![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
DNA
|
is deoxyribonucleic acid, with nucleic referring to DNA's location in the nuclei of eukaryotic cells.
|
A,T,G,C
Double helix |
|
|
Johann Friedrich Miescher
|
He looked at puss cells
|
|
|
|
Nucleotides are made up of...
|
A phosphate group, a 5 carbon deoxyribose sugar, and nitrogen base.
|
|
|
|
Watson and Crick
|
Noble piece prize DNA, discoverers of the double helix.
|
|
|
|
DNA Replication and Repair
|
-Hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases break
- DNA unwinds -Free nucleotides bind to exposed bases forming |

|
|
|
Central Dogma
|
-DNA to mRNA (transcription)
-RNA to protein (translation) |
|
|
|
mRNA to Protein
|
-3 bases on the mRNA code for 1 amino acid
- each set of 3 bases is called a codon -There are 64 codons possible |
|
|
|
Genetic Code
|
-The 64 codons form the genetic code
-Defined as the code that relates nucleotide sequence to amino acid sequence |
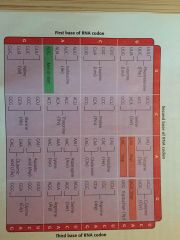
|
|
|
Genotype
|
-Genetic makeup of an organism
-Heritable info contained in the sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA |
|
|
|
Phenotype
|
-Physical traits of an organism
|
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
-Made of a small & a large subunit
-Small subunit has binding site for mRNA -Large subunit has 2 binding sites (P&A) for tRNA |
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
-Made of a small & a large subunit
-Small subunit has binding site for mRNA -Large subunit has 2 binding sites (P&A) for tRNA |
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
-Made of a small & a large subunit
-Small subunit has binding site for mRNA -Large subunit has 2 binding sites (P&A) for tRNA |
|
|
|
Transcription
|
INITIATION:
"start transcribing" (promoter) on the DNA, proteins bring RNA polymerase to the promoter (enzyme binds to promoter), DNA strand unwinds and complementary ribonucleotides are assembled in front of the exposed strand ELONGATION: RNA polymerase overs son the DNA joining nucleotides together, RNA formed elongates TERMINATION: When the enzym reaches a stop sequence or terminator sequence (ATT;ATC), the process stops |
|
|
|
mRNA
|
•Undergoes modification after it is produced in the nucleus
•Cap is attached •Tail is attached •Introns are spliced (RNA splicing) |
|
|
|
mRNA
|
•Undergoes modification after it is produced in the nucleus
•Cap is attached •Tail is attached •Introns are spliced (RNA splicing) |
|
|
|
tRNA
|
•Function: transfer of amino acids to the ribosome and mRNA
•Is single stranded •At one end is a triplet of bases called anticodon •At the other end is a site for attachment of amino acids |
|
|
|
rRNA
|
•Synthesized in the nucleus
•Released into the cytoplasm •Hold the 2 subunits of the ribosome together |
|
|
|
Translation
|
1. tRNA gets charged (Attachment of amino acid to tRNA)
Initiation: •mRNA attaches to the smaller subunit of the ribosome •tRNA with an amino acid binds to the 1st codon on the mRNA •The larger subunit attaches to the smaller subunit; tRNA slips into the P site of the larger subunit Elongation: 1. Codon recognition a. A 2nd charged tRNA comes with its amino acid and pairs with the 2nd codon on the mRNA 2. Peptide bond formation b. A peptide bond is formed between the 1st and the 2nd amino acids; 1st tRNA leaves 3. Translocation c. Ribosomes moves 3 nucleotides to the right; 2nd tRNA moves to the A site and P site is exposed; 3rd tRNA attached to the P site and the process continues. |
|

