![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Synthesis of Macromolecules |
Involves the formation of covalent bonds b/t subunits (monomers) through the removal of water aka dehydration/condensation synthesis |
|
|
Hydrolysis reactions |
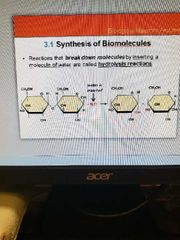
reaction that break down molecules by inserting a molecule of water |
|
|
What are carbohydrates used for? |
energy source (glucose and its polymers) in diverse organisms (prokaryotes and eukaryotes) |
|
|
How are Disaccharides formed? |
Through condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis |
|
|
What are starches? |
Polysaccharides that are formed by chains of glucose molecules |
|
|
What are the 4 major groups of lipids? |
Phospholipids steroids waxes fats and oils all lipids are hydrophobic and nonpolar |
|
|
What is the main function of lipids? |
Long term energy storage structural components of cell membranes Insulation; Cushioning organs cholesterol is a precursor to steroid hormones (sex hormones, estrogen) |
|
|
How can ATP generate in fatty acids? |
carbon hydrogen bonds broken can form ATP |
|
|
Amphipathic |
Both hydrophilic and hydrophobic ex. Phospholipids |
|
|
What are steroids known for? |
notable for having 4 fused carbon containing rings in their structure |
|
|
Functions of amino acids |
building tissue/muscles enzymes hormone production immune function (ex- antibodies) Transport (ex-hemoglobin) |
|
|
Dehydration/condensation synthesis b/t amino acids creates? |
primary level structure |
|
|
How many levels do functional proteins have? |
3 or 4 levels of structure but some are functional when they achieve quaternary structure |
|
|
What are Nucleic acids? |
serve as information storage and transfer molecules. Can also be built from 2 types of monomers, Ribose and deoxyribose |
|
|
Glyosidic Linkage
|
a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
|
|
|
Ester linkage/bond
|
Dehydration synthesis reactions in lipids form an ester linkage between the carboxyl group of a fatty acid and the hydroxyl group of an alcohol monomer such as glycerol.
|
|
|
Monomer
|
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
|
|
|
Hydroxly group
|
a functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an oxygen atom
|
|
|
Saturated fats
|
Single bonds Solid at room temp Have more Hydrogens EX. Coco oil, Butter |
|
|
Unsaturated fats |
Has double or triple bonds Liquid at room temp flexible ex. olive oil
|
|
|
Phospholipids |
Amphipatic Head is hydrophilic Fatty acid tail are hydrophobic |
|
|
Aquaporins
|
protien chanels that allow water to quicklypass thourgh, imbeded in cell memebrane
|
|
|
Protiens
|
Amino acids (monomers and peptide bonds)
|
|
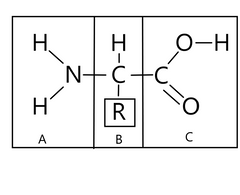
Name A, B, and C
|
A: Amino Group B: Alpha central carbon, R is side chain/R group C: Carboxly group |
|
|
Peptide bond
|
The chemical bond between carboxyl groups and amino groups of neighboring amino acids, forming an amide group and constituting the primary linkage of all protein structures.
|
|
|
Primary structure
|
Liner chain of amino acids
|
|
|
Secondary structure |
B pleated sheet (beta) a helix (alpha) hydrogen bonding |
|
|
Tertiary Structure |
3D folding pattern |
|
|
Quaternary Structure
|
2 or more protiens from the 3rd stage
|
|
|
The function of protein changes.. |
if its shape is changed. If no change then it will not function
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
network of protein fibers that collectively maintain the shape of the cell, secure some organelles in specific positions, allow cytoplasm and vesicles to move within the cell, and enable unicellular organisms to move independently |
|
|
What are the 3 types of fibers within the Cytoskeleton? |
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments and micotubules |
|
|
Covalent bond
|
Sharing an electron
|
|
|
What is an amino functional group?
|
Charged, basic, consists of a nitrogen atom attached by single bonds to hydrogen atoms
|
|
|
What is a Carboxyl functional group?
