![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
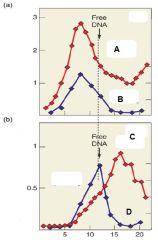
What is the purpose of the experiment |
To compare the size of the transcription between RNA and DNA in the presence or absence of Rho |
|
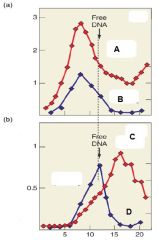
Describe Graph A |
Graph A represences transcription in the absnece of Rho. We see that without Rho, RNA and DNA are relatively the same size |
|
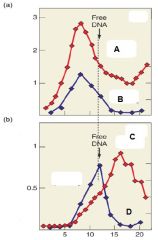
Describe Graph B |
Graph B represents transcription in the presence of Rho. We see that with Rho, RNA appears as smaller fragments compared to DNA. |
|
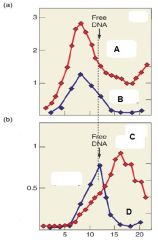
Which of the following lines represents RNA in the presence of Rho? A. B. C. D |
C. |
|
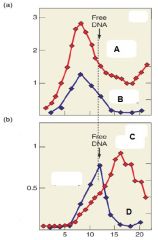
What was the conclusion of the experiment |
Rho helps to release RNA from DNA creating smaller fragments when compared to the DNA |
|
|
T/F: The Rho loading site is approximately 60-100 nucleotides long and is Cytosine-rich |
True |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT true in regards to Rho A. The loading site is Cytosine-rich and is 60-100 nucleotides long B. ATP dependent C. Has RNA-DNA helicase activity D. Binding to the RNA activates ATPase activity. E. None of the above |
E. none of the above |
|
|
Which of the following does affects elongation. A. Rifampicin B. Streptolydigin C. Actinomycin D D. Heparin |
B. Streptolydigin |
|
|
Which of the following blocks initiation by binding to the beta-subunit of RNA polymerase and inhibiting the formation of the first phosphodiester bond? A. Rifampicin B. Streptolydigin C. Actinomycin D D. Heparin |
A. Rifampicin |
|
|
Which of the following blocks initiationby binding tightly and specifically to dsDNA by interlatation forming ssDNA template region. A. Rifampicin B. Streptolydigin C. Actinomycin D D. Heparin |
C. Actinomycin D |
|
|
Which of the following blocks reinitiation by competing with DNA in binding to free RNA polymerase A. Rifampicin B. Streptolydigin C. Actinomycin D D. Heparin |
D. Heparin |
|
|
Name all of the components of the viral RNA |
1. U5 2. PBS 3. GAG 4. Pol 5. Env 6. U3 7. LTR |
|
|
Which of the following codes for the Coat Protein in a viral RNA? A. Gag B. Pol C. Env D. PBS |
A. Gag |
|
|
Which of the following codes for the RTase (integrase and protease) in a viral RNA? A. Gag B. Pol C. Env. D. PBS |
B. pol |
|
|
Which of the following codes for the Envelope protein in a viral RNA? A. Gag B. Pol C. Env D. PBS |
C. Env |
|
|
Which of the following of the following codes for the Integrase in a viral RNA? A. Gag B. Pol C. Env D. PBS |
B. Pol |
|
|
T/F: The provirus can be integrated into the host genome by use of the protease |
False. The provirus can be integrated into the host genome by an integrase |
|
|
