![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
352 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anything which takes up space and has mass is called? |
Matter.
|
|
|
The smallest unit of matter than we can obtain through chemical reaction.
|
An element, or atom.
|
|
|
A recurring combination of different atoms is called a..?
|
Compound.
|
|
|
A compound's characteristics are identical or different from those of its constituents?
|
Different.
|
|
|
About (1.)?% of the (2.)? natural elements are essential to life.
1. 2. a) 0-5% a)92 b) 50-55% b)101 c)20-25% c)118 d)14-17% d)56 |
1. c) 20-25%
a) 92 |
|
|
96% of all living matter is made up of these four elements. What are they?
|
Oxygen, Carbon ,Hydrogen, and Nitrogen.
|
|
|
Calcium, potassium, phosphorus, and sulfur make up approx. (1.)? of the elements essential to life.
1. a)6-8% b)96% c)20-25% d)4% |
d)4%
|
|
|
Things like proteins, fats, carbs, and nucleic acids are called (____)molecules and are made up of units called (____).
|
Macromolecules (polymers)
Monomers |
|
|
Proteins are made up of which of the 4 following elements?
-C (Carbon) -O(Oxygen) -N(Nitrogen) -P (Phosphorous) -Si(silicon) -S(Sulfur) -Na (Sodium) -H(Hydrogen) |
C, H, O, N
|
|
|
Substance which are only required to organism in small quantities are called?
|
Trace Elements
|
|
|
Nucleotides make up which macromolecule?
|
Nucleic Acid
|
|
|
What are the two primary functions of carbohydrates?
|
Energy and storage.
|
|
|
All organisms share a similar characteristic, they are all made up of one or more ____.
|
Cell.
|
|
|
Just as organs are to humans ___ are to cells.
|
Organelles.
|
|
|
A microscope works through a process called ___ which is caused by focusing the direction of light with the use of lenses.
|
Refraction.
|
|
|
What is the difference between atomic mass and an atomic number?
|
An atomic number is gauged by the amount of protons found in the nucleus (physics) while the atomic mass is the overall weight of the nucleus obtained by combining the weight of the protons (p+) and neutron (n) found there.
|
|
|
Where are electrons found?
|
They are found revolving around the atom's nucleus.
|
|
|
Something that that the potential to cause change is something with?
a) Carbohydrates b) Intrinsic motivation c) Energy d) ATP |
c) Energy
|
|
|
How do we define an electron's level of potential energy?
a) By observing it through a microscope b) By its distance from the nucleus c) By the Brownian movement of a substance d) By placing them in a centrifuge |
b) by its distance from the nucleus.
The first shell is the lowest level of energy, the 2nd shell is the 2nd highest level, and so on and so forth. |
|

Associate the following appropriatly:
A. 1.Centrifugation B. 2.Tissue cell C. 3.Homogenization D. 4.Homogenate |
A.2
B.3 C.4 D.1 |
|
|
If one was to subject homogenized cell matter to centrifugation at 150 000g for 3h, which of the following substances would be found at the bottom of the test tube?
A. Chloroplasts B. DNA C. Ribosomes D. Protons |
C. Ribosomes
|
|
|
Bacteria and archaea belong to which type of cell?
|
Prokaryotes
|
|
|
Fungi, animals, plants, and protists are made up of ____ cells.
|
Eukaryotic
|
|
|
Two types of cell are found in nature. What are they known as?
|
Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
|
|
|
Where is the nucleoid found?
1. In prokaryotic cells 2. Inside the nucleus 3. Continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum 4. Controlling the microtubular spindles. |
1. In prokaryotes
|
|
|
All cells share four common features. What are they?
|
1. All cells have a membrane composed of a bi-layer of phospholipids.
2. All cells have chromosomes, this is where genes (segments of DNA) are found. 3. A semi-fluid (gel-like) substance called cytosol. 4. Ribosomes. These make proteins by converting information obtain from RNA molecules. |
|
|
What do eukaryotes have that prokaryotes do not?
