![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Deoxyribose |
Five carbon sugar whose carbons are numbered 1'to 5'. The prime indicate that the carbons referred is not the same as the one in the nitrogenous bases |
|
|
Nitrogenous Bases |
Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, and Cytosine. They are attached to the 1' carbon of the sugar. |
|
|
Purines |
Adenine and Guanine. Structures composed of two rings. |
|
|
Pyrimidines |
Cytosine and Thymine. Structures composed of one ring only. |
|
|
DNA Polymerase |
Enzyme that catalyses DNA replication |
|
|
Phosphodiester back-bone |
Joined deoxyribonucleotides that provide a repeating framework for supporting the DNA structure. |
|
|
Template Strand |
Strand of DNA that is copied |
|
|
Complementary Strand |
Strand of DNA that is a copy of a template strand |
|
|
Histones |
Positively-charged proteins at which the DNA molecule wound around. |
|
|
Chromatin |
High condensed structure, formed by compact DNA and histones. |
|
|
Polyploidy |
Cells that have multiple copies of chromosomes |
|
|
Mitosis |
The process by which one copy of each chromosome is given to the daughter cells. Therefore, providing two cells that are genetically identical to the mother cell. |
|
|
Meiosis |
The process by which the full genetic material of a germ cell is divided amongst four daughter cells. Transforming a diploid cell into unique haploid cells. |
|
|
Haploid Cells |
Cells that have only one copy of each chromosome |
|
|
Diploid Cells |
Cells that have two copies of each chromosome (one copy is maternal, and the other one paternal) |
|
|
Homologous Chromosomes |
Chromosomes that are from different origins (maternal and paternal) but have the same structure. |
|
|
Metacentric |
The arms on either side of the chromosomes are equal in size. |
|
|
Acrocentric |
One arm is bigger than the other. |
|
|
Sister Chromatids |
Two copies of a chromosome attached together by a centromere |
|
|
Non-sister Chromatids |
Chromatids from different chromosomes of each homologous chromosomes. |
|
|
Tetrads |
Homologous chromosomes paired up next to each other |
|
|
Segregation |
The random facing of one of the chromosomes of homologous pairs to one pole, and the other one to another pole of the cell. |
|
|
Independent Assortment |
The arrangement of paternal and maternal copies for each homologous pair happens independently from other homologous pairs |
|
|
SEM |
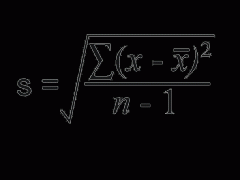
|
|
|
Chi-Square Equation |
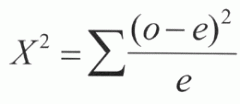
|
|
|
Plasmid |
Small circular piece of DNA that is independent from the bacterium's chromosome. |
|
|
Arabinose |
Sugar which will determine whether the GFP gene will e coded or not |
|
|
Ampicilin |
Antibiotic that prevents the growth of bacteria |
|
|
pGLO |
Engineered plasmid |
|
|
Synonymous Mutations |
Point mutation that leads to the encoding of the same amino acid as before |
|
|
Non-synonymous Mutations |
Point mutation that leads to the formation of a different amino acid |
|
|
Nonsense Mutation |
Point mutation that encondes for a stop codon. |
|
|
Population |
All members of the same specie that live in one location |
|
|
Gene Pool |
Various alleles of all the genes in all the individuals of a population |
|
|
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium |
The genotype frequency of a population will not change from one generation to another. |
|
|
Phylogenetic Tree |
Diagram that demonstrate the evolutionary events throughout the years |

