![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
167 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Oxidation (oxidized) |
A substance that loses one or more electrons to another. |
Happen with the electrons carrier |
|
|
Reduction (reduced) |
A substance that gain electrons. |
Electron carrier |
|
|
In cells, oxidation and reduction never occur independently. If one substance is oxidized, another must be reduced. |
. |
|
|
|
Redox reaction |
The process by which electrons are transferred from one molecule to another. |
|
|
|
Electron carrier |
Molecules that serve to transfer electrons from one molecule to another in ATP formation.
NAD+ - empty - oxidized - ionic NADH - loaded - reduced
They pick up energetic electrons from food and transfer them to later stages of respiration. |
Energy transfer |
|
|
NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) |

Most important electron carrier in energy transfer. |
|
|

|
1: food, phosphate group, ATP |
|
|

|
2: oxidation, reduction, redox 3: electron carriers, NAD+, NADH |
|
|
|
Cellular respiration formula |
C6H12O6 + O2 + ADP + Pi -> CO2 + H2O + ATP |
|
|
|
How much does the breakdown of one molecule of glucose yields? |
36 |
|
|
|
Phases of Respiration |

1: Glycolysis 2: Krebs cycle 3: Election Transport Chain (ETC) |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Glycolysis |
First step in transforming glucose (first stage of energy harvesting) Happens in the cytosol Uses 2 ATP Yields 2 ATP Yields 2 NADH Results in 2 pyruvic acid (derivatives of glucose) |
|
|
|
Yeast |
Single cell fungi that only undergo glycolysis and produces drinking alchohol (ethanol) in an environment without oxigen. |
|
|
|
Lactic acid or lactate fermentation |
Oxygen isn't delivered fast enough to muscles, glycolysis and lactate fermentation are going to supply the ATP needed. |
|
|

|
1: glocolysis, Kreb cycle, electron transport chain. Cytosol, mitochondria 2: energetic electrons, electron transport chain. 3: ATP, NADH, pyruvic acid |
|
|
|
Krebs cycle (or citric acid cycle) |
Takes place in the inner compartment of mitochondria (inner membrane) Happens twice
IN: pyruvic acids (acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl CoA) OUT: 2 ATP CO2 (exhale through breathing) 6 NADH 2 FADH2 |
|
|

|
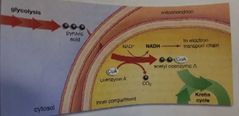
|
|
|

|
1: acetyl CoA |
|
|

|
1: Energetic electrons, ETC. CO2 2: NADH, FADH2 |
|
|
|
Electrons transport chain (ETC) |
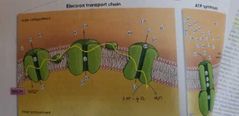
-Happens in the INNER MEMBRANE of mitochondria (inside the membrane wall) -Yields 34 ATP -last electron acceptor in the ETC is oxygen in the inner compartment. (Oxygen is a by-product)
Hydrogen ions are being pumped up the energy hill (against their concentration gradient) with energy supplied by the downhill fall of electrons throught the ETC. Hydrogen ions are moved back down their concentration gradient through the ATP synthase enzyme. The spinning of the ATP synthase puts a thrid phosphate group onto ADP to make it ATP. |
|
|
|
ATP synthase |

An enzyme that creates ATP by adding a phosphate groupe to ADP. It does that through spinning when Hydrogens ions goes through it. |
|
|

|
Water is a by product of respiration as is carbon dioxide |
|
|

|
1: lose (donate), membrane, hydrogen ions |
|
|

|
2: hydrogen ions, ATP synthase, phosphate group, ATP 3: Oxygen |
|
|
|
Plant make their own food |
They use energy from the sun, to take carbon dioxide, join it to a carbohydrate (sugar) and energize that sugar transforming it in food. |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis a trip up the hill |
Electrons are removed from water, bossted to a more energetic state by the power of sunlight and then brought together with a sugar and a carbon dioxide, resulting in food (carbohydrate). |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis |
Is the process by which certain groups of organisms capture energy from sunlight and convert this solar energy into chemical energy that is initially stored in a carbohydrate.
Takes place in the chloroplast
Endergonic reaction (vs exergonic for respiration) |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis formula |