Once the provirus is integrated into the host genome, it is trancribed by A. Host RNA polymerase I B. Viral RNA polymerase II C. Host RNA polymerase II D. Viral RNA polymerase I |
C. Host RNA polymerase II |
|
|
Which of the following is not coded by the Pol gene of the virus? A. Protease B. Coat C. Integrase D. Reverse Transcriptase E. None of the above |
B. Coat |
|
|
How many total enzymes are coded in a viral RNA? A. 1 B. 3 C. 5 D. 7 |
C. 5 |
|
|
Which of the following are not activities directed by RTase in viruses? A. RNA directed DNA polymerase B. RNAseH C. Protease D. DNA dependent DNA polymerase |
C. Protease |
|
|
The process of reverse transcription phase I is provided in the wrong order. Place them in order. i. host DNA jumps from left to right ii. DNA synthesis using Host DNA moves from 5'-3' iii. host tRNA is taken and used at the PBS iv. RNase H removes R and U5 v. RNA dependent DNA polymerase A. iv, ii, ii, v, i B. v, ii, i, iii, iv C.i, v, iv, ii, iii D. iii, ii, iv, i, v |
D. iii, ii, iv, i, v |
|
|
The process of reverse transcription phase II is provided in the wrong order. Place them in order. i. Rnase H ii. DNA dependent DNA polymerase iii. Most viral RNA is removed leaving a small fragment to serve as a primer iv. DNA synthesis in the 5'-3' direction. v. Jumps from right to left to the PBS site A. iii, iv, i, v, ii B. i, v, iv, ii, iii C. ii, v, i, iii, i D. v, i ii, iv, iii |
A. iii, iv, i, v, ii |
|
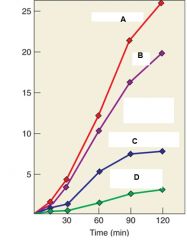
What is the purpose of the experment? |
To determine whether RNA can be used as a template for DNA synthesis |
|
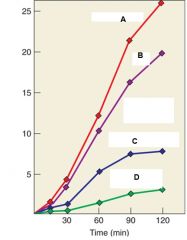
Describe the experiment |
Purified retrovirus was incubated ith dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and [3H]- dTTP under four conditions. Line A indicates DNA synthesis with no treatment, Line B indicates DNA synthesis in water, Line C indicates DNA synthesis with RNase, Line D indicates DNA synthesis after RNase. |
|
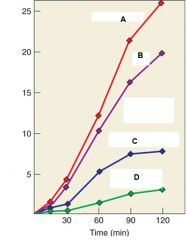
Describe Line A, Line B, Line C, and Line D |
Line A: DNA synthesis with no treatment Line B: DNA synthesis in water Line C. DNA synthesis in RNase Line D: DNA synthesis AFTER Rnase |
|
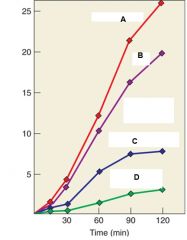
What are the Y axis |
Y axis is amount o tritium incorporated by DNA synthesis |
|
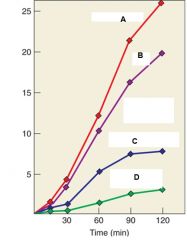
What were the conclusions of the experiment |
RNA acts as a template for DNA synthesis because Line C and D show marked decrease in DNA synthesis when treated with RNA. Line B also shows decrease even though it is treated with water it is because water contains RNase and so there was RNAse contamination. |
|
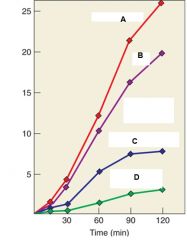
Why is this graph so important? |
It indicated that RNA can be used as a template for DNA synthesis by use of the RNA dependent DNA polymerase |
|
![Which of the following was used to label the DNA in the experiment?
