![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
general signaling |
1. release of signal 2. binding signal to receptor 3. activation of receptor and signal transduction cascade 4. effector mechanism |
|
|
schemes of intracellular signaling |
1. endocrine 2. paracrine 3. autocrine 4. juxtacrine - plasma membrane attached proteins |
|
|
protein kinase |
1. add phosphate moiety from ATP to specific amino acids within proteins 2. either target serine/threonine residues or tyrosine residues |
|
|
protein phosphatase enzymes |
remove phosphates from substrate proteins |
|
|
protein kinase/phosphatase switch |
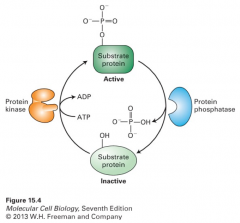
|
|
|
GTPase switch proteins |
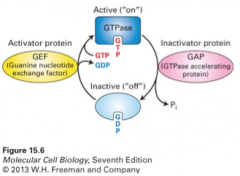
1. GTP-bound active binds effectors that transduce the signal 2. cycling between on and off states is controlled by GEF and GAP activities |
|
|
Switch I and II |
1. binding the gamma phosphate of GTP alters the conformation of the GTP switch molecules 2. when GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP, then the switch I and II domains fall back 3. conformation changes are recognized by downstream effector molecules |
|
|
secondary messengers |
1. low molecular weight 2. high diffusion molecules that change concentration in response to ligand-receptor (first messenger) activation |
|
|
signal amplification |
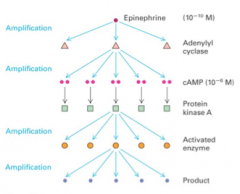
1. receptor activation produces a series of events that often amplify the signal 2. small amounts of ligand produce profound responses in cell |
|
|
receptor binding |
can determine affinity of ligands and numbers of receptors on cell surface
|
|
|
physiological response |
1. can be amplified by signal transduction pathways 2. levels change within a narrow range of concentrations |
|
|
general G-protein coupled receptor systems |
1. receptor, seven membrane spanning domains 2. receptor coupled to trimeric G-protein 3. membrane bound effector protein 4. feedback regulation and desensitization |
|
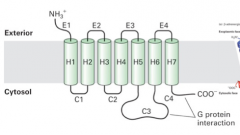
|
G protein-coupled receptor |
|
|
G-protein signaling |
1. regulates ion channels 2. regulates adenylyl cyclase 3. regulate cytosolic calcium |
|
|
muscarinic acetylcholine receptor |
1. acetylcholine receptor slows rate of heart contraction 2. G-protein coupled receptor dissociates trimeric G-protein 3. beta-gamma subunit binds and opens a potassium channel, hyperpolarizing the heart muscle cell 4. GPCR 5. effector protein is a K+ channel |
|
|
light activated rhodopsin pathway |
1. light indirectly inhibits cGMP gated channel 2. hyperpolarizing the photoreceptor membrane |
|
|
GPCR activation |
activation of transcription
|
|
|
G-protein coupling with adenylate cyclase |
1. precise control of cAMP levels is produced by balance of different signals 2. in adipose cells, there are competing responses that stimulate or inhibit fatty acid catabolism |
|
|
PKA activation |
1. affects cytoplasmic mechanisms like glycogen metabolism 2. also activates transcription by phosphorylating CREB factor 3. with CBP/300, stimulates transcription |
|
|
phosphatidylinositol signaling |
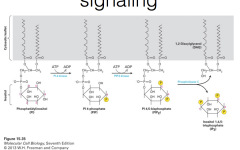
|
|
|
IP3/DAG pathway |
divergent signal transduction pathway producing calcium and protein kinase C signaling |
|
|
smooth muscle relaxation of arteries |
1. endothelial ACh signal activates Ca/CaM 2. Ca/CaM activates NO syntase 3. NO gas diffuses to nearby smooth muscle cell 4. relaxes in response to NO |
|
|
ACh signal activation |
Ach --> ACh GPCR --> Phospholipase C --> IP3 --> Ca2+ calmodulin --> NO synthase --> NO --> NO receptor --> GTP hydrolysis (cGMP and PPi) --> protein kinase G --> muscle cell relaxation |
|
|
external signals |
1. membrane anchored and secreted proteins or peptides 2. small hydrophobic molecules 3. small hydrophilic molecules 4. gases 5. physical stimuli |
|
|
endocrine signaling |
signals from one cell act on distant cells |
|
|
paracrine signaling |
signals from one cell on nearby cells |
|
|
autocrine signaling |
signals from one cell to itself |
|
|
Kd |
