![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the phylums for seedless non-vascular plants (bryophytes)
|
phylum hepatophyta (liverworts), phylum anthocerophyta (hornworts), phylum bryophyta (mosses)
|
|
|
Where are mosses located?
|
deserts, Antarctica, moist areas
|
|
|
Describe bryophytes
|
seedless, non-vascular, heteromorphic alternation of generations (gametophyte dominant), water necessary for sexual reproduction, no true leaves, stems or roots
|
|
|
What is the plant life cycle called?
|
alternation of generations
|
|
|
What are the phases of the alternation of generations?
|
sporophyte-sporangium, spore mother cell, spore (meiosis), gametophyte (2n)-archegonium (egg) or anteridium (sperm)- zygote (fertilization)-embryo-sporophyte
|
|
|
During the sporophytic phase describe the embryo?
|
is completly dependent on the gametophyte
|
|
|
Main groups of plants are called ?
|
embryophytes
|
|
|
What are seedless non-vascular plants called? what is a key characteristic of these plants.
|
bryophytes; they do not have true roots, stems or leaves lack xylem and phloem
|
|
|
What three phylums belong to bryophytes and what are their common names.
|
Phylum Heptaophyta- liverworts
Phylum Anthocerophtya- horn worts Phylum Bryophyta- mosses |
|
|
What is the dominant generation in bryophytes?
|
gametophyte
|
|
|
What is a term used to describe any plant body that is not differentiated into true root, stem and leaf?
|
thallus
|
|
|
Describe the structure of mosses.
|
radially symmetrical plants that are differentiated into leaf-like and stem-like structures
|
|
|
What are three types of liverworts?
|
simple, complex thalloid and leafy liverworts
|
|
|
What type of liverworts compose the majority of liverworts?
|
leafy liverworts
|
|
|
What is a term for flat and branched dichotomously?
|
thalloid
|
|
|
What does bi-sexual mean?
|
male (sperm-producing) and female (egg-producing) gametes are produced on the same plant
|
|
|
What does unisexual mean?
|
different individuals are either male or female
|
|
|
What is an archegonia and an antheridia?
|
archegonia- egg producing structure
antheridia-sperm producing strucutre gametangia embedded in gametophye |
|
|
How are the eggs fertilized in liverworts?
|
sperm swim to eggs and fertilize them at maturity
|
|
|
What does the embryo in liverworts mature into?
|
a mature sporophyte
|
|
|
What are sporocytes and where are they located?
|
spore mother cells in the sporophyte; gives rise to four spores
|
|
|
What are gemma cups?
|
are structures that house gemmae; tiny lens- shaped pieces of thallus that are a form of asexual reproduction in liverworts
|
|
|
Are Marchantia haploid or diploid?
|
haploid
|
|
|
What kind of roots do bryophytes have?
|
rhizoids
|
|
|
What are tubular structures of one or more cells, which is used to anchor the thallus to the substrate?
|
rhizoid
|
|

What kind of plant is this? what phylum does it belong?
|

thallose liverwort
Hepatophyta |
|

Waht kind of plant is this and what Phylum does it belong? is it a female or male?
|

thallose liverwort
Hepatophyta female and male |
|
|
What are antheridiophores and archegoniophores?
|
antheridiophores- disk-headed branches
archegoniophores- spoke-headed branches w/ archegonia |
|
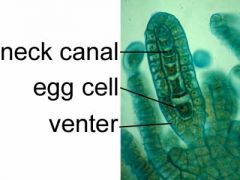
What is the image of?
|
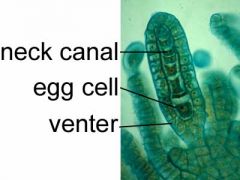
a Marchantia archegonium
|
|
|
Is there archegonia on the lower or upper surface of the archegoniophore? what about the anteridia on the antheridiophore?
|
archegonia aer on the lower surface
antheridia are on the upper surface |
|
|
What does the "spalsh plateform" on the antheridial disk do?
|
serves to transfer sperm
|
|
|
Is the sporophyte on the liverworts haploid or diploid?
|
diploid
|
|
|
Where is the sporophyte located on the liverworts?q
|
grows through the venter of the archegonial head
|
|
|
What are elaters?
|
have spirally arranged hygroscopic (moisture-absorbing) wall thickenings, which are sensitive to light and changes in humidity so they aid in spore dispersal
|
|
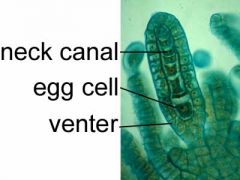
What is the image of?
|
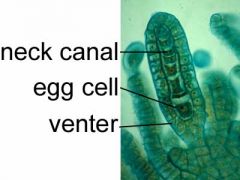
a Marchantia archegonium
|
|

What is this structure?
|

a sporophyte coming from the archegonial head on a liverwort
identify the spores, elater, stalk and capsule |
|
|
Describe the structure of a leafy liverwort.
|
it is bilaterally symmetrical; doesn't have a midrib
|
|

What is this an image of? what phylum does it belong to?
|

leafy liverwort, Hepatophyta
|
|
|
What is different about the Anthoceros hornwort's sporophyte?
|
contains a basal meristem
|
|
|
Which bryophytic phylum has capsules and what do they look like?
|
Hornworts; Anthocerophyta
in the sporophyte; appear like horns |
|
|
What is a protonema?
|
a system of branching filaments derived from a germinating spore
|
|
|
What are the three types of mosses?
|
true mosses, peat moss or SPhagnum,
|

