![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
143 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the fuction of the urinary system?
|
to rid the body of metabolic waste (cellular waste)
|
|
|
What is the breakdown of protein?
|
Protein -> Amino Acid -> NH2 -> Ammonia, Urea, or Uric Acid
|
|
|
What is most likely to put off Ammonia and why?
|
fish, because it requires a lot of water
|
|
|
What is most likely to put off Uric Acid and why?
|
birds and desert animals, because it requires very little water
|
|
|
What is most likely to put off Urea and why?
|
Humans, it falls right in the middle of water requirements
|
|
|
What is the composition of urine? and the %'s
|
water - 95%
solids - 5% |
|
|
What are the 3 main components of urea?
|
Ammonia, uric acid, creatinine
|
|
|
what is the percentage of ammonia in urea?
|
1%
|
|
|
what is the percentage of uric acid in urea? and a reaction if levels get to high?
|
1%, causes gout if levels are too high
|
|
|
what is the percantage of creatinine in urea?
|
1%
|
|
|
what is the percentage of sodium in urea?
|
<1%
|
|
|
what is the percentagage of choride in urea?
|
<1%
|
|
|
What is the percentage of potassium in urea?
|
<1%
|
|
|
What is the percentage of magnesium in urea?
|
<1%
|
|
|
What is the percentage of calcium in urea?
|
<1%
|
|
|
What is the percentage of calcium in urea?
|
<1%
|
|
|
what is the percentage of sulfate in urea?
|
<1%
|
|
|
what is the percentage of phosphate in urea?
|
<1%
|
|
|
what components of urea are all components of salt?
|
sodium, chlorides, potassium, magnesium, calcium, sulfates, phosphates
|
|
|
What is the fuction of blood?
|
carries the waste from the tissue to the kidneys
|
|
|
How many kidneys do we have and where are they located and what shape are they?
|
2 kidneys, located below the diaphram up against the lumbar vertebrae, bean shaped
|
|
|
what is the cortex?
(in regard to the kidney) |
the outer layer of kidney, kinda grainy
|
|
|
what is the medulla?
|
middle region that contains
pyramids & nephrons |
|
|
what is the pelvis (within the kidney)?
|
inner most region, the collection region connects to the ureter
|
|
|
what is a nephron?
|
set of tubes that filter, absorb, and collect waste products from the blood
|
|
|
what is the efferent arteriole?
|
the artery that leads OUT OF the renal corpuscle
E for efferent, E for exit |
|
|
what is the afferent arteriole?
|
the artery that goes INTO the renal corpuscle
|
|
|
what is the renal corpuscle and what is it made of?
|
where all the filtering takes place, made of the glomerulus and bowman's capsule
|
|
|
what is the glomerulus?
|
the wad of arteries located within the bowman's capsule
|
|
|
what is the bowman's capsule?
|
goes around the glomerulus
|
|
|
what is the proximal tubule?
|
tube that connects to the renal corpuscle and winds around and narrows down. used for absorption for salt, sugar, amino acids, ect.
|
|
|
what is the loop of Henle?
|
were the tube narrows and loops around
|
|
|
what is the descending limb?
|
the descending tube in the loop of Henle, absorbs water
|
|
|
what is the ascending limb?
|
the ascending tube in the loop of Henle, absorbs salts
|
|
|
what is the distal tubule?
|
where it starts to widen,the part farther away from the renal corpuscle, leads to the collecting tubule
|
|
|
what is the collecting tube?
|
leads to the ureter
|
|
|
what is the ureter?
|
main tube leading to the bladder
|
|
|
what is the bladder and how much will it hold?
|
storage for urine, will hold 250 ml
|
|
|
how much urine leaves the body each day?
|
between 1-2 liters
|
|
|
what is the urethra?
|
the tube from the bladder to exit the body
|
|
|
after the reabsorption process, how much protein and carbohydrates should be in urine?
|
none
|
|
|
what does the formula for urea composition look like?
|
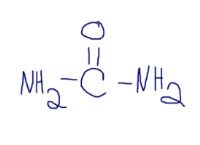
..
|
|
|
What is the function of the respiratory system?
|
take oxygen to the tissues and carbon dioxide away from the tissues
|
|
|
what is inspiration?
|
breathing in; inhale
|
|
|
what is expiration?
|
breathing out; exhale
|
|
|
how much nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide are inhaled?
|
nitrogen- 79%
oxygen - 21% carbon dioxide - .04% |
|
|
how much nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide are exhaled?
