![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
defining characteristics of seed plants
|
-heterosporous (all)
-ovules! -water NOT needed for fertilization -microscopic gametophytes are NOT independent of sporophyte |
|
|
what is the significance of ovules?
|
In the ovule,
-megaspores are produced by meiosis -sperm fertilize the egg to make a diploid zygote -the zygote grows into an embryo sporophyte -becomes a seed |
|
|
Two types of seed plants
|
with exposed seeds/ovules - Gymnosperms
with enclosed seeds/ovules - Angiosperms |
|
|
4 phylums of Gymnosperms?
|
-Cycadophyta
-Ginkgophyta -Gnetophyta -Coniferophyta |
|
|
Which time period and biome are cycads most prominent in
|
- Triassic: "Age of Cycads"
- tropical/subtropical |
|
|
What are cycads (Cycadophyta) used for?
|
-ornamental (slow-growing & expensive)
|
|
|
Which Gymnosperms are dioecious (& what does that mean)
|
-Cycadophyta
-Ginkgophyta -male and female cones on separate plants |
|
|
What is the only existing species of Ginkgophyta?
Where are they native to and what are they used for? |
-Ginkgo biloba (female fleshy ovules are edible and STINKY)
-native to China, ornamental: deciduous & resistant to air pollution -leaf extract promotes blood flow ("memory herb"); can be hemorrhagic |
|
|
Which Gymnosperms have flagellated sperm?
|
-Cycadophyta
-Ginkgophyta -Gnetophyta & Coniferophyta sperm are non-motile |
|
|
What are the only 3 species of Gnetophyta?
|
-Gnetum
-Ephedra -Welwitschia |
|
|
Where does Gnetum thrive? What sort of plant?
|
-tropical
-tree/vine |
|
|
What sort of plant is Ephedra? What is it used for?
|
-leafless shrub
-source of ephedrine -"Mormon Tea" ; Ma Huang |
|
|
Whart sort of plant is Welwitschia, and where does it thrive?
|
--short woody trunk with only 2 leaves and long taproot
-SW Africa: Namib Desert |
|
|
What is the flower peduncle?
What is the flower receptacle? |
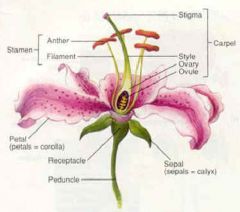
All floral parts are attached in whorls at the tip (receptacle) of the flower stem (peduncle)
|
|
|
Which phylum of Gymnosperms is unique and how?
|
-Gnetophyta
-angiosperm features: 1)vessel elements in xylem 2)double fertilization |
|
|
Which phylum of Gymnosperms is monoecious?
|
-Coniferophyta; male & female cones on same tree
|
|
|
What are two genera of Coniferophyta? What are their characteristics and general location?
|
-Podocarpus: single, fleshy ovules; southern hemisphere
-Pinus: largest genus; needle leaves, woody female cones; northern hemisphere |
|
|
Describe the steps of the life cycle of seed plants.
|
1. Gymno- and Angio- sporophytes produce both male spores: microspores and female spores:megaspores
2.Megaspores formed in protective structure called ovule 3.Microspores produce tiny male gametophytes:pollen which produce sperms 4.Megaspores produce female gametophytes:embryo sac within the ovule 5.Pollination occurs: transfer of pollen to female cone or flower part containing ovules by wind, insects, birds 6.After fertilization the zygote begins to grow into sporophyte within the ovule, but stops as ovule becomes a seed |
|
|
Which phylum are flowering plants in?
|
Anthophyta - angiosperms
|
|
|
What is the Gynoceium?
|
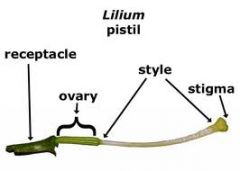
-All the female parts = pistil composed of stigma, style, ovary
|
|
|
What are carpels?
|
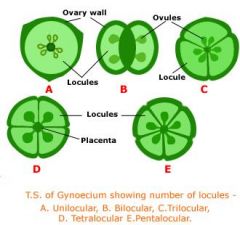
-compose the pistil: subdivisions with an interior cavity called a locule containing ovules
simple: 1 carpel compound: 2+ carpels e.g. bellpepper, tomato (4) |
|
|
Where are pistils located in the floral structure?
|
either:
-on top of receptacle (superior) -within receptacle (inferior) |
|
|
What is the Androecium?
|
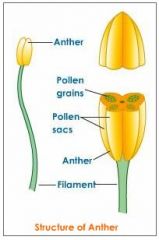
-the male parts of the flower (stamen): anther with pollen sac, stalk called filament
|
|
|
What are the accessory parts of a flower
|
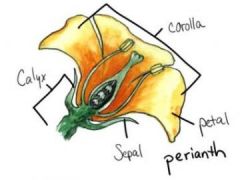
-receptacle
-nectaries -perianth: petals(corolla), sepals(calyx) |
|
|
Distinguish a monocot from a dicot
|
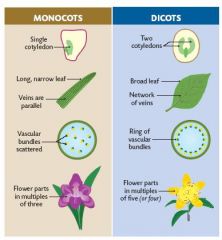
-mono=3
-di=4 or 5 |
|
|
All classifications found from floral structure
|
-monocot: parts in 3's
-dicot: parts in 4's or 5's -complete: all 4 whorls -incomplete:don't have all 4 whorls -perfect: both male and female parts -imperfect: staminate or pistillate -monoecious: staminate & pistillate on same plant -dioecious: staminate & pistillate on different plants |
|
|
What is an inflorescence? What kind are there?
|
many flowers per peduncle held by pedicel, a smaller stalk
includes: spikes, racemes, panicles, corymbs, umbels, dichasium, catkins, cymes, heads |
|
|
How does a microspore becomes pollen grains
|
1. In anthers, each diploid mother cell divides by meiosis to form 4 haploid microspores
2. Each microspore divides to form a 2-celled male gametophyte: pollen 3.One cell, tube cell, produces pollen tube; other: generative cell. forms 2 sperm |
|
|
How does a megaspore become eggs.
|
1. diploid mother cell in ovule divides by meiosisi to form 4 haploid megaspores; one will develop into 7-celled female gametophyte: embryo sac
2. The egg is between 2 cells, synergids, located at the micropyle, the entry of the ovule 3. The cell in the middle of embryo sac has 2 nuclei - the polar nuclei 4. Three more cells, antipodals, are at the back |
|
|
What is double fertilization? How does it happen?
|
when both sperm fuse
-after pollination, tube cells forms pollen tube which grows down the style to the micropyle of ovule -generative cell divides to form 2 sperm, one fertilizes the egg to make zygote, other fuses with 2 polar nuclei to form triploid endosperm = double fertilization! |
|
|
How does a seed form?
|
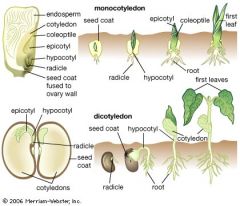
-the zygote develops into an embryo sporophyte with its food source, endosperm, within the ovule
-the mature ovule becomes a seed and its integuments form the seed coat -the embryo plant consists of a radicle, plumule, and cotyledons (1 or 2) -seed germinates/sprouts when the seed swells with water, the seed coat ruptures, and the radicle emerges first |

