light vs Electron Comparison (8) |
Expense Portability Preparation Vacuum Colour Magnification Resolving power Specimens |
|
|
Light vs Electron Magnification |
x2000 vs x500 000 |
|
|
Light vs Electron Resolving Power |
200nm vs 0.5/3-10 nm |
|
|
Laser scanning confocal microscopy |
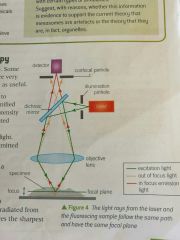
Spot of focused light moved across specimen, illuminating dye |