CO2 + H2O > C6H12O6 + O2
Sunlight energy |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis is driven by part of the visible light spectrum (electromagnetic) |
Absorb much of the blue and red light but reflect of lot the green. This is why plants are green. |
|
|
|
Plants leaf |
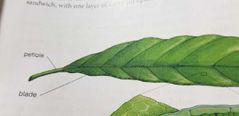
Petiole and blade |
|
|
|
Leaf cross section |
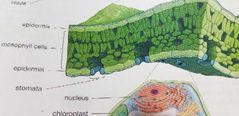
Epidermis Mesophyll cells Stomata (exhale Oxygen, inhale CO2) |
|
|
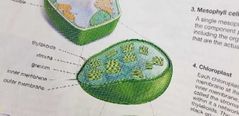
|
Thylakoids (stacked up are granum) Stroma (liquid) Granum (many thylakoids) Inner and outer membrane |
|
|
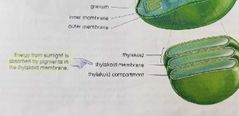
|

Thylakoid membrane contain a pigment called chorophyll a. And chlorophyll absorbs energy from the sun and pass it along. |
|
|
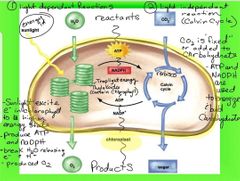
|
2 main stages in Photosynthesis Photo light dependent reaction Synthesis light independent reaction Photo: (in thylakoids) Photosystem 2 & photosystem 1 Power from the sunlight strips water of electrons then boost these electrons to a higher energy level.Happens again in photosystem 1 but this time in the end the energized electrons get attached to NADP+ that will transport them to the second set of reactions (synthesis). Synthesis: (in stroma) The electrons come together with carbon dioxide and sugar. It produces food. |
|
|
|
Photosystem 2 and photosystem 1 |
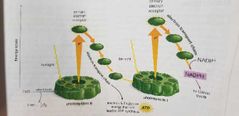
Happens in the thylakoids First stage (photo) Light dependent
Power from the sunlight strips water of electrons then boost these electrons to a higher energy level. Happens again in photosystem 1 but this time in the end the energized electrons get attached to NADP+ that will transport them to the second set of reactions (synthesis). |
|
|
|
Reaction center |
Chlorophyll a and other compounds that first receive solar energy and transforms it into chemical. |
|
|

|
1: electrons, CO2, sugar 2: chloroplast, leaves. Chlorophyll a. 3: light dependent reaction, primary electron acceptor, energy state. |
|
|
|
Why is light so important in photosynthesis |

The light reaction make two things happen: - splitting of water (hydrogen will be used in photosynthesis, oxygen is a reject and is breathable) - transformation of solar energy to chemical energy. (Excited state, up the energy hill, transfers to photosystem 2 and 1). |
|
|
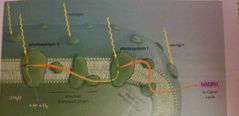
|