|
1. Membrane bound organelles
2. A membrane bound nucleus Note: eukaryotes are generally larger than prokaryotes. |
|
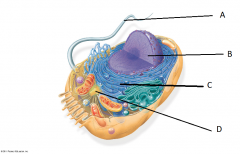
Name the features A to D
|
A. Flagellum
B. Nucleus C. Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) D. Centrosome |
|
|
A selective barrier found in cells that allows the passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste is called ______.
|
A plasma membrane
|
|
|
What is the general structure of biological membranes?
|
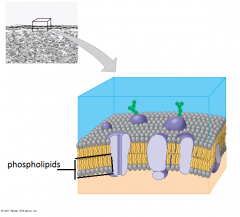
They are generally composed of a bi-layer of phospholipids.
|
|
|
There is something peculiar about phospholipids and their extremities. What is that?
|
The inner-membrane part of phospholipids is hydrophobic, (water-fearing) while the outer part is hydrophilic (water-loving).
|
|
|
A special type of information can be found inside the nucleus. What is this information called?
|
Genetic information, or the genome.
|
|
|
How does the nucleus differ from the nucleoid?
|
The DNA is membrane bound within the nucleus, while the nucleoid is a region in prokaryote where the DNA is found.
|
|
|
Nuclei (plural of nucleus) regulate the flow of molecules with the help of:
1. Ribosomes 2. Microfilaments 3. Calcium ions 4. Pores |
4. Just like human skin, nuclei have pores.
|
|
|
DNA that has been organized in the shape of X's is called?
|
A chromosome.
|
|
|
What is chromatin?
1. An isotope of Chromium. 2. The stuff that chromosomes is made of. 3. A specific segment found in chromosomes. 4. A special type of protein found in the nucleus. |
2. The stuff that chromosomes are made of.
|
|
|
The nuclear membrane is made of one layer of a phospholipid bi-layer. Is this correct?
|
No. The nuclear membrane is a double membrane, each membrane a phospholipid bi-layer.
|
|
|
The (1.) is continuous with the nuclear membrane.
1. a) The endoplasmic reticulum b) The golgi aparatus c) The vesicle d) The plasma membrane |
a) The endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
The site of rRNA synthesis is found within the nucleus in something called the ____.
|
Nucleolus.
|
|
|
There are two types of ribosomes, one of them can be found on the endoplasmic reticulum. What type of ribosome is this?
|
These are called bound ribosomes.
They are found on the rough ER. Ribosome are made up of 2 subunits, the small and the large subunit. |
|
|
There is a theory postulating that larger eukaryotic cells came to posses the organelles that they are now composed of by engulfing other cells which served functions beneficial to them.
What is this theory called? |
The endosymbiotic theory.
|
|
|
The endomembrane system is made up of 6 components. What are they?
|
1. Nuclear envelope
2. Endoplasmic Reticulum 3. Golgi apparatus 4. Lysosomes 5. Vacuoles 6. Plasma membrane All of these are either continuous or connected via transfer vesicle. |
|
|
More than half of the total membrane in eukaryotes is found in this organelle. What is this?
|
The endoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
The is a region in the cell responsible for the synthesis of lipids, the metabolizing of carbohydrates, detoxification from drugs and poisons, and the storage of calcium ions (Ca+). What is this region?
1. Golgi Apparatus 2. The rough ER 3. The smooth ER 4. The cytosol |
3. The smooth ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
The rough ER is the location of bound ribosomes, it is responsible for the distribution of transport vesicles (membrane bound proteins), and it is a membrane factory for the rest of the cell. |
|
|
Cisternae are flattened mambraneous sac found inside which of the following organelles?
1. Mitochondria 2. Endoplasmic reticulum 3. Vacuoles 4. Golgi apparatus |
4. They are found in the golgi apparatus.
|
|
|
A membraneous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules is called_____?
|
A lysosome.
|
|
|
The process where cells engulf other cells to have a lysosome fuse and digest it is called...
1. Meiosis 2. Active transport 3. Phagocytosis 4. Pinocytosis |
3. Phagocytosis
|
|
|
The site for cellular respiration is found in
1. The lungs 2. The flagella 3. The chloroplast 4. The mitochondria |
4. The mitochondria. ATP, or energy, is generated using oxygen.
|
|
|
This is a large membrane bound region found inside plant and fungal cells.
