![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are Lamarck assumptions |
Tendency towards perfection. Organisms grow towards complexity and perfection. Use and disuse. Traits used commonly will be expressed in more organisms. We're as traits not used will disappear. Inheritance of acquired traits. Characteristics can be inharited. |
|
|
The significance of the Galapagos to Darwin. |
Much of his research took place there. |
|
|
What is the struggle for existence. |
An environment demands certain traits. |
|
|
Lamarck vs Darwin's theroy |
Lamarck believed that organisms who used a traits commonly it's offspring would have that trait even if it is unrelated to their genes. Darwin believed change in a organism was pushed by it's environment. |
|
|
What is punctuated evolution |
Rapid change in a organism followed by long periods with none. |
|
|
Why does punctuated evolution suggest that the fossil record is complete. |
Because fossil records barely show organisms going through change. |
|
|
How do marsupials support evolution. |
Australia has a large amount of them where as the rest of the world dose not. Suggesting that the marsupials off Australia evolved into other mamals. |
|
|
How do fossil support evolution |
They show the history of organisms. |
|
|
How dose Biochemistry support evolution. |
Similarities in DNA suggest that a organism is related. |
|
|
How do vestigal structures support evolution. |
Organisms with vestigal structures do not need them so why have them. Evolution fills this gap. |
|
|
What is the system of eon periods eg. |

|
|
|
What is a gene pool and why is it inportant. |
Gene pools are the combined genetic information of all members in a particular population. they are inportant because ratios of certain alleles push evolution. |
|
|
What is the nucleotide |
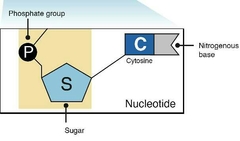
A segment of a DNA bond. |
|
|
What are the 4 base pairs in DNA |
Thymine - Adenine Cytosine - Guanine |
|
|
Genetic drift |
Random selection of a population which Leeds to evolution. |
|
|
Species |
A group of organisms that produce fertile offspring. |
|
|
Speciation |
Is when one species gives rise to many. |
|
|
Evolutionary divergence |
Is when one species gives rise to many. |
|
|
Evolutionary convergence |
Is when organisms with different orgins develop similar traits. These are called analogous structures. |
|
|
Addaptive radiation |
When one organism evolves to fill many niches. |
|
|
Niche |
A job or role of a organism. |
|
|
What is the difference between old and new species |
Older ones are simple and newer ones are complex. |
|
|
Endospore |
A dormant stage of a bacteria, that can withstand harsh enviorments. |
|
|
Conjugation |
When bacteria form a tube between another to trade genetic information. |
|
|
Binary Fission |
Doubling a cells content to later split to form to daughter cells. |
|
|
Prokaryotic |
A cell that lacks a nucleus. |
|
|
Gram positive |
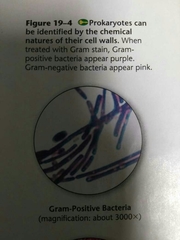
Bacteria Only absorbs Violet, indicating it has one outer membrane layer of peptidoglycan. |
|
|
Gram negative |

Bacteria stained red, indicating a second layer of lipids and carbs. |
|
|
Bacilli |
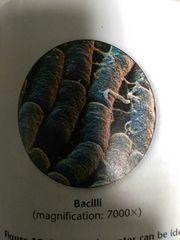
Rod shaped bacteria |
|
|
Cocci |
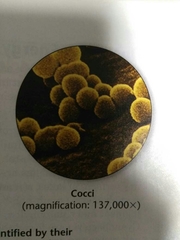
Sphere shaped bacteria |
|
|
Spirilla |

Spiral shaped bacteria |
|
|
Photoheterotrophs |
Is photosynthetic, but also needs to consume organic compounds. |
|
|
Autotrophic |
Creates organic compounds |
|
|
Heterotrophic |
Consumes organic compounds |
|
|
Phototrophic |
Produces organic compounds through photosynthesis |
|
|
Chemotrophic |
Produces organic compounds from inorganic compounds. Through chemical synthesis. |
|
|
Saprophytic |
Absorbs nutrition from decaying matter. |
|
|
Obligate arobes |
Can not live without oxygen, produces energy with it. |
|
|
Anaerobic |
Produces energy without oxygen |
|
|
Facultative anarobes |
Can survive with or without oxygen |
|
|
Symbiotic bacteria |
Break down food in digestion |
|
|
Lysogenic virus infection |
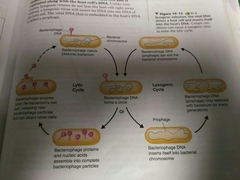
Virus DNA inserts it's self into a cells chromosome, and becomes latent, As the cell divides it's content along with the viruses DNA. |
|
|
First line of protection from pathogens |
Barriers: skin, mucus, hair, |
|
|
Second line of defense from pathogens |
Phagocytes, white blood cells inflame area and destroy. Fever, and interferon protein. |
|
|
Third line of protection from pathogens |
Antibodies |
|
|
Rhizoids |
structures that penetrate a surface |
|
|
Gametangia |

When two different fungi stolons meet. |
|
|
Zygospore |
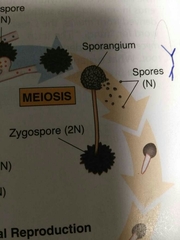
Part of a fungus life cycle that fuses DNA. Later a sporangiophore is produced from it. |
|
|
Sporangium |
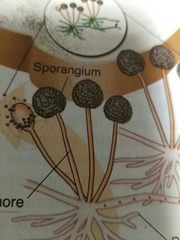
Holds spores in zygomycota |
|
|
Basidiomycota |