|
|
|
|
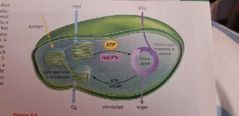
Calvin Cycle (C3) definition |
Set of steps in photosynthesis in which energetic electrons are brought together with carbon dioxide and sugar to produce an energetic carbohydrate. |
|
|
|
Process of fixation |
A gas being incorporated into an organic molecule. (Carbon dioxide that come through the stomata on the leaves of plants, is being fixed into the starting sugar called RuBP). |
Calvin cycle |
|
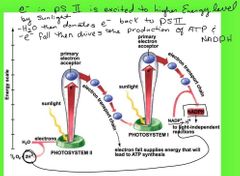
Photosystem 2 and 1 yield ATP and NADPH |
A |
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
1: electrons, NADPH, ATP. Oxygen 2: Calvin 3: sugar, atmosphere, electrons. ATP |
|
|
|
Rubisco |
Enzyme that takes a non- living gas (CO2) and turns it in glucose (which can be used for eveything). - the most abundant protein - he is slow ans prone to mistakes. Sometimes instead of using CO2 he uses O2, creating photorespiration |
Photosynthesis, Calvin cycle |
|
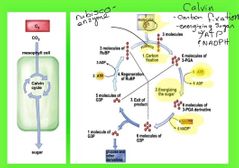
Calvin cycle: - Carbon fixation - Energizing sugar with ATP & NADPH |
A |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
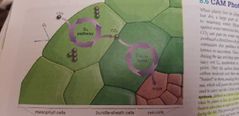
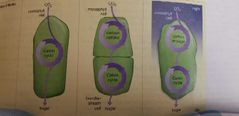
C4 photosynthesis |
A form of photosynthesis in which carbon dioxide is first fixed to a four-carbon molecule and then transferred to "bundle-sheath cells" where the Calvin cycle will take place.
Due to rubisco that binds to oxygen sometimes, some plants take a first step with another enzyme that only binds to CO2. That enzyme then take that CO2 to rubisco for them to bind (without possible mistakes since oxygen is not present at that point). |
|
|
|
CAM Photosynthesis |
Photosynthesis undertaken by plants in hot, dry climates, in which carbon dioxide takes place at night and the Calvin cycle occurs during the day. |
|
|

3 form of Photosynthesis |
|
|
|

|
1: low-energy sugar, CO2. O2, photorespiration. 2: warm, C4. 3: CAM, at night. During the day. |
|
|

Calvin cycle resume |
RuBP low energy sugar (binds with CO2) G3P high energy sugar (product of the CO2 fixation) |
|
|

|
C. Stored in Carbohydrates - released from food storage. |
|
|

|
E |
|
|

|
C |
|
|
|
From smallest to largest: nucleotide, gene, chromosome, genome. |

Nucleotides are the smallest building blocks of DNA. There are four nucleotides (A, G, T, C) which arrange in pairs to form the long double strands typical of DNA molecules.
A gene is a segment of DNA which codes for the amino acid sequence of a particular protein. A gene is therefore composed of many pairs of nucleotides. A chromosome is a long strand of DNA which is coiled up with various proteins. A chromosome contains many genes. The genome is all the DNA of a particular organism. All of an organism's chromosomes compose the organism's genome. To summarize, we can think of the genome as being composed of a collection of chromosomes, of chromosomes as being a collection of genes, and of genes as being composed of nucleotides. |
|
|
|
What human pass on in reproduction? |
Half of a father's genome and half of a mother's genome. Producing a full genome. |
|
|
|
Genetics definition |
The study of physical inheritance among living things. Storage, duplication, transfer of information |
|
|
|
How much genes in a genome? |
Estimates of 20-25,000. |
|
|

|
1: proteins. Bases, Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine. 2: amino acids. Bases, gene. 3: mRNA, rybosome. Amino acids, mRNA bases, protein. |
|
|
|
Cells dies and need to be replaced |
Brain cells and leaf cells in plants, almost never divides While the bone marrow ceels never stop dividing (produce red blood cells). |
|
|
|
Chromosomes |
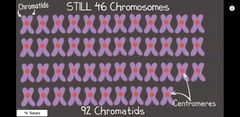
DNA in each cell that is packaged into individual units. 46 chromosomes 92 sister chromatids |
|
|
|
From DNA to Chromosomes |
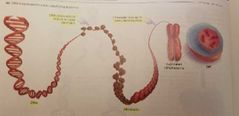
DNA Chromatin (DNA+Proteins) Chromosomes (folded chromatin) Chromosome duplicated to take a X shape. |
|
|
|
Chromosomes vs duplicated chromosomes |