A. [alpha32P]- TTP
B. 35S
C. [3H]
D. [Gamma32P]-ATP
E. All of the above](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/27/41/83/13274183_m.jpg)
Which of the following was used to label the DNA in the experiment? A. [alpha32P]- TTP B. 35S C. [3H] D. [Gamma32P]-ATP E. All of the above |
C. [3H] |
|
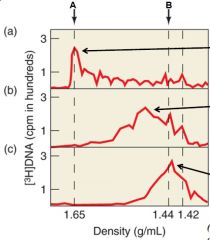
What was the purpose of the experiment |
To determine if RNA was used as a primer. |
|
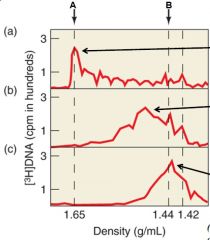
What does the A arrow represent |
Where RNA peaks |
|
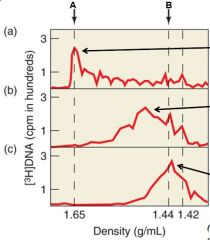
What does the B arrow represent |
Where DNA peaks |
|
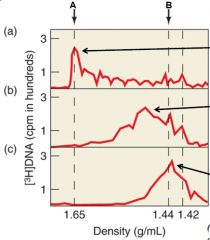
Describe the experiment |
[3H] dTTP was used to label the reverse transcript (DNA) in order to determine if RNA was used as a primer. Graph A shows the presence of the label at RNA indicating that there was a DNA-RNA hybrid between the reverse transcript and the viral RNA. Graph B was under heat which separated the DNA and the RNA indicated by the line. Graph C used Rnase to completely remove RNA and so the label was found in the DNA. |
|
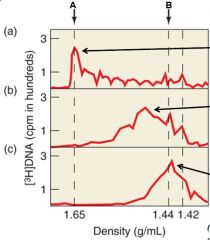
What conclusions were drawn from the experiment? |
RNA is used as a primer during reverse transcription. At this point it is not certain whether tRN is used. |
|
|
Polymerase activity and Ribonuclease activity can be found in what domain of the reverse transcriptase? |
p66 |
|
|
What is the difference between an Open Reading Frame and a Reading Frame? |
Reading Frame: The 6 different ways that it can be read on the original strand. Open Reading Frame: The sequence which is actually being translated |
|
|
T/F: mRNA is read in the 5'-3' direction and DNA is synthesized from N-terminus to C-terminus during translation |
True |
|
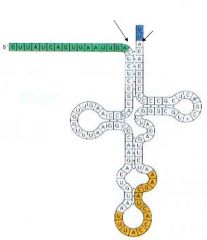
This is an image of A. Mature tRNA B. RNA polymerase C. Ribosome D. Proteon |
D. Proteon |
|
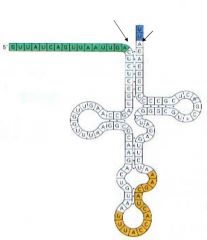
T/F: This is a mature tRNA |
False. This is a proteon, an immature tRNA |
|
|
What necessary steps must be taken in order to produce a mature tRNA? |
1. The leader sequence is removed by Ribonuclease P activity 2. CCA sequence is added to the 3'-OH 3. Modification of bases and ribose 4. Remove of the intron by tRNA endonuclease and ligase (only in eukaryotes) |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a component found in mature tRNA? A. T-Loop B. D-Loop C. Leader sequence D. Anticodon Loop |
C. Leader sequence |
|
|
T/F: Amino acids attach on the 3' end of the tRNA |
True |
|
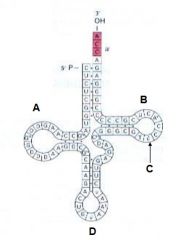
The image depicts: A. Mature tRNA B. RNA polymerase C. Ribosome D. Proteon |
A. Mature tRNA |
|
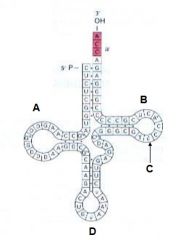
Which of the following indicates the T-Loop |
B |
|
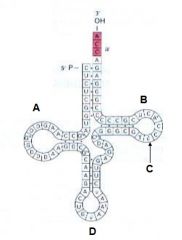
Which of the following indicates the D-Loop? |
A |
|
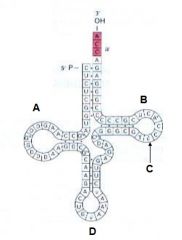
Which of the following indicates the pseudouridine? |
C |
|
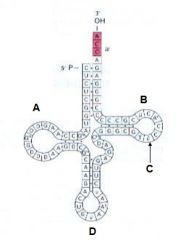
Which of the following indicates the anticodon loop? |
D |

