![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Aldehyde |

Functional group |
|
|
Glycogen |
A Polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy |
|
|
Polymer |
Starch, Glycogen and Celluose (carbohydrate); triglycerides and phospolipids |
|
|
Amino |
Subunits of amino acids |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
Breaks biological macro-molecules apart and consumes a molecule of H2O in the process |
|
|
Polypeptide |
Long chain of amino acids; A protein |
|
|
Amino Acid |
Organic compounds composed or amine and carboxylic acid functional groups that are the foundation for protein synthesis |
|
|
Hydroxyl |
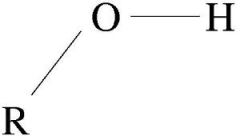
Functional group |
|
|
Polysaccharide |
Polymeric carbohydrate molecules composed of long chains of mono-saccharides bound by glycosidic links |
|
|
Carbohydrate |
Energy source, energy storage, and structure |
|
|
Ketone |
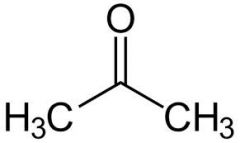
Functional group |
|
|
Protein |
Macromolecules consisting of one or more chains of amino acid residues |
|
|
Carbonyl |

Functional group |
|
|
Lipid |
Naturally occurring molecules such as fats, waxes, sterols and gycerol |
|
|
Purine |
A double ring nitrogenous base (Adenine, Guanine) |
|
|
Carboxyl |
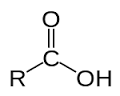
Functional group |
|
|
Methyl |

Functional group |
|
|
Pyrimidine |
A single ring nitrogenous base (Cytosine, Thymine, & Uracil) |
|
|
Cellulose |
A carbohydrate found in plant cell walls |
|
|
Monomer |
One molecule that can bind to another and form a polymer |
|
|
RNA |
A single strand of ribose that holds the code for making proteins |
|
|
Conformation |
Any of the spatial arrangements that the atoms in a molecule may adopt and freely convert between |
|
|
Monosaccharide |
Simple sugar |
|
|
Saturated |
Containing the greatest number of hydrogen atoms and having no C-C double or triple bonds |
|
|
Condensation |
The change of water from its gaseous form into liquid water |
|
|
Nucleic Acid |
Roles: Cellular energy currency (ATP), info storage, info transfer, electron carriers |
|
|
Starch |
A Polysaccharide Carbohydrate consisting of a lot of glucose units; produced by most green plants as energy store |
|
|
Denaturation |
A process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose their structure due to a strong acid or base |
|
|
Nucleotide |
Building blocks of nucleic acids: Composed of a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and at least one phosphate group |
|
|
Steroids |
A carbon structure |
|
|
Disaccharide |
A sugar composed of two monosaccharides (lactose, sucrose) |
|
|
Peptide bond |
Joins two adjacent amino acids in a protein (covalent bond) |
|
|
Sulfhydryl |
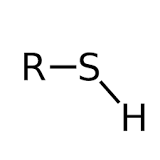
Functional group |
|
|
DNA |
A double stranded of Deoxyribose that is the code for everything |
|
|
Phosphate |
An inorganic salt of phosphoric acid |
|
|
Triglyceride |
A blood lipid derived from fatty acids that helps enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver |
|
|
Fatty acid |
Building blocks of fat; are absorbed into the blood; form a triglyceride |
|
|
Phospholipid |
The fundamental building blocks of cellular membranes; consist of a polar or charged head group and a pair of non-polar fatty acid tails |
|
|
Unsaturated |
Having a double or triple bond capable of taking on elements by direct chemical combination w |

