![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Evolutionary |
Adapted to the demands of our individual environment. Genetically determined behaviour that enhances chance of survival and reproduction. Environment of evolutionary adaptiveness- adapted and selective pressures. |
Natural Selection |
|
|
Localisation of Function |
Certain areas of the brain are responsible for different functions. Frontal- thinking & creativity Parietal- sensory info Temporal- memory & auditory info Occipital- visual info |
|
|
|
Neurotransmission |
1) Release of neurotransmitters. 2) Neuron is stimulated and releases action potential. 3) Action potential travels down the axon. 4) Causes release of neurotransmitters from presynaptic vesicles. 5) Post-synaptic neurons detect this and get stimulated. 6) Overstimulation (too much) e.g. dopamine-shizophrenia Understimulation (too little) e.g. serotonin-depression. |
Chemicals in our brain have an effect on our emotions. |
|
|
Formation of Relationships |
Evolutionary: Traits that enhance successful reproduce. Different selective pressures: Men look for women younger and healthy Women look for resources Kin selection- genes to pass on Neurotransmission: Influence perception Dopamine- pleasure seeking & rewaes driven behaviour Oxytocin- human bonding i.e. trust |
Chemical drive to bond with others. Mother & infant- genes/oxytocin Pet & owner- survival & protection/enhanced levels of dopamine |
|
|
Drug Therapy |
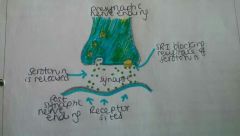
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. 1) Reabsorbs serotonin into presynaptic cell. 2) More serotonin is left in synapse 3) Makes transmission easier for next impulse. |
Manipulate physiology in order to treat disorders. Conventional antipsychotics- CAs (Chloropomazine-blocking agent) Atypical antipsychotics- AAs (Clozapine- bind more loosely) |
|
|
Drug Therapy- Effectiveness |

|
|
|
|
Drug Therapy- Ethics |

Tardive dyskenisia- involuntary muscle movements. Angranulocytosis- drop in white blood cells. |
|
|
|
PET Scans |
1) Administer slightly radioactive glucose. 2) Most active areas of the brain use the glucose. 3) Radiation detector builds up picture of activity. A- Reveals chemical info otherwise unavailable. Can distinguish between benign or malignant tumours. D- Costly technique. Can only be used a few times. Less precise than MRI scans. |
|
|
|
Raine et al- Characteristics |
41 murderers (39 men & 2 women) Mean age of 34.3 years Charged with murder or manslaughter. All pleaded not guilty by reason of insanity or incompetence to stand trial. Control group- matched pairs (same age and sex) None were taking medicaion. |
Quasi-experiment Matched pairs Opportunity sample |
|
|
Raine et al- Procedures |
Ps were referred to the University of California (selected by opportunity sample). Allowed to practice a CPT. 30 seconds before receiving tracer injection, Ps started CPT. Injected with flueodeoxyglucose. 32 minutes after, Ps were scanned. 10 horizontal scans (peel and box technique) 14 different brain regions and structures compared. |
|
|
|
Raine et al- Findings & Conclusions |
Findings: Reduced activity in... Lateral prefrontal cortex Left angular amygdala Hippocampus in left hemisphere Thalamus Increased activity in... Cerebellum Right hemisphere
Conclusions: Murderers had reduced activity in some areas (notably ones previously linked to violence). Abnormal asymmetries. No differences in many brain structures. Preformed similarly in CPT. |
Overall, only some differences between murdere's and 'normal' brain. |
|
|
Evaluating Findings & Conclusions |

|
|
|
|
Evaluating Ethical & Social Implications |

|
|

