![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Photosynthesis definition and equation |
Process of making carbohydrates - autotrophic nutrition
6 CO2 + 6H2O + energy ➡️ C6H12O6 + 6O2 |
Equation |
|
|
What are the three raw materials for photosynthesis to occur... |
Carbon dioxide: diffuses through small holes in the underside of the leaf called stomata
Light: leaf has large surface area to absorb light. Palisade cell is adapted for this function
Water: get it from the roots, passed through the xylem tubes.. Keeps plant sturdy and prevent it from dying |
|
|
|
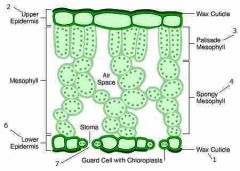
What are the for main layers of a leaf? |
upper epidermis Palisade layer Spongy mesophyll layer Lower epidermis
|
|
|
|
Function and structure of upper epidermis |
Functions: Helps maintain shape Prevents invasion of pathogens Cuticle helps reduce water loss
Structure: Single layer No chloroplast Covered my waterproof waxy cuticle
|
|
|
|
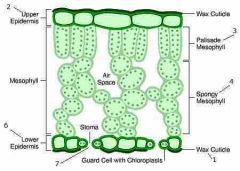
Function and structure of palisade layer |
Functions Produces food via photosynthesis
Structure 1 or more layers of elongated tightly packed cells Contains large no. Of chloroplast
|
|
|
|
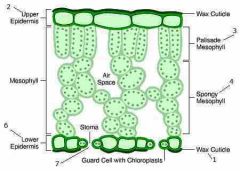
Function and structure of the spongy mesophyll layer |
Functions Abundant air spaces for gaseous exchange
Structure Layers of loosely packed cells Many air spaces |
|
|
|
Function and structure of lower epidermis |
Functions Controls amount pf gases/ water entering and exiting leaf
Structure Single layer Thinner cuticle Have stomata Stomata protected by guard cells |
Respiration and photosynthesis |
|
|
Adaption of leaves for photosynthesis |
Large surface area - absorbtion of CO2 and sunlight
Large air spaces to allow diffusion
Thin leaves for short diffusion
Leaves have pores to allow gaseous exchange
|
|
|
|
Gaseous exchange in plants Chemical and written equations |
Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 ➡️ 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy [ glucose + oxygen ➡️ carbon dioxide + water + energy]
Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy➡️C6H12O6 + 6O2 [carbon dioxide + water + sunlight ➡️ glucose + oxygen] |
|
|
|
What is the compensation point? |
It is when the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration. So the oxygen produce during photosynthesis is used up during respiration and the carbon dioxide produce during respiration is used up by photosynthesis so there will be no intake or output of carbon dioxide or oxygen.
This happens at the time of dim light. |
|
|
|
What process happens in darkness |
There is no light so photosynthesis cant take place
The plant is only respiring. |
|
|
|
What process occurs in bright light |
The rate of photosynthesis is greater that respiration so the plant takes in carbon dioxide and the excess oxygen is given out. |
|
|
|
Usage of glucose in plants |
Energy - released from glucose in leaf
Turned into starch and stored
Transported to other parts pf the plant
|
|
|
|
Two elements need for healthy plant growth |
Nitrogen - to make proteins
Magnesium - to make chlorophyll |
|
|
|
Deficiency diseases caused by absence of elements |
Nitrogen - poor growth, yellow leaves
Magnesium - yellowing between veins of leaves |
|
|
|
How do you de starch a plant? |
Place it in darkness for 2-3 days |
|
|
|
What does boiling a leaf do? |
It kills the leaf tissue and breaks down the waxy cuticle |
|
|
|
What happens when a leaf is boiled through ethanol |
The ethanol removes chlorophyll |
|

