![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Neurophysiology |
The study of life processes within neurons |
|
|
Action potential |
The rapid electrical signal along its axonal pathway from knee yo spinal cord |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
The chemical released when the action potential reaches the axon terminal |
|
|
Ions |
Electrically charged molecules that a neuron contains |
|
|
Anions |
Negatively charged ions |
|
|
Cations |
Positively charged ions |
|
|
Intracellular fluid |
AKA cytoplasm The watery solution found within cells |
|
|
Extracellular fluid |
The fluid in the spaces between cells (interstitial fluid) and in the vascular system |
|
|
Cell membrane |
The lipid bilayer that ensheathes a cell |
|
|
Microelectrode |
An especially small electrode used to record electrical potential from living cells |
|
|
Resting membrane potential |
An electrical potential difference across the membrane during and inactive period |
|
|
Millivolt (mV) |
A thousandth of a volt |
|
|
Negative polarity |
A negative electrical potential difference relative to a reference electrode |
|
|
Lipid bilayer |
To layers of linked fatty molecules; within which many sorts of specialized proteins float |
|
|
Ion channel |
A tubelike pore that allows ions of specific type to pass through the membrane |
|
|
Gated |
Certain ion channels that open and close rapidly in response to various influences. |
|
|
Potassium ion (K+) |
A potassium atom that carries a positive charge because it has lost one electron |
|
|
Selective permeability |
The property of a membrane that allow some substances to pass through, but not others |
|
|
Diffusion |
The forces that causes molecules of a substance to diffuse from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentrations |
|
|
Concentration gradient |
Variation of concentration of a substance within a region |
|
|
Electrostatic pressure |
The propensity of charged molecules or ions to move, via diffusion, toward areas with the opposite charge |
|
|
Sodium-potassium pump |
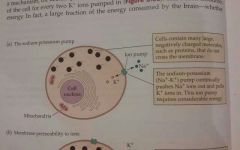
The energetically expensive mechanism that pushes sodium ions out of a cell, and potassium ions in |
|
|
Sodium ion (Na+) |
A sodium atom that carried a positive charge because it has lost one electron |
|
|
Equalibrium |
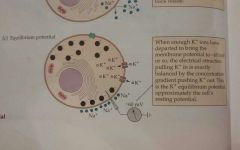
When movement of ions across the cell membrane is balanced, as the electrostatic pressure pulling ions in one direction is offset by the diffusion force pushing them in the opposite direction |
|
|
Nerst equation |
Mathematical function predicting the voltage needed to counterbalance the diffusion force pushing an ion across a semipermiable membrane |
|
|
Axon hillock |
The specialized membrane located where the axon emerges from the cell body |
|
|
Hyperpolarization |
An increase in membrane potential |
|
|
Depolarization |
A decrease in membrane potential |
|
|
Local potential |
An electrical potential that is initiated by stimulation at a specific site, which is a graded response that spreads passively across the cell membrane, decreasing in strength with time and distance |
|
|
Threshold |
The stimulus intensity that is just adequate to trigger an action potential at the axon hillock |
|
|
All-or-none property |
The size (or amplitude) of the action potential is independent of the stimulus magnitude Either it fires at full amplitude or it doesn't fire at all |
|
|
Afterpotential |
The positive or negative change in membrane potential that may follow an action potential |
|
|
Voltage-gated Na+ channel |
A Na+- selective channel that opens or closes in response to changes in the voltage of the local membrane potential |
|
|
Refactory |
Unresponsive |
|
|
Absolute refractory phase |
A brief period immediately following the production of an action potential |
|
|
Relative refractory phase |
Period following the absolute refractory phase that is less sensitive during which only strong stimulation produces action potential |
|
|
Conduction velocity |
The speed at which an action potential is propagated along the length of an axon |
|
|
Node of Ranvier |
Small gaps spaced about every millimeter along the axon |
|
|
Saltatory conduction |
When the action potential jumps from one node of Rangier to the next |
|
|
Postsynaptic potential |
Brief changes when neurotransmitters alter the resting potential of the postsynaptic cell |
|
|
Excitatory Postsynaptic potential (EPSP) |
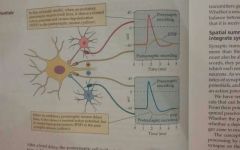
A depolarizing potential in the postsynaptic neuron that is caused by Excitatory presynaptic potentials. EPSP increases the probability that the postsynaptic neuron will fire an action potential |
|
|
Synaptic delay |
The brief delay (half a millisecond) between the arrival of an action potential at the axon terminal and the creation of a postsynaptic potential |
|
|
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) |
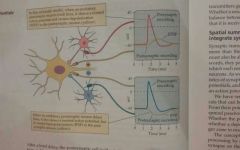
A hyperpolarizing potential in the postsynaptic neuron that is caused by inhibitory connections. IPSP decrease the probability that the postsynaptic neuron will fire and action potential. |
