![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What Is a cell |
It is a unit of life |
|
|
What is a cell made up of |
It is made up of protoplasm |
|
|
What is protoplasm |
Jelly like substance in which chemical activities of cell are carried out |
|
|
Name the parts of a cell |
Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell surface membrane |
|
|
What is a nucleus |
Organelle containing chromatin, nucleoli, and nuclear envelope |
|
|
What is the chromatin |
Network of large thread like structures, contain hereditary material, and controls activities of cell. Become chromosomes |
|
|
What is the function of nucleoli |
They build up proteins |
|
|
What does the nucleus do |
It is responsible for cell division, continuing the life of cell and repair |
|
|
What is a cytoplasm |
It surrounds the nucleus, and is where most life processes occur |
|
|
What does the cytoplasm consist of |
Vacoule, chloroplasts, centrioles |
|
|
What does the mitochondria do |
Power house of cell, releases energy stored in ATP |
|
|
What is ATP |
Adenosine triphosphate, gives energy to perform activities |
|
|
What are chloroplasts |
The site where plants make foods, contain chlorophyll |
|
|
What is a vacuole |
A fluid filled space enclosed by the membrane |
|
|
Describe Vacuole in animals and plants |
Animals: Temporary, small, contain food and water Plants: large, in the center, contain cellsap, surrounded by tonoplast |
|
|
What are centrioles |
Organelle, They play a part in cell division |
|
|
Describe the cell surface membrane |
Surrounds the cytoplasm, partially permeable |
|
|
What is a cell wall |
An organelle which encloses the cell, made of cellulose |
|
|
Show a drawing of a cell |
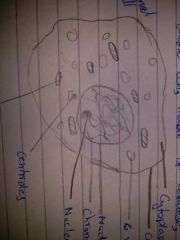
|
|
|
Draw a plant cell |
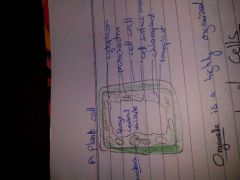
|
|
|
What is an organelle |
A highly organized structure in a cell |
|
|
What is differentiation |
The process in which after cell divisions, some cells form tissues, which get specialized for specific actions |
|
|
What are specialized cells |
Cells specialized for specific function |
|
|
Name 3 specialized cells |
Root hair cell Xylem vessel Red Blood Cell |
|
|
Describe adaptation of root hair cell |
- Long and narrow, more surface area to volume ration, efficient absorption |
|
|
Describe red blood cells adaptation |
Contain hemoglobin THEY'RE bioconcave, higher S. A, no nucleus, higher diffusion rate |
|
|
Describe adaptation of Xylem vessels |
No cross walls, no protoplasm, allow transfer of water. Lignin which strengthen wall |
|
|
Why is a Xylem dead |
No protoplasm |
|
|
What are tissues |
They're found in multicellular organisms, they're group of specialized cells |
|
|
Name an example of tissues |
Epithelial, |
|
|
Organ |
Group of tissues |
|
|
Organ systems |
Several organs working together eg digestive system |

