![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
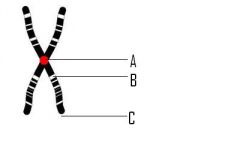
Label the parts of a chromosome |
A: Centromere B: Gene C: Sister Chromatid |
|
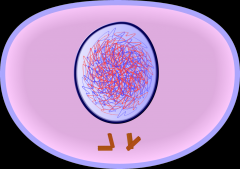
State which Mitosis phase is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Interphase: cell grows and duplicates its genetic material, prepares for division |
|
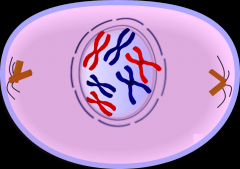
State which Mitosis phase is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Prophase: chromosomes shorten and thicken, centrioles move to opposite poles, nuclear envelope dissolves, spindle fibres grow |
|
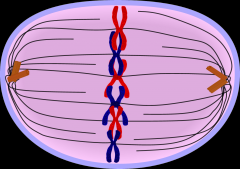
State which Mitosis phase is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Metaphase: spindle fibres join to chromosome by connecting to centromere, chromosomes line up on the equatorial plate |
|
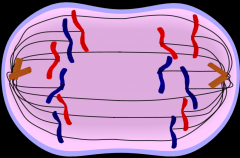
State which Mitosis phase is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Anaphase: centromeres split, sister chromatids (chromosomes) move to opposite poles, spindle fibres shorten |
|
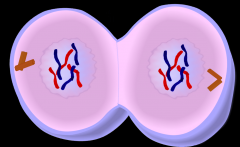
State which Mitosis phase is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Telophase/Cytokinesis: nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes begin to revert back to chromatin, centrioles duplicate (2 at each side) |
|

State which phase of Meiosis is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Prophase 1: chromosomes shorten/thicken, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrioles move to opposite poles, spindle fibres form, homologous chromosomes pair up, synapsis occurs, crossing over occurs |
|
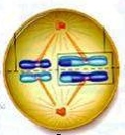
State which phase of Meiosis is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Metaphase 1: tetrads move towards the centre of the cell, tetrads line up along equatorial plate |
|

State which phase of Meiosis is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Anaphase 1: one chromosome of each homologous pair moves toward opposite poles, each chromosome in new cell is made of two sister chromatids |
|
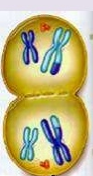
State which phase of Meiosis is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Telophase 1: nuclear membrane begins to form, cytoplasm divides, chromosomes in each nuclei are not identical |
|

State which phase of Meiosis is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Prophase 2: immediately after prophase 1, no duplication of chromosomes, nuclear membrane dissolves, spindle fibres begin to form |
|

State which phase of Meiosis is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Metaphase 2: chromosomes line up along the equator, sister chromatids remain attached at centromere |
|

State which phase of Meiosis is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Anaphase 2: sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles, nuclear membranes begin to form, each single chromatid (chromosome now) single stranded |
|

State which phase of Meiosis is shown; give a short description of what is going on in the cell |
Telophase 2/Cytokinesis: 2nd nuclear division completed, division of cytoplasm to four new daughter cells, not identical |
|