|
|
Chloride ion (CI-) |
A chlorine atom that carries a negative charge because it has gained one electron |
|
|
Spatial summation |
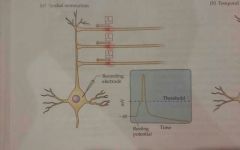
The summation of potentials originating from different physical locations across the cell body |
|
|
Temporal summation |
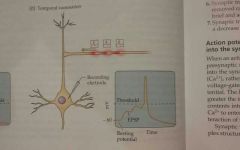
The summation of postsynaptic potentials that reach the axon hillock at different times. The closer in time that the potentials occur, the more complete the summation |
|
|
Calcium ion (Ca2+) |
A calcium atom that carries a double positive charge because it has lost 2 electrons |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
The process by which synaptic neurotransmitter is repackaged into synaptic vesicles |
|
|
Ligand |
A substance of a correct shape that binds to receptor molecules, such as those at the surface of the cell |
|
|
Endogenous ligand |
Neurotransmitters and substances made inside the the body |
|
|
Exogenous ligand |
Drugs and toxins that originate from outside the body |
|
|
Acetylcholine (ACh) |
A neurotransmitter produced and released by parasympathetic post ganglionic neurons, by motoneurons, and by neurons throughout the brain |
|
|
Receptor molecule |
AKA receptor A protein that captures and reacts to molecules of a neurotransmitter or hormone |
|
|
Curare |
An arrowhead poison used by South Americans that causes paralysis by blocking acetylcholine receptors in the muscle |
|
|
Bungarotoxin |
A neurotoxin found in the venom of the banded kraut (snake native to Taiwan) that blocks acetylcholine receptors |
|
|
Agonist |
A molecule, usually a drug, that binds a receptor molecule and initiates a response like that of another molecule, usually a neurotransmitter |
|
|
Antagonist |
A molecule, usually a drug, that interferes with or prevents the action of a transmitter |
|
|
Cholinergic |
Cells that use acetylcholine as their synaptic transmitter |
|
|
Up-regulation |
Increase in receptor numbers |
|
|
Down-regulation |
Decrease in receptor density |
|
|
Ionotropic receptor |
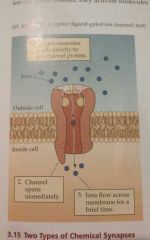
Directly control an ion channel |
|
|
Ligands-gated ion channel |
Ion channel that opens or closes in response to the presence of a particular chemical. |
|
|
Metabotropic receptor |
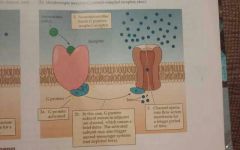
A receptor that recognizes the synaptic transmitter, but doesn't directly control ion channels |
|
|
G protiens |
A class of proteins that reside next to the intracellular portion of a receptor and that are activated when the receptor binds an appropriate ligand on the extracellur surface |
|
|
Second messenger |
The second chemical signal activated inside the cell |
|
|
Degradation |
The chemical breakdown of a neurotransmitter into inactive metabolities |
|
|
Reuptake |
When transmitter molecules may be rapidly cleared from the synaptic cleft by being take up into the presynaptic terminal |
|
|
Tramsporters |
Specialized receptors for the transmitter |
|
|
Axo-dendritic |
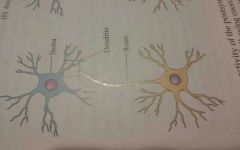
A synapse where the presynaptic axon terminal attaches onto the dendrite of the postsynaptic neuron, either via a dendritic spine or directly onto the dendrite itself
|
|
|
Axo-somatic |
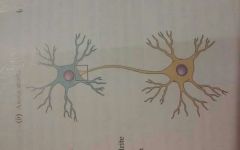
A synapse in which a presynaptic axon terminal attaches onto the cell body (soma) of the postsynaptic neuron |
|
|
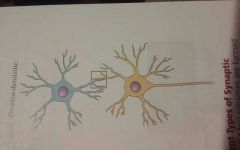
Axo-axonic |
A synapse in which a presynaptic axon terminal attaches onto another axons terminal |
|
|
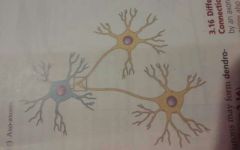
Dendo-dendritic |
A synapse in which a synaptic connection forms between two dendrites of two neurons |
|
|
Retrograde synapse |
A synapse where a signal (usually a gas neurotransmitter) flows from the postsynaptic neuron to the presynaptic neuron, thus counter to the usual direction of synaptic connection. This signals the presynaptic cell to release more transmitter |
|
|
Ectopic transmission |
The location of the transmitter release and the sites at which the transmitter acts are both well outside the normal boundaries of nearby synapses |
|
|
Varicosity |
Axons with regular swellings |
|
|
Nondirected synapses |
A type of synapse in which the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells are not in close apposition |
|
|
Neural chain |
The simplest neural circuit that is regularly encountered in the nervous chain |
|
|
Knee jerk reflex |
A variant stretch reflex in which stretching of the tendon beneath the knee leads to an upward kick of the leg |
|
|
Convergence |
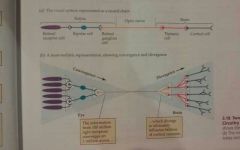
The phenomenon of neural connections in which many cells send signals to a single cell |
|
|
Divergence |
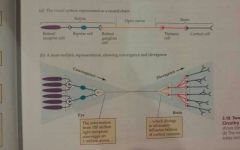
The phenomenon of neural connections in which one cell sends signals to many other cells |
|
|
Electroencephalogram (EEG) |

A recording of gross electrical activity of the brain recorded from large electrodes placed on the scalp |
|
|
Event-related potential (ERP) |

AKA evoked potential Averaged EEG recordings measuring brain responses to repeated presentations of a stimulus |