|
nitrogen - 79%
oxygen - 16% carbon dioxide 4% |
|
|
what is external respiration?
|
breathing exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with the air and blood within the lungs; from high concentration to low concentration called simple diffusion
|
|
|
what is internal respiration?
|
exchange of oxygen and carbod dioxide within the tissues and blood withing the body; a subcomponent of external respiration
|
|
|
what is cellular respiration (an abbreviation)
|
ATP, subcomponent of internal respiration
|
|
|
38ADP + ________ = 38ATP
|
38 phosphate
|
|
|
What do the nasal cavities do?
|
filter and warm the air
|
|
|
where is the nasopharynx and what does it do?
|
behind the nasal caviites, and connects the nose to throat
|
|
|
place where nose, mouth, trachea, and esophagus come together?
|
pharanx
|
|
|
what is the pharanx?
|
place where nose, mouth, trachea, and esophagus come together
|
|
|
what is the glottis?
|
the opening to the trachea
|
|
|
what is the epiglottis?
|
the flap covering the glottis
|
|
|
what is the trachea?
|
the main air tube
|
|
|
what is the larynx?
|
the enlarged area of the upper part of the trachea; holds voice box
|
|
|
what is the bronchi?
(bronchus) |
two branches, first branching of the pathway to the lungs.
|
|
|
what are the bronchioles?
|
second branching of pathway to the lungs
|
|
|
how many times do the bronchioles branch to the left?
|
2 times
|
|
|
how many times do the bronchioles branch to the right?
|
3 times
|
|
|
what are the alveoli?
|
microscopic air sacs, the point where gases are exchanged; oxygen and carbon dioxide
|
|
|
where are the lungs?
|
glued to the walls of the thoracic cavity.
|
|
|
how many lungs are on the right?
|
3
|
|
|
how many lungs are on the left?
|
2
|
|
|
what do the pleural membranes do?
|
holds the lungs to the thoracic cavity
|
|
|
what does the diaphram do?
|
contracts to inhale
|
|
|
what do the ribs do in relation to respiration?
|
spring back into place to produce the exhale.
|
|
|
common cold
|
caused by a rhinovirus
|
|
|
what does rhino mean?
|
nose
|
|
|
infuenza
|
flu/ 35 different flus
|
|
|
pneumonia
|
fluid on lungs
|
|
|
bronchitis
|
inflammation of bronchi or bronchioles
|
|
|
strep throat
|
caused by bacteria 'Streptococcus pyogens'; if it gets into the blood stream, it can be deadly
|
|
|
tuberculosis
|
bacterial - 'Mycobacteria tuburclosis'; eats holes in lungs
|
|
|
emphysema
|
destruction of lungs tissue, trapping air
|
|
|
pulmonary fibrosis
|
scar tissue inside the lungs from silia (spun glass, insulation), dust, asbestos
|
|
|
lung cancer
|
accessive growth of cells inside the lungs. #1 cause is smoking
|
|
|
sudden infant death syndrome
|
SIDS baby stops breathing
|
|
|
what are some of the substances that can cause pulmonary fibrosis?
|
silia (spun glass, insulation), dust, asbestos
|
|
|
what is the #1 cause of lung cancer?
|
smoking
|
|
|
what does SIDS stand for?
|
sudden infant death syndrome
|
|
|
what is the function of the digestive system?
|
(1) breakdown of food
(2) absorbs food (3) get rid of undigested food |
|
|
how long is the digestive system?
|
app. 28 foot long; is just one long tube
|
|
|
what is another name for the mouth and what is its main function?
|
called the oral cavity; main function is to receive food and starts digestion
|
|
|
what do the teeth do?
|
mechanical process to breakdown food (grinding)
|
|
|
how many incisors are there and what are the main function(s) for them?
|
8 - cutting and tearing
|
|
|
how many canines are there and what are the main function(s) for them?
|
4 - puncturing
(no real use in humans) |
|
|
how many premolars are there and what are the main function(s) for them?
|
8 - crushing and grinding and chewing
|
|
|
how many molars are there and what are the main function(s) for them?
|
12 - crushing and grinding and chewing
|
|
|
where is the enamel located and what is special about it?
|
located on top of the tooth, the hardest substance in the body
|
|
|
where is the dentin located?
(in regard to the tooth) |
middle layer
|
|
|
where is the pulp located and what does it contain?