Duplicated chromosomes has the X shape (composed of 2 sister chromatids) Chromatid is ONE of the two identical strands of chromatin that make up a chromosome) |
|
|
|
Homologous chromosomes |
Paternal and maternal copies of a given chromosome that are the same in function. 22 homologous chromosomes are autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) 1 is XX for femal or XY for male. |
|
|
|
Karyotype |
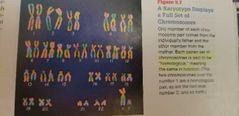
Pictotal arrangement of a complete set of human chromosomes. |
|
|

|
1: replicate, duplicate 2: proteins, sister chromatids 3: homologous,. X. X. Y |
|
|
|
Mitosis definition |
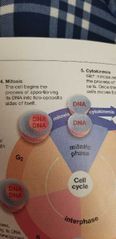
Is the separation of a cell's duplicated chromosomes prior cytokinesis. |
|
|
|
Cytokinesis definition |
The physical separation of one cell into two daughter cells. |
|
|
|
Cells cycle |
Interphase: - G1 - S: Synthesis - G2 Mitotic phase: (M phase) - Mitosis (PMAT) - Cytokinesis Last about 24 hours. Only 30min in mitotic phase |
|
|
|
Mitosis phase |
PMAT Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
4 |
|

Prophase |
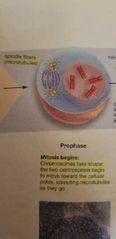
- thickening of chromosomes - sprouting of microtubules - centeosomes move to the opposites poles - nucleus dissipate |
|
|

Metaphase |
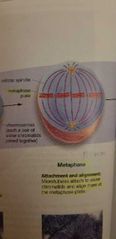
- attachment and alignment of the chromosomes to the metaphase plate. |
|
|

Anaphase |
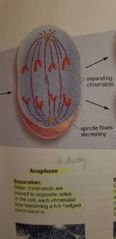
- separation of the sister chromatids |
|
|

Telophase and cytokinesis |
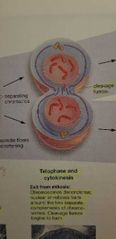
- chromosomes decondense - nuclear envelope form And cleavage furrow begins. |
|
|

Completion of cytokinesis |
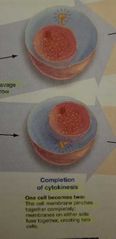
- One cell become 2 - membranes fuses Ready to start over |
|
|
|
Mitotic spindle |
Microtubules together active in cells division. |
|
|

|
1: chromosomes, daughter cells |
|
|

|
2: mitotic phase, interphase. 3: sister chromatids, chromosomes. |
|
|
|
Cytokinesis in plants |

Vesicles begins accumulating near the metaphase plate and then fuse together. |
|
|
|
Binary fission |
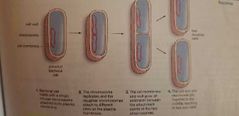
Division in prokaryotic cells (bacteria and archaea) Takes about 20 min |
|
|

|
1: cytokinesis, cell wall, plasma membrane. 2: nucleus, Plasma membrane, binary fission |
|
|

|
E |
|
|

|
D: a serie of DNA bases that contain information for the production of a protein. |
|
|
|
E: 23 pairs of chromosomes and as many as 25,000 genes. |
|
|
|
Somatic cells |
Cells that undergo mitosis. All animals cells except one type, sex cells or gametes |
|
|
|
Gametes |
Sex cells (eggs and sperm) Have only 23 chromosomes in a sperm or an egg. |
|
|
|
Meosis definition |
Cell division that results in the halving of chromosomes. Or Process in which a single diploid cell divides to produce 4 haploid reproductive cells. |
|
|
|
Haploid (n) |
Possess a single set of chromosomes Haploid=half 23 |
|
|
|
Diploid (2n) |
Possess 2 sets of chromosomes Diploid = double haploid 46 |
|
|
|
Mitosis stages |
Duplicate one, divides twice PMAT 1 & PMAT 2 |
|
|
|
Tetrad |
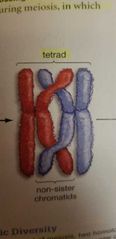
Mix of 2 homologous chromosomes. One from mom one from dad |
|
|
|
Crossing over or recombination |
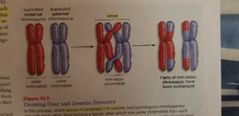
Occurs in prophase 1 |
|
|
|
Meiosis Prophase 1 |
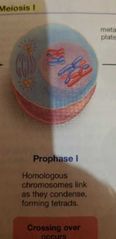
Chromosomes condense and link forming tetrads |
|
|
|
Meiosis Metaphase 1 |
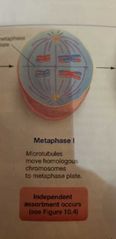
Chromosomes randomly aligns in the metaphase plate |
|
|
|
Meiosis Anaphase 1 |