|
Charged, acidic, ionizes to relase H+
|
|
|
What is a chemical weak bond?
|
Hydrogen bonds
|
|
|
What is the most abundant molecule in the atmosphere?
|
Nitrogen
|
|
|
As water vaporizes, energy is ___________ from the environment. This process ____________ the surrounding environment.
|
absorbed; cools
|
|
|
Anions and cations can form what bond?
|
ionic
|
|
|
What describe sodium atoms? |
contains 1 valence electron can lose one electron easily forms cations closest to the left side of the periodic table has 2 electrons in the first energy level |
|
|
What describe chlorine atoms? |
contains 7 valence electron easily forms ionic bonds can gain one electron easily forms anions has 2 electrons in the first energy level |
|
|
Carbon represents less than 1% of the Earth’s crust, but is 18% of the composition of living things. Why? |
The unique bonding properties of carbon allow it to create a huge variety of biological molecules. |
|
|
When atoms share electrons and electrons spend more time with one atom, what bond is formed? |
polar covalent bond
|
|
|
A(n) ________ is a compound that yields hydroxide ions when dissolved in a solution.
|
base
|
|
|
Atoms are considered stable when the outermost shells have eight electrons. This is the ______ rule.
|
Octet
|
|
|
Hydrogen atoms attach to water through ______ bonds. Water molecules are cohesive because of _______ bonds.
|
Covalent Hydrogen |
|
|
What structures are found in all nucleotides?
|
nitrogenous base pentose sugar phosphate group |
|
|
What nitrogenous base is only found in RNA?
|
uracil
|
|
|
A DNA strand with a 5’ GCATTA 3’ will pair with
|
3’ CGTAAT 5’
|
|
|
______are the building blocks of RNA and DNA.
|
Nucleotides
|
|
|
A monomer with a central carbon, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a carbon containing group are _____ |
Amino acids
|
|
|
During hydrolysis of an amino acid chain, what bonds are broken?
|
peptide bonds
|
|
|
statements that support the relationship between protein and structure
|
A protein that unfolds or is incorrectly folded can use chaperones to correct the structure. when some proteins are denatured, with return of the normal environmental conditions they might refold. A disease may occur if proteins do not fold correctly. |
|
|
____are used for energy storage.
|
Triglycerides
|
|
|
RNA dictates the structure of a protein in a process known as:
|
translation
|
|
|
Fatty acids are attached to glycerol to form triglycerides through ____________ bonds. |
Ester |
|
|
Carbohydrates, proteins, and collagen collectively make up the |
extracellular matrix |
|
|
Cilia and flagella have what common feature? |
Microtubule filaments in a 9 + 2 array. |
|
|
The _____ is involved in the synthesis of proteins on the surface of the rough ER. |
ribosome |
|
|
____digest macromolecules and breakdown old nonfunctional organelles. |
Lysosomes
|
|
|
The process that created chloroplasts and mitochondria is ________
|
Endosymbiosis
|
|
|
Schleiden and Schwann are responsible for proposing the _______
|
Cell theory
|
|
|
The cell theory states
|
all organisms are composed of one or more cells, all cells are the smallest living things and all cells arise from other cells.
|
|
|
This cytoskeletal element has the smallest diameter at 7 nm
|
microfilaments
|
|
|
The smooth ER is involved in the production of:
|
lipids. |
|
|
The central vacuole is important in regulating the amount of _____________ in the cell.
|
Water
|
|
|
Plant cells do not have _______
|
centrosomes.
|
|
|
Ribosomes are involved in the formation of:
|
proteins
|
|
|
Plants become turgid in |
hypotonic solutions
|
|
|
A solution with a low amount of solutes is |
h |
|
|
Cell drinking is accomplished by
|
Pinocytosis
|
|
|
Sugars moving into the cell can occur through
|
co-transport facilitated transport |
|
|
Large quantities of macromolecules enter the cell through: |
receptor-mediated endocytosis. |
|
|
Which type of cellular transport requires ATP?
