![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
How is ADH released and what does it do? |
Too little water in the blood reaching the pituitary gland - Pituitary gland secretes ADH into the blood - ADH makes the kidneys reabsorb more water - A smaller volume of more concentrated urine is produced. |
Pituitary, Secrete, Absorb, Concentrated. |
|
|
The Double Circulatory System. |
Vena cava - Right atrium - Valve - Right ventricle - Valve - Pulmonary artery - Lungs. Pulmonary veins - Left atrium - Valve - Left ventricle - Valve - Aorta - Around the body. |
Pulmonary. |
|
|
Red Blood Cells. |
Have no nucleus and carry oxygen around the body. They are produced by bone marrow. |
Oxygen.
|
|
|
White Blood Cells. |
Their function is immunity. They fight off diseases by taking microorganisms into their cells and digesting them. We say they ingest them. |
Immunity, ingest. |
|
|
Plasma. |
This is straw coloured and carries glucose. Carbon dioxide is its waste product. It is made up of 45% water and 5% dissolved substances. |
Waste, dissolved substances. |
|
|
Arteries. |
Carries blood from the heart to the organs and muscles in the body. They have a thick layer of muscle and elastic fibres so that they recoil. |
Organs, muscle. |
|
|
Veins. |
Carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. They have a thin layer of muscle and elastic fibres. |
Deoxygenated. |
|
|
Capillaries. |
Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the capillary wall. They are very thin and fragile, so blood cells can only pass through single file. |
Exchange. |
|
|
ADH. |
Anti Diuretic Hormone. |
|
|
|
Phagocyte. |
Absorbs the pathogens and constantly moves. |
|
|
|
Lymphocyte. |
Produces antitoxins that neutralise toxins made by bacteria. |
Antitoxins. |
|
|
What does the MMR vaccine protect us against and how? |
Measles, mumps and rubella. The MMR vaccine contains weakened versions of live measles, mumps and rubella viruses. The vaccine works by triggering the immune system to produce antibodies against measles, mumps and rubella. |
|
|
|
How to measure microbes? |
The Aseptic Technique. Firstly you flame the loop over a Bunsen burner until it turns bright red so that it is sterilised. You then dip it into the UHT milk and spread it on the agar jelly in the petri dish then seal it. You then do the same with the pasteurised milk. Then you leave them both to incubate at room temperature and then saw which of them had grown the most bacteria. |
|
|

Label the parts of the kidney tubule. |
Filtration - small molecules such as water, glucose, salts and urea are squeezed out of the blood into Bowman's capsule.
Reabsorption - any useful substances such as water and glucose are taken back into the blood.
The remaining liquid, called urine, flows into the ureter. |
Bowman's, Absorb, Ureter. |
|

Label this kidney. |
Top left - Cortex.
Middle left - Medulla.
Bottom left - Pelvis.
Right - Ureter. |
|
|
|
Nephrons. |
Tiny tubes that make up the kidneys. |
|
|
|
What are the blood vessels that bring blood to the kidneys? |
Renal arteries. |
|
|
|
What is a glomerulus? |
A tangle of blood capillaries. |
|
|

Label the fermenter. |
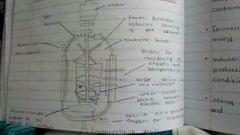
|
|