Separation of homologous chromosomes (not the separation of sister chromatids like in mitosis). |
|
|
|
Meiosis Telophase 1 |

Cell undergo cytokinesis and divides in 2 daughter cells (two haploid cells) |
|
|
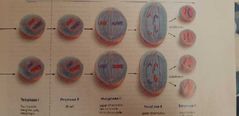
|
- now in prophase 2 there are chromosomes and not tetrads. - Anaphase 2 separated sister chromatids now and not the homologous chromosomes. - Telophase resuls now in 4 haploid cells. |
|
|

|
1: eggs, sperm. Diploid, haploid. 2: homologous chromosomes. Sister chromatids. 3: 46, 23 |
|
|
|
Meiosis diversity is due to: |
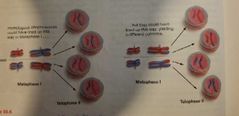
- crossing over - independent assortment (random distribution of homologous chromosomes pairs during meiosis) Offspring diversity and natural world diversity |
|
|
|
Genes in X and Y chromosomes |
X has about 1500 genes Y has about 78 genes |
|
|

|
1: Homologous chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes pairs 2: differ 3: X, X, Y |
|
|
|
Starting femal cells in gamete formation. |
Oogonia |
|
|
|
Starting mal cells in gamete formation |
Spermatogonia |
|
|
|
Primary oocytes |
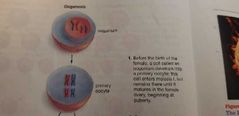
Oogonia is the starting cell in gamete formation for female, primary oocyte is the following stage. Primary oocyte is the cell undergoing meiosis. |
|
|
|
Primary spermatocytes |
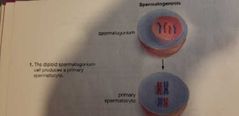
Spermatogonia is the starting male cell in the gamete formation. Primary spermatocyte is the next cell produced. Primary spermatocyte is the cell undergoing meiosis. |
|
|
|
Oogenesis |
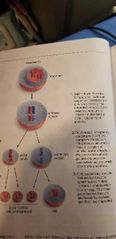
Starts with Oogonium Develops into Primary oocyte (only the primary oocyte released each month during ovulation completes meiosis 1) 2 cells are produced (1 polar body, waste, and 1 secondary oocyte, good egg) Only 1 cell fertilized by a sperm undergo meiosis 2, producing 4 cells (3 polar bodies, waste and 1 good egg)
|
|
|
|
Spermatogenesis |
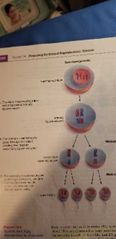
- Starts with a spermatogonium. - Develops into Primary Spermatocyte (undergo meiosis) - results in 2 haploid Secondary spermatocyte. - both undergo meiosis and yields 4 haploids spermatids (spermatids will develop into mature sperm) |
|
|
|
Life cycle definition |
The repeating series of steps that occur in the reproduction of an organism. |
|
|
|
Sexual reproduction definition |
The union of two reproductive cells to create a new organism. |
|
|
|
Asexual reproduction definition |
Reproduction that does not in involve sex.
(Mammal never do asexual reproduction) (Bacteria do that through binary fission) |
|
|
|
Parthenogenesis |
Reproduction only through femal, no fertilized egg by male, only one set of chromosomes. Results in clones, and only females. |
|
|