State which each pedigree symbol means |
Normal Male |
|

State which each pedigree symbol means |
Affected Male |
|
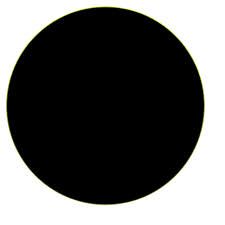
State which each pedigree symbol means |
Affected Female |
|
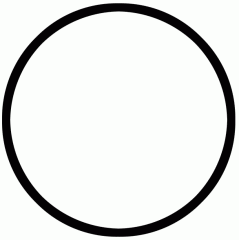
State which each pedigree symbol means |
Normal Female |
|
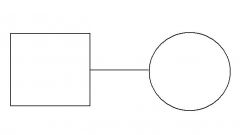
State which each pedigree symbol means |
Mating |
|
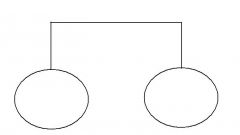
State which each pedigree symbol means |
Siblings |
|
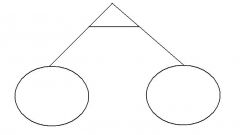
State which each pedigree symbol means |
Identical Twins |
|
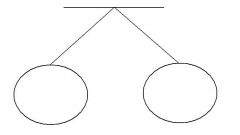
State which each pedigree symbol means |
Fraternal Twins |
|
|
What is a sister chromatid? |
The identical copy of a single chromosome that remains attached to the original chromosome at the centromere |
|
|
What is the centromere? |
The middle of a double stranded chromosome; attaches the sister chromatids together |
|
|
What is a gene? |
A segment of a DNA molecule that codes for a particular trait; found at a specific location on a chromosome |
|
|
What is an allele? |
A specific form of a gene |
|
|
What is the locus? |
The location of a gene on a chromosome |
|
|
What is a karyotype? |
The chromosomes of an individual that have been sorted and arranged according to size and type |
|
|
Why are karyotypes useful? |
Karyotypes are useful in diagnosing non-disjunction disorders (chromosomal disorders) |
|
|
What is a trisomy? Give an example of a disorder |
A chromosomal abnormality in which there are three homologous chromosomes in place of a homologous pair eg. Down Syndrome, Patau Syndrome, Edward's Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome |
|
|
What is a monosomy? Give an example of a disorder |
A chromosomal abnormality in which there is a single chromosome in place of a homologous pair eg. Turner Syndrome |
|
|
What is non-disjunction? |
The failure of homologous chromosomes to move to opposite poles of the cell during meiosis; results in an abnormal number of chromosomes in the daughter cells |
|
|
What is mitosis? |
The process by which a eukaryotic cell divides the genetic material in its nucleus into two new identical nuclei |
|
|
What is meiosis? |
A form of cell division in which a single cell gives rise to four haploid daughter cells |
|
|
How does meiosis lead to genetic variation? |
1. Crossing Over- exchange chromosome segments 2. Law of Independent Assortment- chromosome pairs arrange independently and can receive either chromosome from homologous pair |
|
|
Using humans as an example, explain the difference between haploid (1N) and diploid (2N) |
Haploid: one nuclei Diploid two nuclei During fertilization, one haploid sperm cell and one haploid egg cell form a diploid zygote. Considering each sperm cell and egg cell have 23 pairs of chromosomes, the zygote has 46. The diploid parent goes through cell division and splits into two new daughter cells each with 23 pairs of chromosomes (haploid), which then divides again into 4 haploid cells with 23 single chromosomes |
|
|
State Mendel's three laws of genetics |
1. Law of Independent Assortment 2. Law of Segregation 3. Law of Dominance |
|
|
What is a punnett square? |
A diagram that summarizes every possible combination of each allele from each parent; a tool for determining the probability of a single offspring having a particular genotype |
|
|
List the genotypes of the four blood types |
IAIA, IAi IBIB, IBi IAIB ii |
|
|
List the phenotypes of the four blood types |
Type A Type B Type AB Type O |
|
|
What is a pedigree? |
A diagram of an individual's ancestors used in human genetics to analyze the Mendelian inheritance of a certain trait; also used for selective breeding of plants |
|
|
Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous. Give an example of each |
Homozygous: describes an individual that carries two of the same alleles for a given characteristic eg. Pea Plants: tt- homozygous short Heterozygous: describes an individual that carries two different alleles for a given characteristic eg. Pea Plants: Tt- herterozygous tall |
|
|
Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype. Give an example of each |
Genotype: the genetic makeup of an individual eg. Pea Plants: Tt Phenotype: an individual's outward appearance with respect to a specific characteristic eg. Pea Plants: Heterozygous Tall |
|
|
Explain the difference between a dominant allele and a recessive allele. Give an example of each |
Dominant Allele: the allele that, if present, is always expressed eg. Pea Plants: T- Tall Recessive Allele: the allele that is expressed only if it is not in the presence of the dominant allele; that is, if the individual is homozygous for the recessive allele eg. Pea Plants: t- short |
|
|
Explain the difference between monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross. Give an example of each |
Monohybrid Cross: a cross designed to study the inheritance of only one trait eg. Red Bull+ White Cow Dihybrid Cross: a cross that involves two genes, each consisting of heterozygous alleles eg. Roan Calf+ Roan Calf |
|
|
Explain the difference between incomplete dominance and codominance. Give an example of each |
Incomplete Dominance: a situation where neither allele dominates the other and both have an influence on the individual; results in partial expression of both traits eg. Red Flowers+White Flowers=Pink Flowers Codominance: a situation where both alleles are expressed fully to produce offspring with a third phenotype eg. Red Bull+White Cow=Roan Calves |
|
|
Explain the difference between the F1-generation and the F2-generation. Give an example of each |
F1-generation: the offspring of a P-generation cross eg. Red Bull+White Cow=4 Roan Calves F2-generation: the offspring of a F1-generation cross eg. Roan Calf+Roan Calf=1 Red, 2 Roan, 1 White |