1. Vacuole 2. Lysosome 3. Vesicle 4. Ligand |
1. Vacuoles
Food vacuoles are formed during phagocytosis and contractile vacuoles are responsible for pumping out water in many freshwater protists. |
|
|
Do lysosomal enzymes work best in acidic or basic environments?
|
They work best in acidic environments.
|
|
|
The folds of the mitochondria's inner-member are called...
1. Cristae 2. Cisternae 3. Thylakoids 4. Vesicles |
Cristae
This is the location of enzymes responsible for ATP production. |
|
|
What is the purpose of mitochondria?
|
They are the sight of cellular respiration; they produce ATP.
|
|
|
Where in nature might we expect to find chloroplasts?
|
In plants and algae.
|
|
|
There are two compartments in the mitochondria. What are these called?
|
The intermembrane space and the mitochondrial matrix.
Some steps of cellular respiration are catalyzed in the mitochondrial matrix. |
|
|
Plants are green due to a special pigment. What is this pigment called?
|
Chlorophyll.
|
|
|
Inside chloroplasts stacks of _____ form ______.
|
Thylakoids, granums.
|
|
|
The fluid inside the chloroplasts is called...
1. Chloroplasm 2. Thylakoid leumen 3. Stroma 4. Cytoplasm |
3. Stroma
|
|
|
The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers extending throughing the cytoplasm. It organizes the cell's structures and activities, and anchors many organelles.
There are three different types of molecular structures that make up the cytoskeleton's fibers. What are these called? |
Microfilaments
Microtubules Intermediate filaments Microtubules are very important for cell seperation. |
|
|
Locomotor appendages are protrusions that some organisms have that allow them to move. Two are found in cells. What are they called.
|
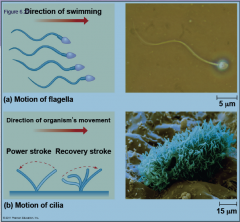
They are called cilia and flagella.
They differ in their beating patterns |
|
|
There is an easy way to distinguish plant cells from animals cells. How?
|
Plant cells have cell walls.
Note: prokaryotes, fungi, and protists may also have cell walls. |
|
|
Cellulose fibers embedded in polysachrides and proteins are the composites of which plant cell structure?
1. Mitochondria 2. Intermediate filaments 3. Cell walls 4. Mitochondrial matrix |
Cell walls.
|
|
|
Plant cells may have multiple wall layers.
What are these called? Name 3 |
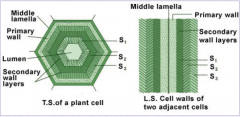
1. Primary cell wall - Relatively thin and flexible
2. Secondary cell wall - Between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall 3. Middle lamella - Thin layer between primary walls and adjacent cells. |
|
|
Intercellular junctions are used by cells for interactions of various sorts through direct physical contact.
There are 4 primary types of junctions. What are they known as? |
1. Plasmodesmata
2. Tight junction 3. Gap junctions 4. Desmosomes |
|
|
____ are channels that perforate plant cell walls.
|
Plasmodesmata.
Water and small solutes such as proteins and RNA may traverse these. |
|
|
Which of the following junctions is responsible for preventing the leakage of extracellular fluids?
1. Plasmodesmata 2. Gap junction 3. Tight junction 4. Desmosomes |
3. Tight junctions. These keep cells pressed together.
|
|
|
Desmosomes provide which of the following functions:
1. Allow nutrients to travel from one cell to another 2. Allow nutrients to travel form one organelle to another 3. Allow waste to be ejected from the cell 4. Fasten cell together into strong sheets |
4. Fasten cells together into strong sheets.
|
|
|
What is the feature found in all cell that separate them from their environment?
|
Plasma membranes.
|
|
|
Molecules which contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions such as phospholipids are know as what?
|
Amphipathic molecules
|
|
|
There is a model that suggests that membranes are fluid structures riddled with embedded proteins.
What is this model known as? |
The fluid mosaic model.
|
|
|
Can polar molecule such as sugar and ions easily cross the cell membrane?
|
No they can not.