1. concentration of ligand at which half the ligand's receptors are occupied 2. determined experimentally and is a measure of the affinity of the receptor for the ligand |
|
|
affinity chromatography |
use to purify receptors even when they are present in low abundance |
|
|
immunoprecipitation assasy |
use antibodies specific for protein kinases to measure kinase activity |
|
|
pull down assays |
1. use protein-binding domain of a target protein 2. used to quantify activation of GTP-binding protein within a wall |
|
|
GPCRs |
1. large and diverse family 2. seven membrane spanning alpha helices 3. internal ligand-binding pocket that is specific for ligands 4. range of cellular effects 5. coupled to trimeric G proteins (contain alpha, beta and gamma subunits) 6. can function as GEF from conformational change |
|
|
fluorescence energy transfer |
demonstrate receptor-mediated dissociation of coupled Galpha and Gbeta-gamma subunits in living cells |
|
|
Galpha subunit |
determines the function of the G protein and affords it specificity |
|
|
effector proteins |
1. activated or inactivated by trimeric G proteins 2. form second messengers or ion channels |
|
|
rhodopsin pathway |
1. effector protein: cGMP phosphodiesterase 2. activated by Galpha-GTP mediated release of inhibitory subunits 3. reduction of cGMP leads to closign of cGMP-gated Na/Ca channels --> hyperpolarization --> decreased NT release |
|
|
terminate visual signaling |
1. GAP proteins inactivate G.GTP 2. Ca sensing proteins activate guanylate cylcase 3. rhodopsin phosphorylation 4. binding of arrestin |
|
|
cAMP |
1. ligand binding of GPCR --> adenlyl cyclase --> ATP to cAMP 2. binds cooperatively to a regulatory subunit of protein kinase A --> releases the active kinase catalytic subunit 3. levels measured by hormonal stimulation |
|
|
PKA |
1. mediates the diverse effects of cAMP 2. localization restricts cAMP to particular subcellular locations |
|
|
GPCR/adenylyl cyclase/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway |
amplified tremendously by second messengers and kinase cascades |
|
|
feedback repression |
1. downregulated by GPCRs 2. end product of a pathway blocks an early step in the pathway 3. activation of coupled G proteins is inactiviated |
|
|
BARK |
1. phosphorylates cytosolic residues of receptor in its active conformation 2. leads to binding of b-arrestin and endocytosis of receptors 3. deactivate b-adrenergic receptors |
|
|
GPCR-arrestin complex |
1. functions as a scaffold that activates several cytosolic kinases 2. initiates cascades that lead to transcriptional activation of genes controlling cell growth |
|
|
down-regulation of Gs-coupled receptors |
1. affinity of the receptor for its ligand decreases when GDP bound to Galpha is replaced with GTP 2. intrinsic GTPase activity fo G that converts the bound GTP to GDP is enhanced when G binds to adenylyl cyclase 3. cAMP acts to hydrolyze cAMP to 5'-AMP, terminating the cellular response |
|
|
small rise in Ca |
1. induces a variety of responses in different cells 2. hormone secretion, contraction of muscle, platelet aggregation |
|
|
phospholipase C enzyme |
1. effector protein activate by GTP bound G 2. cleaves a phospholilpid known as PIP2 3. makes two secondary messangers |
|
|
secondary messengers made by PIP2 cleavage |
1. diffusable IP3 2. membrane bound DAG |
|
|
IP3 |
1. triggers opening of IP3-gated Ca channels in ER 2. elevation of cytosolic free Ca 3. protein kinase C recruited into plasma membrane 4. activated by DAG |
|
|
depletion of ER Ca |
1. leads to opening of plasma membrane store-operated Ca channels 2. influx of Ca from extracellular medium |
|
|
Ca-calmodulin complex |
regulates activity of cAMP phosphodiesterase and protein kinases
|
|
|
ACh GCPR stimulation |
1. induces increase in cytosolic Ca 2. synthesis of NO |
|
|
NO |
activates intracellular guanylate cyclase to synthesize cGMP |
|
|
increase in cGMP |
1. activation of protein kinase G 2. triggers a pathway resulting in muscle relaxation and vasodilation |
|
|
glycogen breakdown and synthesis |
1. coordinately regulated by secondary messengers Ca and cAMP
|