Club fungi |
|
|
Ascomycota |
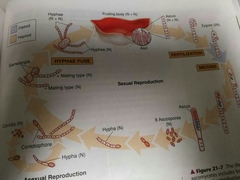
Sac fungi |
|
|
Asci in fungi |
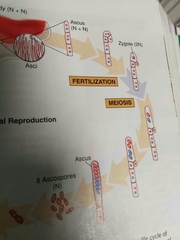
Sexual Reproductive filament like structures in ascomycetes |
|
|
How does the fruiting body form in ascomycetes |
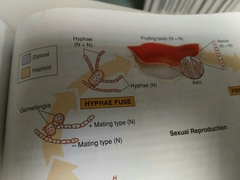
From the gametangia |
|
|
Name as many parts of a bacteria as you can. |
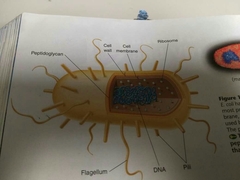
|
|
|
What is the function pili on bacteria |
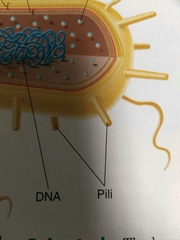
To attach to surfaces |
|
|
What the trichocysts |
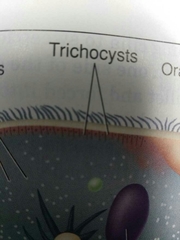
Structures that release stiff projections as defense |
|
|
Contractive vacuole |
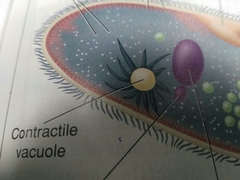
Controls amount of water in a cell |
|
|
Macronucleus |
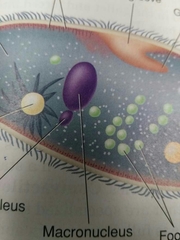
Contains multiple copies of DNA |
|
|
Micronucleus |
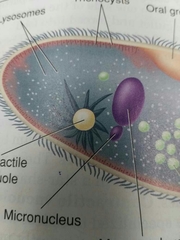
Contains the reverse copy of genes |
|
|
Gullet and oral groove |
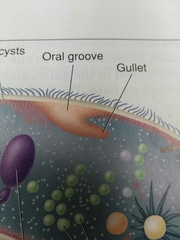
Digestive indent on the cell, used to sweep food particles into. |
|
|
Plasmodium sporozoites |
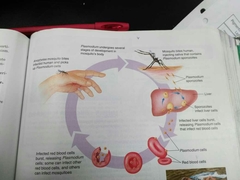
Protist responsible for Malaria |
|
|
Food vacuole |
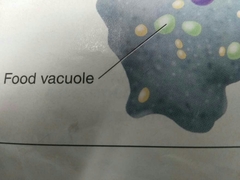
A digestive sac in a cell |
|
|
Basidia |
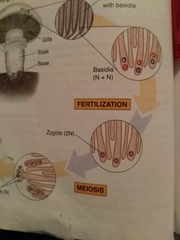
Hair like structures in basidiomycota enrolled with fertilization. |
|
|
Stolons |
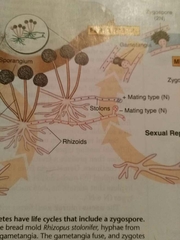
Reporductive root part of zygomycetes |
|
|
Red alge |

Rhodophyta |
|
|
Green algae |

Chlorophyta |
|
|
Brown algae |
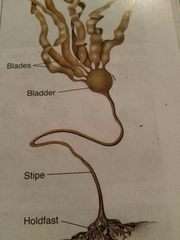
Phaeophyta |
|
|
Where do each phylum of algae live in the water level. |
Green high Brown mid Red deep |
|
|
Chlorophyll types in algae |
Green a,b Brown a,c Red a,d |
|
|
Gonad |
Gametes producing organs. |
|
|
What is the dominant part of moss |
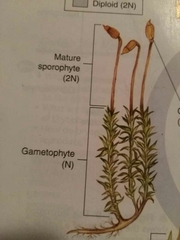
Gametophyte |
|
|
What is the female part of bryophytes |
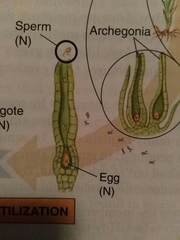
Archegonia |
|
|
What is the male part of byrophytes |

Antheridia |
|
|
What is the immature stage of a bryophyte |
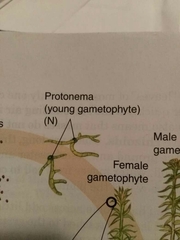
Protonema |
|
|
Deuteromycota |
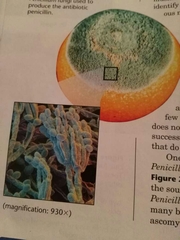
Imperfect fungi |
|
|
How do zygomycetes sexually reproduce |
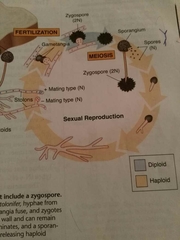
A positive and negative stolon meet and create a gametangia which forms a zygospore and shuffles their DNA to create a sporangiophore. |
|
|
Mycelium |
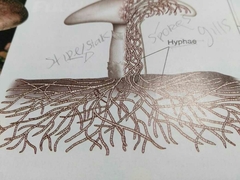
Underground network of hyphae |

