![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three hypotheses on the origin of viruses? |
1. Progressive (Escape): Viruses originally were in host cells but gained the ability to move between cells 2. Regressive (Reduction): Viruses are actually remnants of other cellular organisms and rely on host cells to reproduce 3. Virus First: Viruses predate or coevolved with current cellular hosts. |
|
|
Provide an example that supports the Progressive hypothesis of the origin of virus |
Viral-like transposons |
|
|
Provide an example that supports the Regressive hypothesis of the origin of viruses |
Mimivirus: putative genes associated with translation |
|
|
Provide an example that supoprts the Virus First hypothesis of the origin of viruses |
Complexity leads to cells |
|
|
Which of the following does NOT support the progressive hypothesis of the origin of viruses? A. Self-replicating units B. Genetic elements gained ability to move between cells C. Viral-like transposons D. Retrovirus mirrors retrotransposons |
A. Self-Replicating Units |
|
|
Which of the following does NOT support the Regressive hypothesis of the origin of viruses? A. Remnants of cellular organisms B. Originally symbiotic, then turned parasitic C. Mimivirus D. Complexity leads to cells |
D. Complexity leads to cells |
|
|
Which of the following does NOT suppot the regressive hypothesis of the origin of viruses? A. Genetic elements gained ability to move between cells B. Viruses predate or coevolved with current cellular hosts C. Self-replicating unit D. Complexity leads to cells |
A. Genetic elements gained ability to move between cells |
|
|
Why is a virus called the ultimate hitch hiker? |
1. It is an infectious obligate intracellular parasite. This means that it requires a host in order to survive 2. RNA or DNA genome. It can have either 3. Genome replication & protein production. All it does is replicate viruses and utilizes host machinery to do so 4. Virions-virus progeny. Its goal is viral reproduction |
|
|
A virion is composed of what two main components? |
1. Nucleic acids 2. Proteins |
|
|
Define a "Naked Virus" |
A virus surrounded only by viral proteins. It lacks an envelope |
|
|
Define an "Enveloped Virus" |
A virus surrounded by the host plasma membrane |
|
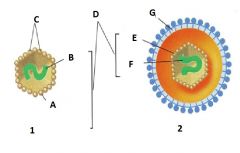
Which of the following is the "Naked Virus" A. 1 B. 2 |
A. 1 |
|
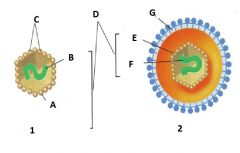
Which of the following is the "Enveloped Virus"? A. 1 B. 2 |
B. 2 |
|
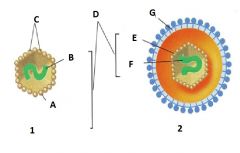
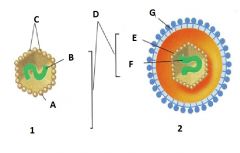
Identify A |
Capsid |
|
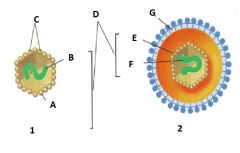
Identify B |
Nucleic Acid |
|
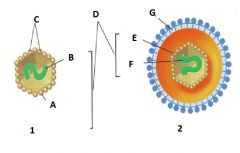
Identify C |
Capsomere |
|
Identify D |
Nucleocapsid |
|
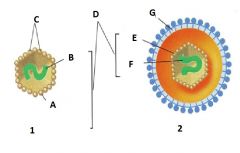
Identify E |
Capsid |
|
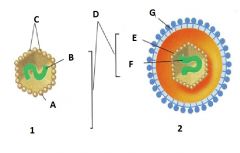
Identify F |
Nucleic Acid |
|
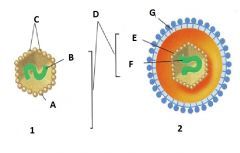
Identify G |
Envelope |
|
|
What three common functions do viruses share? |
1. Replication of viral genome 2. Packaging of viral genome into virions 3. Alter structure of the host cell making the host cell a virocell |
|
|
Deine "Virocell" |
A host cell that no longer does it's host function |
|
|
T/F: A virus requires cellular resource for replication |
True |
|
|
What type of organic molecules will a virus require for replication? |
1. Amino Acid 2. Sugar 3. Nucleoside 4. LIpids |
|
|
What type of naming conventions do viruses follow? |
There is no consistent naming system |
|
|
How have viruses been named in the past? |
1. Named after the type of disease caused 2. Origin of location 3. Discoverer 4. Associated diseases 5. Geographic location 6. How they are contracted |
|
|
Provide an example of a virus named after the specific type of disease it caused |
1. Poliovirus 2. Rabies virus |
|
|
Provide an example of a virus named after the origin of location |
1. Rhinovirus 2. Adenovirus |
|
|
Provide an example of a virus named after its discoverer |
1. Epstein-Barr |
|
|
Provide an example of a virus named after the associated disease |
1. Murine Leukemia Virus 2. Cricket Paralysis Virus |
|
|
Provide an example of a virus named after the geographic location |
1. Ebola 2. Coxsackievirus |
|
|
Provide an example of a virus named after they method of contraction |
