![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If the distance from the source of sound doubles, what happens with sound pressure and sound pressure levels?
|
For every doubling of distance, sound pressure halves and SPL drops by 6dB accordingly.
|
|
|
Which frequencies are more strongly absorbed in air?
|
High frequencies are more strongly absorbed than low frequencies.
|
|
|
What is the reason why you hear the lowest sounds of an open air concert from greatest distances?
|
Air absorbs sound energy. High frequencies are more strongly absorbed by air than low frequencies.
|
|
|
What are the relationships between sound speed and temperature?
|
Speed of sound increases with temperature.
|
|
|
Why almost no airborne sound enters water and vice versa?
|
Because the impendances of these media are too different: 1:3600.
|
|
|
why sound travels much further under water than in air?
|
Because the absorption in the air is 1000 times larger than in water.
|
|
|
What does the speed of sound depend on in sea water?
|
It depends on salinity, temperature and pressure.
|
|
|
Is the speed of sound constant in different depths in sea water?
|
No. From the top of the sea level it decreases, has a minimum at several hundred meters, and increases after that.
|
|
|
Where does the whale singing spreads its sound energy not spherically but in a disc?
|
At a several hundred meters under the sea level, where the speed of sound has its minimum.
|
|
|
How elephants are able to send sounds through the forest?
|
With their low frequency, long wavelength sounds. Diffraction bends sounds around objects if the wavelength is longer than the object size.
|
|
|
What is the substrate-born sound detector in insects?
|
Subgenual organ in the tibia of each leg. The substrate vibrations move haemolymph (a fluid in the circulatory system of some arthropods) in the legs of the insects and it is picked up by the subgenual organ.
|
|
|
Name three insect detectors of the air-born sounds.
|
1. Hair-like sensillae or trichobothria (in arachids) that follow that movement of particles in air and are sensed by mechano-sensory cells at the base;
2. In flies, at the base of the antennae is the Jonston's organ, highly sensitive detector of antennal movement; 3. Tympanal ears that measure sound pressure. Often sensitive to ultrasound. |
|
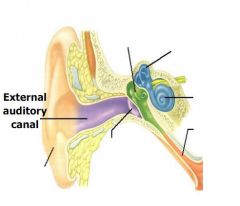
Label.
|
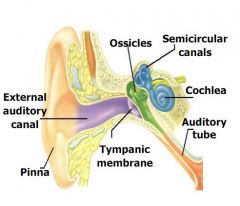
|
|
|
What is the name of external ear structure of mammals that collects sound?
|
Pinna.
|
|
|
After the sound goes through the external auditory canal, what do sound vibrate?
|
Sound waves vibrate the
tympanic membrane. |
|
|
Fill in missing words:
___ of middle ear transfer ___ ___ of eardrum to oval window of ___ ___ inducing ___ waves in fluid of ___. Pressure waves detected in ___ by receptor cells in ___ _ ___. |
Ossicles of middle ear
transfer vibratory motion of eardrum to oval window of inner ear inducing pressure waves in fluid of cochlea. Pressure waves detected in cochlea by receptor cells in Organ of Corti. |
|
|
In cochlea of the ear where are the pressure waves detected?
|
Pressure waves detected
in cochlea by receptor cells in Organ of Corti. |
|
|
How do mammals receive sound in water?
|
In water mammals
receive sound mainly via their bones/skulls - not via their eardrums. |
|
|
Which ear organs do toothed whales lack?
|
Toothed whales have no outer
and middle ear and no eardrum. |
|
|
How is the sound picked by a toothed whales in water?
|
By the lower jaw. Fatty tissue as well as their teeth seem to be involve. Sound conducting tissue leads sound to the inner ea.
|
|
|
What is the name of a main mammalian sound receptor?
|
Organ of Corti.
|
|
|
In Organ of Corti which cell receives sound wave vibrations?
|
Inner hair cells (without aouter hair cells).
|
|
|
What is the function of outer hair calls in the Organ of Corti?
|
Outer hair cells have both sensory and motor capabilities and possess electromotility that underlies the cochlear amplifier. They have a sparse afferent innervation and are contacted mainly by efferent nerves, which regulate the electromotility and influence cochlear sensitivity.
|
|
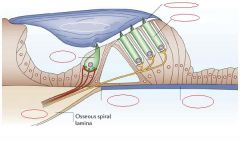
Label.
|
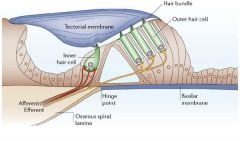
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of work of inner hair cells in Organ of Corti?
|
When deformed, hair cells change the rate of neurotransmitter release which then effects the number of action potentials generated by the sensory neurone.
|
|
|
How can the activity of outer cells in Ogran of Corti be charachterised?
|
Mechanically active (not sensory).
|
|
|
How do Egyptian Fruit bats echolocate?
|
The Egyptian Fruit Bat
clicks with its tongue to echolocate. |
|
|
What is the most popular theory for evolution of echolocation?
|
Bats and birds ave evolved
echolocation because they breed in caves, and the availability of light is limited, so vision cannot be used as primary sensory organ. |
|
|
What are two primary reasons for animals to use echolocation for?
|
Orientation and feeding.
|
|
|
What is Biosonar?
|
“Analysis by an animal of the echoes of its own emitted sound waves, by which it builds a sound-picture of its immediate surroundings.
|
|
|
What is the reason for some bats of having small ears?
|
Because they are fast flyers, to reduce wind resistance.
|
|
|
How echolocating animals can get long detection range?
|
By giving very loud calls.
|
|
|
Why do Passive gleaners have big ears?
|
Locate prey by their walking noises or communication signals.
|
|
|
Do passive gleaners use echolocation for finding prey?
|
No, they give very weak calls only for orientation, find prey by their walking noises or communication signals.
|
|
|
How do active gleaners find their prey?
|
Echolocate. They find motionless i.e. silent prey sitting on substrate based only on their echo signature.
|
|
|
Are bats insectivores, carnivores,
frugivores, nectarivores considered active or passive gleaners? |
Active, because they echolocate for finding their prey.
|
|
|
Shortly present beam forming in bats.
|
Oral emitters:
– broad beams • Nasal emitters: – Narrow beams – Hor: Interference between nostrils – Ver: Action of noseleaf. |
|
|
Why bats reduce inter call intervals when approaching a target?
|
Because when a bat gives a call, it cannot hear the echo. Once the echo of interest has been heard the next call can be produced.
|
|
|
How can echolocating animals detect the distance until the target?
|
The delay between sound emission and echo reception indicates the range (distance) of the target.
|
|
|
What is the formula for calculating the distance until the target using echolocation?
|
Range (distance) = delay x speed of sound / 2 (m).
|
|
|
What is approximate range until the target in air/ water if the animal is echolocating and hears the echo after 0.1s?
|
Air - 17m; Water - 75m.
|
|
|
Why do bats reduce call duration (i.e. shorten the single overlap zone) when approaching a target?
|
FM bats have difficulties hearing echoes while calling. The echoes of objects in the signal overlap zone are thus masked by the call.
|

