![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
procreate:
|
reproduce
|
|
|
cell division:
|
reproduction of cells
- unicellular organisms:divides & forms duplicate offspring (reproduces an entire organims) - on a larger scale: produce progeny from some multicellular organisms - enables sexually reproducing from a single cell -- fertilized egg (zygote) - continues function in renewal & repair, replacing cells that die from normal wear & tear or accidents. |
|
|
the functions of cell division:
|

|
|
|
cell cycle:
|
the life of a cell from the time it is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two cells.
|
|
|
what is most remarkable of cell division?
|
the fidelity with which the DNA is passed along from one generation of cells to the next.
|
|
|
genome:
|
a cell's endowment of DNA, its genetic information.
|
|
|
chromosomes:
|
structure carrying genetic material, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Each one consists of one very long DNA molecules and associated proteins.
|
|
|
somatic cells:
|
- all body cells except the reproductive cells.
- contain 46 chromosomes made up of two sets of 23, one set inherited form each parent. |
|
|
Gametes:
|
- reproductive cells
- sperm and eggs - have 1/2 as many chromosomes as somatic cells. (contain 23 chromosomes) |
|
|
Chromatin:
|
- complex of DNA & associated protein molecules
- this is what chromosomes are made out of. |
|
|
sister chromatids:
|
containing an identical DNA molecule, are initially attached all along their lengths by adhesive protein complexes called cohesins.
|
|
|
Centromere:
|
a specialized region where the two chromatids are most closely attached.
|
|
|
Gametes:
|
- reproductive cells
- sperm and eggs - have 1/2 as many chromosomes as somatic cells. (contain 23 chromosomes) |
|
|
Chromatin:
|
- complex of DNA & associated protein molecules
- this is what chromosomes are made out of. |
|
|
sister chromatids:
|
containing an identical DNA molecule, are initially attached all along their lengths by adhesive protein complexes called cohesins.
|
|
|
Centromere:
|
a specialized region where the two chromatids are most closely attached.
|
|
|
1. sister chromatids
2. chromosome 3. centromere 4. arm 5. chromatin |
|
|
Mitosis:
|
the division of the nucleus
|
|
|
cytokinesis:
|
the division of the cytoplasm
|
|
|
what happens to the chromosome # as we follow the human life cycle through the generations?
|
you inherited 46 chromosomes, one set of 23 from each parent. they were combined in the nucleus of a single cell when a sperm from father united with egg from mother forming a fertilized egg (zygote).
Mitosis & cytokinesis produced the 200 trillion somatic cells that now make up your body. the same process continues to generate new cells to replace dead and damaged ones. you produce gametes --eggs or sperm by meiosis, which yields nonidentical daughter cells that have only one set of chromosomes,. |
|
|
Meiosis:
|
a variation of cell division which yields nonidential daughter cells that have only one set of chromosomes, thyus 1/2 as many chromosomes as the parent cell.
- occurs only in gonads (ovaries/ testes) |
|
|
Chromosome duplication and distribution during cell division.
|
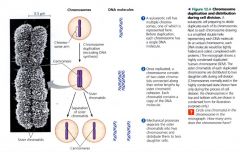
|
|
|
Mitotic (M) phase:
|
includes both mitosis and cytokinesis.
- usually the shortest part of the cell cycle. |
|
|
Interphase:
|
- much longer stage of the cell cycle.
- often accounts for about 90% of the cycle. - cells grows & copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division. - can be divided into subphases: G1 phase S phase G2 phase (cells grows by producing proteins & cytoplasmic organelles. ) |
|
|
which phase do chromosomes duplicate?
|
S phase
|
|
|
what happens in the G1 phase?
|
cell grows
|
|
|
what happens in the S phase?
|
cell continues to grow as it copies its chromosomes.
|
|
|
what happens in the G2 phase?
|
cell grows more as it completes preparations for cell division.
|
|
|
what happens during the M phase?
|
cell divides.
|
|
|
Mitosis is broken down into what stages?
|
- prophase
- prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase - telophase. |
|
|
the cell cycle:
|
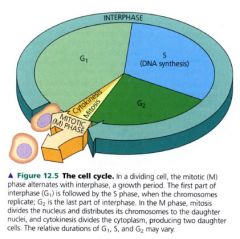
|
|
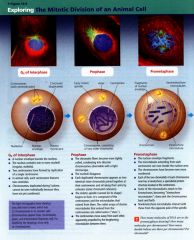
The Mitotic Division of an Animal Cell:
|
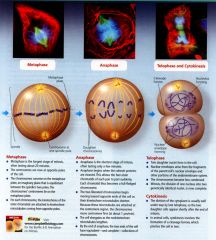
|
|
|
Mitotic Spindle:
|
- many of the events of mitosis are dependent.
- begins to form in the cytoplasm during prophase. - consists of fibers made of microtubles and associated proteins. - while they assemble, the other microtubles of the cytoskeleton partially disassemble (Prob. providing the material used to construct the spindle). |
|
|
Where does the assembly of spindle microtubules start at?
|
at the centrosome
|
|
|
Centrosome:
|
a subcellular reagion containing material that functions throughout the cell cycle to organize the cell's microtubles
aka: microtubule-organizing center. |
|
|
Aster:
|
a radial array of short microtubules extends from each centrosome.
|
|
|
Kinetochore:
|
- a structure of proteins associated w/ specific sections of chromosomal DNA @ the centromere.
- Face opposie directions in teh two sister chromatids of a replicated chromosome. |
|
|
metaphase plate:
|
- the imaginary plane located between the spindle's two poles.
- where the centromeres of all the duplicated chromosomes are at metaphase. |