|
Active transport
|
|
|
When red blood cells are placed in a hypotonic solution, the cells will:
|
swell
|
|
|
Which substance does NOT pass easily through the membrane
|
lons
|
|
|
What does the fluid mosaic model describe
|
The ability of components of the plasma membrane to change position in relation to one another
|
|
|
Integral proteins contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. The hydrophobic region is located:
|
within the membrane
|
|
|
The hydrophobic portion of a phospholipid is made up of __________ and is found on the ___________ of the lipid bilayer
|
fatty acids; inside
|
|
|
The plasma membrane contains all of the following EXCEPT: carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic acids. |
nucleic acids
|
|
|
Substrates
|
bind to the active site of enzymes
|
|
|
The inorganic non-protein substances that aid in enzyme function are
|
Cofactors
|
|
|
Noncompetitive inhibition occurs when
|
a substance binds on a site away from the active site
|
|
|
According to the 2nd law of thermodynamics
|
energy transfer increases the disorder of a system
|
|
|
Archaea that make energy without O2 perform
|
anaerobic respiration
|
|
|
Enzymes act as catalysts for chemical reactions by decreasing the ______________ energy.
|
activation
|
|
|
Low entropy means ________ disorder and ___________ energy
|
low; high
|
|
|
The small amount of energy input necessary for all chemical reactions to occur is called the:
|
activation energy.
|
|
|
The type of energy held within the bonds of gasoline prior to burning it as fuel is;
|
Chemical
|
|
|
______________________ is the type of energy associated with objects in motion.
|
Kinetic energy
|
|
|
Anabolic pathways
|
use more energy than they release.
|
|
|
The breakdown of glucose is an example of
|
a catabolic pathway
|
|
|
The sum of all chemical reactions in the body is its
|
Metabolism
|
|
|
What does the smooth ER do? |
store calcium production of lipids detoxification |
|
|
What is a gap junction and what is it called in plants? |
Allow water and small molecules to pass between cells (ions, small sugars, and amino acids), called plasmadesmate in plants |
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Semi permeable or selectively permeable, anything large and polar will not diffuse in |
|
|
Where does cellular respiration take place |
mitochondria |
|
|
Where does cellular respiration take place |
mitochondria |
|
|
Centrosome |
Consist of a pair of centrioles-play a role in cell reproduction in animals also known as microtubule organization sensor (MTOC) |
|
|
Transcription |
the first step in gene expression. It involves copying a gene's DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule. |
|
|
Translation |
the process where the information carried in mRNA molecules is used to create proteins. |
|
|
What is cisface and transface |
Cisface is receiving side of the Golgi apparatus Transface is the side of the Golgi apparatus that sends vesicles off to other locations within the cell. |
|
|
What is active transport |
Uses energy to push material against its concentration gradient maintaining the concentration difference across membranes, requires energy or ATP |
|
|
Which characteristic of a phospholipid contributions to the fluidity of the membrane |
Double bonds in the fatty acid tail, more flexible |
|
|
Anabolic |
Small molecules are assembled into large ones, energy is required, can also be known as dehydration synthesis |
|
|
Catabolic |
Large molecules are broken down into smaller ones, energy is released, can also be known as hydrolysis |
|
|
How do enzymes help lower activation energy |
Proper ph for substrate and active site Help orient substrate for proper binding Brief covalent ionic bonding plus hydrogen bonding |
|
|
1st law of thermodynamics |
The amount of energy in the universe cannot change therefore energy can neither be created nor destroyed |
|
|
2nd law of thermodynamics |
Energy transfers inefficient therefore in every energy transfer some energy is lost (release in an unusable form) this increases Entropy-measure of this order or randomness in a system |
|
|
Allosteric agent |
Manipulate and I'm function by binding to another part of the enzyme, other than the out active site, and changing the active site remotely, Non-competitive inhibitor |
|
|
Competitive inhibitor |
A molecule mimics the normal substrate and tricks the enzyme - mimic binds to active site and blocks normal substrate |
|
|
The active site of an enzyme is the region that |
Is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme |

