![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is Biodiversity |
The variety of life within an ecosystem or an area |
In one ecosystem |
|
|
Negative effects of pesticides |
It would seep into the soil Bioexponential Growth |
|
|
|
What does ecological footprint of 1.3 mean |
The lifestyle we live required 1.3 earths to support it |
|
|
|
An example of decomposers |
Fungi |
|
|
|
What is a cell |
The smallest unit in all living organisms, formed by macromolecules |
|
|
|
Name 7 Organelles |
Cytoplasm, Cell Membrane, Mitochondria, Cell Wall, Vacuole, Nucleus, Ribosomes, Lysosomes |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Jelly like substance that supports all the organelles in the cell |
|
|
|
Cellular Membrane |
Semi-Permeable membrane that filters what is allowed in and out of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitochondria |
The powerhouse of the cell - Transforms energy through cellular respiration |
|
|
|
Cell Wall |
Supports and surrounds the plant cell's structure |
|
|
|
Vacuole |
Storage sac for water and waste |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
The control center of the cell, directs all of the cells functions |
|
|
|
Ribosomes |
Reads instructions in DNA to make protiens |
|
|
|
What's special about the plant cell |
Cell Wall, Chloroplast, Larger Vacuole |
|
|
|
What's special about the Animal Cell |
Centrioles, Smaller Vacuoles, Flagella |
|
|
|
Cell Theory |
- Cells are the basic unit of life - All living thins are made up of one or more cells - All cells come from pre-existing cells |
|
|
|
What is the Cell Cycle |
The process cells go through throughout their lifetime |
|
|
|
Describe the Cell Cycle |
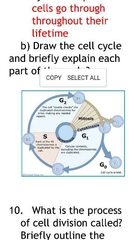
|
|
|
|
Mitosis : Interphase |
The cell carries out all of life's functions, Removes waste, Duplicates strands of DNA |
|
|
|
Mitosis : Prophase |
Nuclear membrane breaks down, spindle fibres form, DNA compacts into chromosomes |
|
|
|
Mitosis : Metaphase |
Chromosomes line up in the middle , Attached to spindle fibres |
|
|
|
Mitosis : Anaphase |
Centromere Splitz, Sister chromatids split, pulled by spindle fibres, to opposite sides of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitosis : Telophase |
A new nuclear membrane forms Spindle fibres break down Chromatids thin out |
|
|
|
Mitosis: Cytokinesis |
Cytoplasm Divides Cell Membrane pinches off in the middle |
|

