![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Derived Trait |
a novel and more recent trait different from that of the anscestral trait.Evolves once and is shared only among descendants of the ancestral species in which itevolved. |
|
|
Homologous Trait |
traits with similar structure and function inherited from a commonancestor. May be masked by divergent evolution which leads to changes inhomologous traits. (eg., wing bones in birds and bats) Divergence makes homologoustraits look different! |
|
|
Analogous Trait |
similar traits not due to common ancestry, but aproduct of convergent evolution. |
|
|
Convergent Evolution. |
Convergent evolution leads to resemblance between unrelated structures via natural selection to perform a similar function (eg., wing structures in insects are analogous to those in birds/bats) Convergence makes analogous traits look similar! |
|
|
Taxa |
Any or all of the organisms in your tree (singular: taxon) |
|
|
Clade |
Any portion of a phylogenetic tree that is descended from a common ancestor. |
|
|
Outgroup (control) |
most closely related ancestor outside the group that is underphylogenetic analysis, closest to the root of the tree. Determine ancestral andderived traits based on the outgroup. |
|
|
In what way is all life interconnected? |
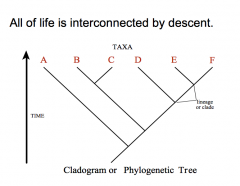
|
|
|
Monophyletic Clade |
clade contains all descendantsof a particular ancestor. |
|
|
Paraphyletic Clade |
clade with only some, not alldescendants of a particular ancestor |
|
|
what is the most commonly used method for constructing cladograms? |
Method Of Parsimony |
|
|
synapomorphies |
shared and uniquely-derived characters |