|
1: stem. Before birth. 2: polar bodies. 3: identical |
|
|
|
Vegetative reproduction |
A tree branch properly planted that sprouds and and grows as an independent plant (can take part in sexual reproduction). |
|
|
|
Regeneration |
The self regrowth of a cut limb (like the sea start and the lizard tail) |
|
|
|
What genes do? |
They bring about the production of proteins. They are composed of DNA There is about 30,000 genes They are smaller than chromosomes in which they reside |
|
|
|
Molecular biology definition |
The investigation of life at the level of its individual molecules. |
|
|
|
Who discovered double helix? |
Watson and Criks, and Wilkin and Franklin in 1953 |
|
|
|
What did they use |
X-ray crystallography or X ray difraction |
|
|
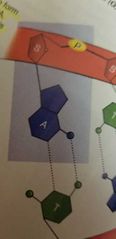
DNA Structure |

|
|
|

|
1: structure of DNA 2: A, C 3: nitrogen base, protein |
|
|
|
Helicase |

|
DNA |
|
|
DNA polymerase |
Enzyme who moves along each strand of the double helix, joining together nucleotides as they are added to form new complementary strands of DNA. Can also perform editing by replacing a mismatched nucleotide and replace it with a proper one. |
|
|
|
Mutation definition |
A permanent alteration of a DNA base sequence. |
|
|
|
Point mutation |
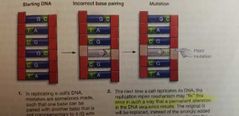
|
|
|
|
Somatic cells definition |
Cells that do not become sperm or eggs. |
|
|
|
Germ-line cells |
Cells that do become eggs or sperm. They are heritable. |
|
|
|
Mutagen definition |
A substance that can mutate DNA |
|
|

|
1: a new complementary strands 2: DNA polymerase 3: mutation |
|
|
|
Polypetide |
Strings of amino acids (forms proteins) |
|
|
|
Protein synthesis stages |

Transcription: the process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is copied onto messenger RNA. Happens in the nucleus. Translation: photo |
|
|

|
1: amino acids 2: mRNA, ribosome, |
|
|
|
RNA |
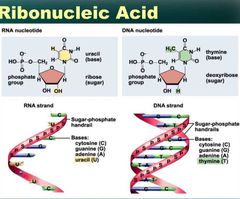
Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T) Single stranded instead of double Ribose sugar instead of Deoxyribose sugar |
|
|
|
RNA polymerase |
Enzyme that unwinds DNA and strings together RNA nucleotides to make up a primary transcript (that will become mRNA) |
|
|
|
RNA polymerase vs DNA polymerase |

|
|
|
|
Codon and tRNA |

Codon are a coding triplet on the mRNA (each codes for an amino acid)
tRNA, transferRNA latches onto the mRNA codon with his anticodon and brings the appropriate amino acid that it picked up in the cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
Binding sites in ribosomes |
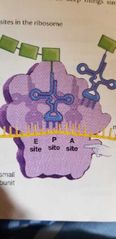
E, P, A |
|
|
|
Start codon |
mRNA codon - AUG amino acid tRNA anticodon - UAC amino acid Methionine (mat) is the starting amino acid. |
|
|

|
1: complementary base paring 2: DNA, RNA, amino acid 3: amino acid, mRNA codon |
|
|
|
Human genome |
Defines as the full complement of DNA found in the nucleud of each human cell. Less than 2% of the human genome codes for proteins. |
|
|
|
The editing of the primary transcript of DNA onto the mRNA. |