1. Dengue 2. Influenza |
|
|
What criteria were used in the classical system of virus classification? |
1. Nature of nucleic acid in the virion 2. Symmetry of the protein shell 3. Presence of absence of lipid 4. Dimensions of the virion & capsid |
|
|
Baltimore Classification System classifies viruses based on the nature of.. |
VIral Nucleic Acid |
|
|
How many groups are found in the Baltimore Classification System? |
7 |
|
|
Describe Class I viruses in the Baltimore Classification System |
Class I virus genomes are double stranded DNA. They require DNA Dependent DNA polymerase to produce more double stranded DNA and DNA Dependent RNA polymerase to turn DNA to RNA |
|
|
What enzymes are used in Class I viruses? |
1. DNA Dependent DNA polymerase 2. DNA Dependent RNA polymerase |
|
|
Name all of the Baltimore Classes which use Double Stranded DNA |
1. Class 1
2. Class 7 (requires Reverse Transcriptase) |
|
|
Describe Class 2 viruses in the Baltimore Classification System |
Class 2 viruses have Single Stranded DNA. They require DNA dependent DNA polymerase to produce double stranded DNA intermediates. From these intermediates they can use DNA Dependent DNA polymerase again to produce more single stranded DNA or they can use DNA dependent RNA polymerase to produce single stranded viral mRNA |
|
|
What enzymes are used in Class 2 viruses? |
1. DNA dependent DNA polymerase 2. DNA dependent RNA polymerase |
|
|
Provide examples of Class I viruses |
1. Adenoviridae 2. Herpesviridae 3. Papillomaviridae 4. Polyomaviridae 5. Poxviridae 6. Siphoviridae |
|
|
Provide examples of Class II viruses |
1. Anelloviridae 2. Parvoviridae |
|
|
Name all classes which use single stranded DNA |
1. Class 2 |
|
|
Describe Class 3 viruses in the Baltimore Classification System |
Class 3 viruses use double stranded RNA. They use RNA dependent RNA polymerase to both produce more double stranded RNA but also produce single-stranded viral mRNA |
|
|
What enzymes do Class 3 viruses use?
|
1. RNA dependent RNA polymerase |
|
|
Provide examples of Class 3 viruses |
1. Birnaviridae 2. Picobirnaviridae 3. Reoviridae |
|
|
Name all classes which use double stranded RNA |
1. Class 3 |
|
|
Describe Class 4 viruses in the Baltimore Classification System |
Class 4 viruses use single stranded (+) RNA. The single stranded (+) RNA itself can be used as a template for protein synthesis, however to produce more templates, the virus uses RNA dependent RNA polymerase to produce a single stranded (-) RNA intermediate which is then transformed to a single stranded (+) RNA using RNA dependent RNA polymerase |
|
|
Name the enzymes used by Class 4 viruses |
1. RNA Dependent RNA polymerase |
|
|
Name all of the Classes which use Single Stranded (+) RNA |
1. Class 4 2. Class 6 (With reverse transcriptase) |
|
|
Provide examples of Class 4 viruses |
1. Corona viridae 2. Flavivirdae 3. Herpeviridae 4. Picornaviridae |
|
|
Describe Class 5 viruses in the Baltimore Classification System |
Class 5 viruses have single stranded (-) RNA. (-) RNA can't be used to produce proteins and so RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase must first convert the single stranded (-) RNA to single stranded (+) RNA. Once it is single stranded (+) RNA it can be used as a template for protein synthesis or it can be used to produce more single stranded (-) RNA using RNA dependent RNA polymerase. |
|
|
What enzymes are used by Class 5 viruses? |
1. RNA dependent RNA polymerase |
|
|
T/F: Single Stranded (-) RNA can be used as a template for protein synthesis |
False. It must first be turned into single stranded (+) RNA by RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase |
|
|
What Classes use Single stranded (-) RNA? |
1. Class 5 |
|
|
What viruses fall under Class 5? |
1. Filoviridae 2. Paramyxoviridae 3. Arenaviridae 4. Orthomyxoviridae |
|
|
Describe Class 6 viruses in the Baltimore Classification System |
Class 6 viruses use Single-stranded (+) RNA. They use RNA Dependent DNA Polymerase (Reverse transcriptase) to produce Double stranded DNA. Then it uses Integrase to incorporate the viral DNA into the host genome allowing the host to translate the viral DNA along with the host. |
|
|
What enzymes are used in class 6 viruses? |
1. RNA Dependent DNA polymerase (Reverse Transcriptase) 2. Integrase |
