![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fungi
|
- Diverse and widespread
- essential for the well being of most terrestria ecosystens because the break down organic materials and recycle vital nutrients |
|
|
Who are fungi closer related to, plants or animals? Why?
|
- animals
- fungi are heterotrophs ( no chloroplast, therefore, they are non-photosynthetic) |
|
|
How do fungi absorb nutrients?
|
They absorb nutrients from outside their body with enzymes.
|
|
|
Fungi's ecological roles.
|
- Decomposers
- Parasites - Mutualists |
|
|
Body structure of fungi
|
-multi cellular filaments and single cells (yeasts)
- grow as either filaments (multicellular) or yeasts(unicellular). - some grow as both |
|
|
Morpholy
|
A branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features.
|
|
|
What is the advantage of multicellular fungi?
|
Being multicellular enhances their ability to absorb nutrients. (think about surface area)
|
|
|
Morpholy (body structure) of Fungi.
|
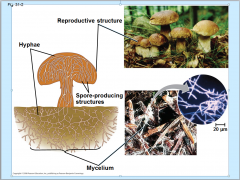
- consists of "mycelia", networks of branched hyphae adapted for absorption.
- Most fungi have cell walls made of chitin. |
|
|
Hyphae
|
A long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus
|
|
|
Fungi structure diagram
|
|
|
|
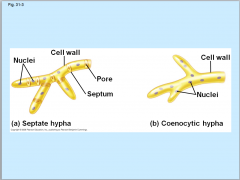
Septate Hypha and Coencytic hypha
|
|
|
|
Some fungi have hyphae divided into cells by septa, with pores allowing cell to cell movement of organelles
|

|
|
|
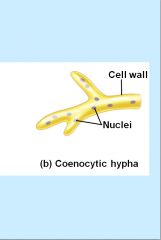
Coencytic fungi are fungi that lack septa
|
|
|
|
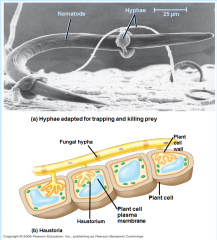
Some unique fungi have specialized hyphae called _____ that allow them to penetrate the tissues of their host.
|
Haustoria
|
|
|
- Some fungi are predators.
- have specialized hyphae called haustoria |
|
|
|
What is Mycorrhizae?
|
mutually beneficial relationships between fungi and plant roots
|
|
|
How is Mycorrhizae beneficial to plants?
|
The mycorrhizae facilitate the fixation which supplies the plants with a usable nitrogen source.
|
|
|
Ectomycorrhizal fungi
|
- form sheats of hyphae over a root and also grow into the extracellular spaces of the root cortex
- ( does not penetrate their host’s cell walls) |
|
|
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
|
- extend hyphae through the cell walls of root cells and into tubes formed by invagination of the root cell membrane
- ( penetrates their host's cell walls) |
|
|
spore
|
a spore is a unit of asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavorable conditions.
|
|
|
How do fungi produce spores?
|
Through sexual or asexual life cycles
|
|
|
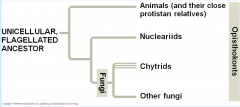
EVOLUTION OF FUNGI DIAGRAM
|
|
|
|
hypothesis on the evolutionary origin of fungi
|
- Fungi and animals are more closely related to each other than they are to plants or other eukaryotes
- from the opisthokonts clade - DNA evidence suggests that fungi are most closely related to unicellular nucleariids, which suggests that fungi and animals evolved from a common flagellated unicellular ancestor. - oldest fungal fossil are only about 460 million years old - A flagellated, aquatic, heterotrophic protist appears to be the common ancestor of both animals and fungi |
|
|
Ecological roles of Fungi
|
- Decomposers
- Parasites - mutualists |
|
|
Fungi as decomposers
|
- efficient decomposers
- perform essential recycling of chemical elements between the living and non living world. |
|
|
Fungi as Mutualists
|
- Fungi form mutualistic relationships with plants (mychorrhizae), animals, algae, and cyanobacteria
- All of these relationships have profound ecological effects |
|
|
Fungus-plant mutualism
|
- mycorrhizae are enormously important in natural ecosystem and agriculture
- Plants harbor harmless symbiotic endophytes that live inside leaves or other plant parts. |
|
|
How are endophytes beneficial to plants?
|
Endophytes make toxins that deter herbivores and defend against pathogens
|
|
|
Fungus-Animal Symbioses
|
- some fungi share their digestive services with animals
|
|
|
How do fungi help animals?
|
By breaking down plant material ( cellulose) in the guts of cows and other grazing mammals.
|
|
|
Lichens
|
A symbiotic association between a photosynthetic microorganism and a fungus in which millions of photosynthetic cells are held in a mass of fungal hyphae.
|
|
|
Lichens
|

|
|
|
Fungal component of a lichen.
|
- ascomycete
- Algae or cyanobacteria occupy an inner layer below the lichen surface\ - fungi of lichens can reproduce sexually or asexually |
|
|
How do fungi of lichens produce asexually?
|
by fragmentation or formation of soredia, small cluster of hyphae with embedded algae
|
|
|
Lichens
|
- algae provide carbon compounds (although photosynthetic, can also produce CO2 through cellular respiration)
- cyanobacteria provide organic nitrogen (nitrogen fixation) - fungi provide the environment for growth (mycorrhizae) |
|
|
Lichen's ecological role
|
- important pioneers on new rock and soil surfaces
- sensitive to pollution, and their death can be a warning that air quality is deteriorating |
|
|
Fungi as Pathogens
|
- about 30% of know fungal species are parasites or pathogens, mostly on or in plants
- fungi that attack food crops are toxic to humans - the general term for fungal infection in animals is mycosis |
|
|
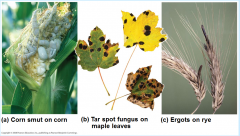
Parasitic fungi on plants
|
|
|
|
e.g. of a decomposer fungi
|
- black bread mold ( breaks down organic material in bread)
-mushrooms, morels, and truffles ( break down organic material in soil) |
|
|
e.g. of pathogenic fungi
|
- plant disease : root rot, powdery mildew, Dutch elm disease ( specific for particular plants and break down plant tissues)
- animal diseases: athlete's foot, vaginal infections ( skin infections) - psittacosis ( lung disease) - mold ( grows on grains, produces carcinogenic compounds ( causes cancer)) |
|
|
Growth promoters
|
Mycorrhizae: inhance uptake of minerals from the soil in 95% of vascular plants
|
|
|
Distinguishing characteristics of fungi
|
- they are eukaryotic and multicellular
- non motile ( not moving) - have cell walls made of chitin |
|
|
what have we learned about fungi?
|
- diverse and widespread
- plays important ecological roles in terrestrial environments (mycorrhizae) - have various ecological roles ( mutualistic, parasitic, decomposers) - closer related to animals ( heterotrophs) |
|
|
Kingdom plantae
|
:D
|