RNA polymerase is an enzyme coding for RNA, it must align to the promoter for transcription to happen. The transcription rate of RNA polymerase is influenced by its alignment to the promoter. It's alignment is best when the enhancer proteins are set in a way where they properly align to the promoter. |
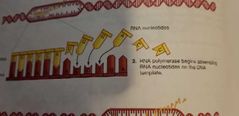
|
|
|
Transcription factors |
Transcription factors are the proteins that binds to the promoter and enhancer in the Transcription process from DNA to mRNA. They help accelerate the transcription rate when they bind properly. |
|
|
|
Micro-RNA (gene silencing) |

Micro-RNA is a non-coding RNA sequence. Micro-RNA is transcribed from DNA, and binds to mRNA in the cytosol where with the help of an enzyme called Slicer, it cuts in two the strand of mRNA This decreases the production of protein. |
|
|
|
3 form of genetic regulation (the editing step between DNA transcription to the mRNA transcript) |
- Alignment of RNA polymerase with the Promoter and the enhancer aided by the transcription factors. - Micro-RNA that binds to mRNA and cut it with a Slicer enzyme. - Alternative splicing. Introns, non-coding sequences are removed by enzymes while exons are spliced back together. |
|
|
|
Alternative splicing |
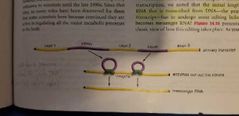
Primary transcript (is the step between DNA and mRNA)
The non-coding sequences in the primary transcript (the introns) are cut out to leave only the coding sequence (exons). Results is a mRNA with only coding exons. The exons can be put together in alternative ways, yielding different proteins. |
|
|

|
1: DNA, transcription 2: Micro-RNA, mRNA 3: Editing, mRNA. Introns, exons |
|
|
|
D |
|
|
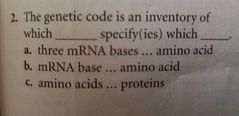
|
A |
|
|

|
C |
|
|
|
Biotechnology - definition |
Biotechnology is the use of technology to control biological processes as a means of meeting societal needs. |
|
|
|
Transgenic organisms |
Is one whose genome has stably incorporated one or more gene from another species. |
|
|
|
Restrictions enzyme |
Enzyme that can cut DNA in a specific place. |
|
|
|
Plasmids |
Plasmids are small, extra-chrosomomals rings of bacterial DNA, that can exist outside of bacterial cells and that can move into these cells through the process of transformation. |
|
|
|
Transformation |

A cell's incorporation of genetic msterial from outside its boundary. |
Plasmid |
|
|
Recombinant DNA |
Two or more segments of DNA that have been combined by humans into a sequence that does not exist in nature. |
|
|
|
Cloning vectors |
Self-replicating agents that serve to transfer and replicate genetic material. (Plasmid is a cloning vector). |
|
|

|
1: gene, another species 2: restriction enzymes 3: human, protein |
|
|
|
Reproductive cloning |
Is the process ok making adult clones of mammals of a define genotype. |
|
|
|
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) |
2 eggs, one has it nucleus removed to other not, they are fused together and get implanted into a surogate mother after the cell start developing as an embryo. |
Cloning of the goat |
|
|
2 ways to generate human cells |
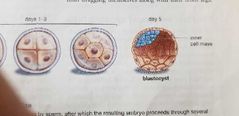
- embryonic stem cells (ESCs): embryonic cells that are capable of giving rise to all types of cells in the adult body. (Found in the blastocyst, fertilized egg that has about 150 cells inside) - Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPS cells). Man made stem cells. (Plutipotent, means a cell that can give rise to all type of cells). |
ESCs iPS |
|
|
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) |

A technique for quickly producing many copies of a specific segment of DNA. |
Used by the police to duplicate DNA |
|

|
1: gene, another species 2: restriction enzymes 3: human, protein. |
|
|

|
1: genetic copy 2: adult mammals 3: provided the donor cell containing DNA |
|
|

|
1: 5 days 2: all, ordinary 3: own cells |
|
|

|
1: DNA 2: small 3: short tandem repeats (STRs) |
|
|
|
Short tandem repeats (STRs) |
Repeated tandem in a given location of DNA. This is what is used to compare with DNA found on a crime scene. |
Dna police investigation |

