![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Speciation
|

The process by which one species split into two or more species
|
|
|
Micro Evolution
|
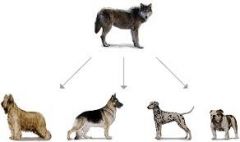
Change in genetic makeup of a population from one generation to the next
Ex: Cross Breeding Dogs |
|
|
Macro Evolution
|
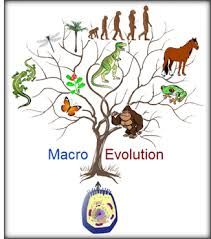
change in the genetic makeup leading to the appearance of major evolutionary development
Ex: Development of wings and feathers |
|
|
Species
|

population of Organisms capable of naturally breeding and producing fertile offspring
|
|
|
Reproduction Isolation
|

existence of biological factors (barriers) that impede members of two different species from producing fertile offspring
Ex: Liger |
|
|
Prezygotic Barriers
|

factors that impede mating between species or hinder ova fertilization if members of different species attempt to mate
Ex: Blue footed Booties and red footed booties Dance ( mating ritual. |
|
|
Postzygotic Barriers
|

Factors that prevent the hybrid zygote from development into a viable, fertile adult
Ex; Mules |
|
|
Limitations
|
1.Difficult to uses reproductive isolation when only fossile are available
2. Doesn't apply to animal that reproduce asexually 3.Exceptions to Rule ( Organisms with distinct ecologices and morphologies where gene flow can sill occur |
|
|
Morphological Species
|
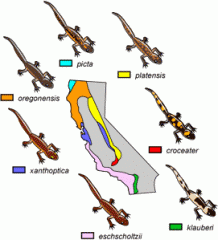
Characterizes a species based on body shape and other structural features
Ex: Salamanders |
|
|
Plaeotological Species
|

Based on Morphologies from fossil records only
Ex: Long Extinct Animals |
|
|
Ecological species
|

characterizes a species based on its ecological niche; the sum of how members of one species interact with the ecosystem
Ex: Hyenas |
|
|
Phylogenetic species
|

characterizes a species as the smallest group of individuals that share a common ancestor
a. Ex. salamanders |
|
|
Allopatric Speciation
|
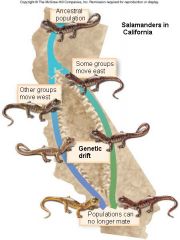
gene flow becomes interrupted when a population is divided into geographically isolated subpopulations
B. Geographical barriers include water, canyons, mountains, etc. |
|
|
Selecting agents
|
any factors that affect the probability that certain traits will be passed on to the next generation
|
|
|
Sympatric speciation
|

formation of new species due to genetic change in the species from the original population; no geographic barrier
a. Ex. snails |
|
|
Polyploidy
|
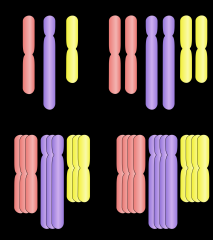
chromosomal alteration in which an organism possesses more than two complete sets of chromosomes
|
|
|
Habitat differentiation
|

a change in vegetation could alter the niche of members of a species living in the same habitat
Ex. North American apple maggot fly (native Hawthorne berries v. introduced apples) |
|
|
Sexual selection
|
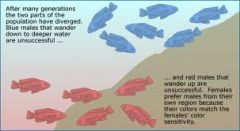
individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more likely to obtain mates with similar characteristics
a) Color change could alter the mate selection b) Examples: African cichlids |
|
|
Hybrid zones
|

region in which members of different, but similar species meet and mate, producing at least some offspring of mixed ancestry (hybrids)
a. Ex. European fire-bellied toad |
|
|
Reinforcement
|
process in which natural selection strengthens prezygotic barriers to reproduction, thus reducing formation of hybrids
|
|
|
Fusion
|
process in which natural selection weakens prezygotic barrier to reproduction, thus reversing the process resulting in the formation of hybrids
|
|
|
Stability
|
prezygotic barriers to reproduction are neither strengthened nor weakened, allowing hybrids to persist
|
|
|
Gradualism
|

profound changes occur through the cumulative effect of slow, but continuous processes
|
|
|
Punctuated equilibrium
|
profound changes that occur in spurts between which are long periods of little or no evolutionary changes
|
|
|
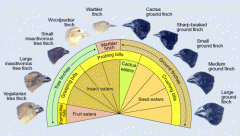
Adaptive radiation
|
period of evolutionary change in which groups of organisms form many new species whose adaptations allow them to fill vacant ecological niches in their new communities
a. Ex. Australian marsupials |
|
|
Convergent evolution
|
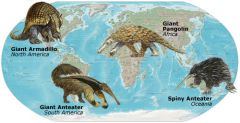
pattern in which similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar adaptations in organisms from different evolutionary lineages
Ex. Echidna, hedgehog, tenrec |