|
|
What is the main difference between Class 4 and Class 6 if both use Single Stranded (+) RNA |
Class 6 utilizes reverse transcriptase while Class 4 does not |
|
|
Provide examples of viruses that are Class 6 |
1. Lentivirus 2. Spumavirus |
|
|
Describe Class 7 viruses in the Baltimore Classification System |
Class 7 Viruses are Double Stranded DNA and use Reverse transcriptase. |
|
|
Name viruses that would fall under Class 7 |
1. Hepadnaviridae |
|
|
What ist he primary function of the capsid |
Protect |
|
|
Define "Metastable" and why must a virus be Metastable? |
A virus must be metastable meaning that it must both be strong enough to withstand harsh elements while being flexible enough to enter a host cell without rupturing it. |
|
|
Provide examples as to how a virus is strong |
1. The protective coat is capable of withstanding environmental assault 2. Protein-protein interactions in the coat provides resistance to many proteases |
|
|
T/F: Enveloped viruses have an additional layer of protection due to additional proteins and sugars provided by the host |
True |
|
|
How do enveloped and naked viruses differ in terms of exiting a cell? |
Enveloped viruses acquire the envelope by budding off of the host cell and taking with it a portion of the host's lipid membrane. Nake viruses do not have an envelope and so they leave the cell through lysis or secretory pathways |
|
|
T/F: The size of the virion is generally proportional to the size of the genome |
True
|
|
|
T/F: There is a constraint on virus particle size |
True |
|
|
Rod-shaped virus type of symmetry |
Helical symmetry
|
|
|
The length of a virus is determined by |
The length of nucleic acid |
|
|
The width of a virus is determined by |
Size and packaging units of protein subunits |
|
|
Spherical virus. Type of symmetry |
Icosahedral Symmetry |
|
|
How are viruses transmitted? |
1. Aerosal 2. Food & Water 3. Fomites 4. Body secretions 5. Sexual activity 6. Birth 7. Transfusion or transplant 7. Zoonoses (Animals, insects) -Rabies |
|
|
What are Pre-Infection precautions that can be taken? |
1. Vaccines |
|
|
What are the two types of vaccines? |
1. Live attenuated virus vaccines: Limited viral replication. progeny contained at site of infection. Infection induces mild or unapparent disease 2. Inactivated "killed" vaccines. Use chemical or physical means to eliminate infectivity but not antigenicity. |
|
|
What are some Post-Infection precautions that can be taken? |
Antivirals |
|
|
What are some targets of antivirals? |
1. Attachment 2. mRNA synthesis 3. Protein synthesis 4. DNA Replication |
|
|
HIV Antivirals target A. Attachment B. mRNA Synthesis C. Protein Synthesis D. DNA Replication |
A. Attachment |
|
|
Hepatitis A, B, and C Antivirals target A. Attachment B. mRNA Synthesis C. Protein Synthesis D. DNA Replication |
B. mRNA Synthesis |
|
|
HPV Antivirals target A. Attachment B. mRNA Synthesis C. Protein Synthesis D. DNA Replication |
C. Protein Synthesis |
|
|
Herpes Antivirals target A. Attachment B. mRNA Synthesis C. Protein Synthesis D. DNA Replication |
D. DNA Replication |
|
|
Provide some techniques used in identifying viral morphology |
1. X-Ray crystallography 2. Electron Microscope 3. Light Microscope (in rare cases) |
|
|
This technique is used to characterize virions by characterzing protein |
X-Ray crystallography. |
|
|
What alternative technique can be used if X-Ray crystallography can be done? |
1. Cryo-EM (Cryogenic Electro Microscopy) |
|
|
What is the difference between "Susceptible" and "Permissive" Cells? |
1. Susceptible cells mean that the host has the correct receptor which would allow the virus to enter. 2. Permissive cells mean that the host has the correct machinery which would allow the virus to synthesize more viruses |
|
|
T/F: A virus does not need to be Permissive in order to enter a Cell |
True |
|
|
T/F: A virus does not need to be Permissive to produce virus |
False. |
|
|
T/F: A virus must be both Permissive and Susceptible to enter a cell and produce viruses |
True |
|
|
What are the two types of cell lines |
1. Primary Cell Lines. These are obtained from tissues and subcultured. They have limited life span 2. Continuous cell lines. Often transformed and subcultured from cancer cells. They are immortal. |