(pertaining to the tooth) |
inside layer, all nerves and vessels
|
|
|
what part of a tooth is the crown?
|
the part sticking up out of the gums
|
|
|
where on the tooth is the neck located?
|
along the gum line
|
|
|
where on the tooth is the root located?
|
below the gum line
|
|
|
what is "gum" pertaining to the teeth?
|
the part where the gums and tooth meet
|
|
|
what do the salivary glands do?
|
produce saliva which is largely water but contains amylase too
|
|
|
what does amylase do?
|
breaks down starch
|
|
|
name the salivary glands
|
parotid, sublingual, and submandibular
|
|
|
where are the parotid glands located?
|
around cheeks
|
|
|
where are the sublingual glands located?
|
under tongue
|
|
|
where are the submandibular glands located?
|
below mandible (lower jaw)
|
|
|
what is the pharynx?
|
common cavity of nose, mouth, and esophagus
|
|
|
what is the esophagus?
|
tube leading to the stomach
|
|
|
what is peristalsis?
|
involuntary contractions that carry food through the digestive system
|
|
|
what is the function of the stomach?
|
used for storage - very acidic - a lot of chemical digestion (HCL)(hydrochloric acid)
|
|
|
what are the sphincters at each opening of the stomach for?
|
circular ringed muscles at the entrance and exit of the stomach to control the movement of food
|
|
|
what is the small intestine - with villi?
|
the main area for food breakdown and absorption; fingerlike structurs called villi are located on inside wall of intestine to enlarge surface area;
is about 20 foot long |
|
|
what are the 3 parts of the small intestine?
|
duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
|
|
|
how long is the small intestine?
|
about 20 foot long
|
|
|
how long is the duodenum?
|
about 11 inches long
|
|
|
what is the duodenum?
|
the first part of the small intestine, main function is the addition of bile
|
|
|
what is the main function of the jejunum?
|
breakdown and absorption
|
|
|
what is the main function of the ileum?
|
breakdown and absorption
|
|
|
what is the cecum?
|
a blind sac that has no exit; pretty useless to humans
|
|
|
what is the appendix?
|
sticks off of cecum, no function in humans, can be deadly if ruptures
|
|
|
what are the 3 parts of the colon?
|
ascending, transverse, and descending
|
|
|
what is the main function of the colon? (includes all 3 parts)
|
water absorption
|
|
|
why is the ascending colon called ascending?
|
it goes up
|
|
|
why is the transverse colon called transverse?
|
it goes across from one side to another (it transverses)
|
|
|
why is the descending colon called descending?
|
it goes down
|
|
|
what is the rectum?
|
is at the end of the colon, storage for fecal material
|
|
|
what is the anus?
|
a sphincter muscle at the exit of rectum; controls fecal material exiting the body
|
|
|
what is an ulcer
|
lesions in the digestive membrane
|
|
|
what are 4 types of ulcers can occur?
|
oral, peptic, gastric, and duodenal
|
|
|
where would an oral ulcer be and what causes one?
|
in the mouth on the lips caused by a virus (herpes)
|
|
|
where would a peptic ulcer be and what causes one?
|
in the lower esophagus
caused by acid from stomach |
|
|
where would a gastric ulcer be and what causes one?
|
in the stomach
caused by a bacteria - easily treated with antibiotics |
|
|
where would a duodenal ulcer be and what causes one?
|
in the duodenum right below stomach
can be caused by virus, bacteria, and/or stomach acid - usually caused by stomach acid |
|
|
what are dental caries and what causes them?
|
cavities -
caused by breakdown of carbs which produces acid which eats through the enamel |
|
|
what is periodontal disease and what causes it?
|
disease of the gum - largely bacterial
|
|
|
what is appendicitis?
|
inflammation of appendix- if it ruptures, can be deadly
|
|
|
what is anorexia nervosa?
|
largely psychological, caused by malnourishment
|
|
|
what is bulimia?
|
largely psychologlical, overeating then purging by vomitting or using laxatives
|
|
|
what is food poisoning
|
some sort of toxin in food
(1) 'Salmonella enterilidis' (2) 'Clostridium botulinum' |
|
|
describe vitamin A deficiency
|
in child - bad bone growth and teeth development
in adult - dry skin, dry hair and decrease in night vision |
|
|
describe vitamin C deficiency
|
wounds won't heal rapidly, swollen gums, and teeth can start falling out (called scurvy)
|
|
|
describe vitamin B12 deficiency
|
pernicious anemia; nerve problems
|
|
|
describe vitamin D deficiency
|
loss of muscle tone and weak bones - ricketts
|
|
|
describe vitamin K deficiecy
|
lack of blood clotting
|

