![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do plants respond to environmental cues:
|
1) through evolution (very long term)
2) growth differences (trees vs. wind; yrs) 3) change developmental processes (make roots or leaves, wks) 4) change physiological processes (CAM responds to day vs. night) |
|
|
What controls responses over the course of a plants life?
|
hormones
|
|
|
what are hormones?
|
chemical produced in one part of body and affects another part of the body.
- actions are specific and they affect specific tissues - active in minute concentrations. |
|
|
Who discovered the first hormone?
|
Darwin and Darwin
|
|
|
What was the first hormone discovered?
|
the hormone responsible for phototropism
|
|
|
coleoptile:
|
grows straight up in normal overhead light and in the dark
- grows toward light when the light comes form one side. |
|
|
define tropisms:
|
growth responses towards or away from a stimulus
|
|
|
what are 3 examples of tropisms?
|
1) gravitropism
2) phototropism 3) thigmotropism |
|
|
define thigmotropism:
|
directional growth in response to touch.
- touching a plant at a site, has been demonstrated to slow growth at that site. ----- if one side of a vine or tendril is touching something.... that side will grow slowly and the other side will grow more quickly |
|
|
What is thought to be the cause of thigmotropism?
|
an increased ethylene in response to mechanical stimulation ---> decreased cell elongation at site of stimulation
|
|
|
define circadian rhythm:
|
responses that are based on a 24 hr. time period.
|
|
|
define biological clock:
|
the internal clock that allows circadian rhythms to occur.
- are usually set by the light/dark cycle of the sun. |
|
|
what do biological clocks modulate (control)?
|
- metabolism/ metabolic rate
- cell division rate - blood cell deposition into blood stream - alertness etc.... |
|
|
In plants what do biological clocks modulate (control)?
|
- metabolism/ metabolic rate
- opening and closing of stomata - legume sleep movement - long term growth responses to day length etc.... |
|
|
define photoperiodism:
|
responses dependent on day vs. night length.
|
|
|
Plants need to be able to tell when the change of seasons occur for.... in other words photoperiodism controls?
|
- seed germination
- flowering - entering or breaking winter or summer dormancy |
|
|
what is photoperiod?
|
the determination of relative length of day vs. night.
|
|
|
Describe the best studied example of photoperidism
|
study used a variety of mutant tobacco (Maryland mammoth)
- it grew tall in summer, but would not flower during the summer, finally flowered in dec. in a greenhouse. - found that it was short winter days that induced plant to flower. ---- by manipulating the daylight period so that the day was 14hrs. or shorter, they were able to induce flowering. |
|
|
What is the mutant tobacco called a short day plant?
|
because it was a shortened day that induced flowering.
ex: soy and poinsettias. |
|
|
what are some plants called long day plants?
|
because they flower when days are longer than a certain period of time.
ex: plants that flower in the summer, spinach flowers... |
|
|
What are day neutral plants?
|
plants that flower at a certain maturity stage and are not photoperiodic
ex: tomato |
|
|
it was discovered that it was not day length but actually _______ length that was the controlling factor in photoperiodism plants.
|
night length
|
|
|
flowering and night length:
|
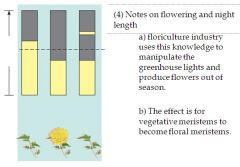
|
|
|
Phytochrome:
|
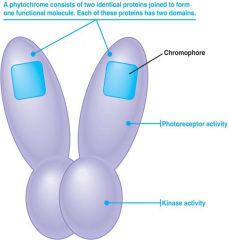
- a light absorbing protein pigment
- exist in leaves - the protein is a dimer and an enzyme and it exists in 2 states. - can be turned on and off by red light. |
|
|
what occurs when phytochrome is flashed with red light at night?
|

the night is interrupted and flowering is inhibited.
|
|
|
What occurs if the phytochrome is shined with red light twice?
|
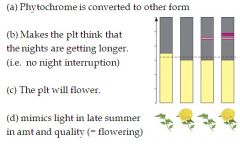
|
|
|
what does photoreversible mean?
|
Describing any compound or system that can exist in two forms, and can be changed from one to the other by the appropriate influence of light.
|
|
|
Phytochromes allow plants to adapt to certain conditons such as and fine tuning of?
|
- day/night length
- light intensity - light quality (wavelength) fine tuning of: - flowering time - growth spurts - breaking dormancy - seed germination |

