![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
central nervous system
|
the brain and spinal cord.
brain-voluntary and involuntary behaviors spinal cord-involved in reflexes |
|
|
sensory (afferent) neurons
|
carry info towards the CNS from the periphery.
|
|
|
motor (efferent) neurons
|
carry info to periphery from CNS
|
|
|
interneurons
|
connect the sensory and motor neurons
|
|
|
peripheral nervous system
|
all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
somatic Nervous system
|
part of PNS. controls voluntary muscle movement
|
|
|
autonomic nervous system
|
part of PNS. regulates the automatic bodily functions and homeostasis, controls fight or flight
|
|
|
sympathetic nervous system
|
dominates when the body in under physically or mental stress
|
|
|
parasympathetic nervous system
|
dominates when in a relaxed state after SYNS
|
|
|
nervous system branches
|
nervous system
central nervous sys peripheral nervous sys brain&spinal cord. somatic ns autonomic ns pans & Syns |
|
|
structure of a nueron
|
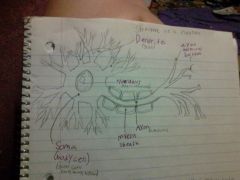
dendrite, axon terminal button, nucleus , axon , myelin sheath, soma(body cell)
|
|
|
neuron
|
-thin cells of nerve tissue which communicate through an electronic chemical process to, from and in the brain.
group of neurons make a nerve |
|
|
dendrites
|
gather\receives neurotransmitters from the sending neurons
|
|
|
axon
|
carries an electrical charge (action potential) from the cell body to the ATB
|
|
|
myelin sheath
|
fatty substance that protects the axon
|
|
|
axon terminal buttons
|
hold neurotransmitters until released
|
|
|
soma(body cell)
|
contains nucleus and provides cell structure
|
|
|
epinephrine
|
adrenaline
|
|
|
dopaminine
|
pleasure, emotion, attention,arousal
to much - schizophrenia to little- Parkinson's drugs-cocaine, amphetamines |
|
|
seritonin
|
affects mood, sleep, appetite
lack of- depression to much-ocd drugs- antidepressants ,prozack |
|
|
acetylcholine
|
muscle action, attention, memory
receptor sites may be stimulated by nicotine botox black widow venom to much-muscle contractions, suffocating |
|
|
endorphines
|
brains attempt to block/handle pain and pleasurable emotions
exercise may stimulate the body to produce it |
|
|
GABA
|
natural inhibator on all receptor sites
drugs-valium and other anti anxiety drugs |
|
|
norepindphrine
|
helps regulate mood and emotion
effected by cocaine and amphetamines |
|
|
glutimate
|
excitatory
helps with memory and learning to much- migraine seizures or anxiety |
|
|
what is biological phycology?
|
the scientific study of the influence of the nervous system, hormones and chemicals on behavior thinking and emotions
|
|
|
antagonist
|
block receptor sites inhibitor
|
|
|
agonist
|
mimic neurotransmitters excitatory
|