Hydrophobic, or nonpolar, molecule such tryglycerols may, however, be easily dissolved in the membrane and absorbed by the cell. |
|
|
For substances that do not easily cross the membrane, the are _____ proteins to assist their absorption.
|
Transport proteins.
|
|
|
A type of transport protein responsible for the passage of water is called..?
|
Aquaporin.
|
|
|
Some transport proteins change shape when bound to their target molecule to pass them through the cell membrane. What are these known as?
1. Channel proteins 2. Plasmodesmata 3. Vesicles 4. Carrier proteins |
4. Carrier proteins
|
|
|
Proteins which are used as tunnels for specific molecules or ions are known as what?
|
Channel protein.
|
|
|
There is a tendency for molecules to spread out evenly in their given space. What is this phenomenon known as?
|
Diffusion.
Stems from the latin word diffūsiō; spreading out. |
|
|
When observed through a microscope, particles suspended in fluid can be observed as moving.
What is this phenomenon known as? |
Brownian movement.
|
|
|
While active transport requires energy (ATP), ______ transport does not.
|
Passive.
|
|
|
The region along which the density of a substance increases or decreases is known as its what?
1. Concentration gradient 2. Refraction gradient 3. Tonicity 4. Differential centrifugation |
1. Concentration gradient
|
|
|
Water diffuses across cell membranes to maintain an equal level of concentration in solutes on both sides of this one. What is this phenomenon known as?
|
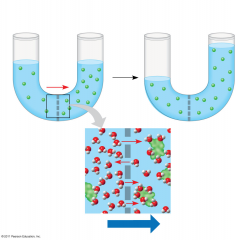
Osmosis.
|
|
|
Tonicity is the potential for a solution surrounding a cell to cause the cell to either gain or lose water.
There are 3 different terms used to gauge the tonicity of the cell's environment. What are these? Remember: tonicity refers to the solution OUTSIDE the cell. |
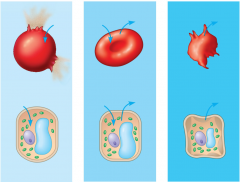
Isotonicity- The level of solutes is the same (Isos is greek for equal) in and out of the cells. No osmosis occurs.
Hypertonicity- There are MORE solutes (hyper- = excessively) outside the cell, therefore the cell loses water and shrinks Hypotonicity- There are LESS solutes (hypo- = lacking) outside the cell, therefore the cell gains water and expands. |
|
|
Some channel proteins open or close in response to stimulus. These are know as?
1. Sodium-potassium pumps 2. Transport proteins 3. Aquaporins 4. Gated channels |
4. Gatted channels
|
|
|
While passive transport uses no energy thanks to the phenomenon of diffusion _________ works against this and requires energy.
|
Active transport.
|
|
|
Though diffusion happens on its own, in _______ transport proteins speed the process at which this occurs
|
Facilitated diffusion.
|
|
|
Energy in the form of _____ is required for active transport.
|
ATP
|
|
|
_____ occurs when active transport of a solute causes the transport of other solutes.
|
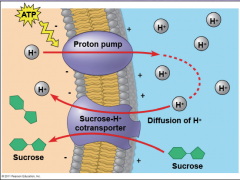
Cotransport
Plants use the gradient of H ions generated by proton pumps to drive the transport of nutrients into the cell. |
|
|
Though smaller nutrients may enter and leave the cell through its membrane, in bulk transport larger molecules cross the membrane with ________.
1. Sodium-potassium pumps 2. Channel proteins 3. Vacuoles 4. Vesicles |
4. Vesicles.
Bulk transport requires energy. |
|
|
Cells take in macromolecules by forming vesicles from their membranes through a process known as?
1. Endocytosis 2. Cellular respiration 3. Cytokinesis 4. Osmosis |
Endocytosis. (Endo- =within) Think Endo - Into
This is the reversal of exocytosis. (Exo - =outside) |
|
|
There are 3 types of the phenomenon known as endocytosis, that is the cell's taking in of nutrients via vesicles. What are these known as?
|
1. Phagocytosis
2. Pinocytosis 3. Receptor-mediated endocytosis |
|
|
The form of endocytosis when molecules are taken in when extracellular fluid is absorbed into vesicle is know as?
|
Pinocytosis
|
|
|
Receptor-mediated endocytosis happens when (1.)? binds to a receptor and triggers vesicle formation.
1. a) Gamete b) Ligands c) Nanoparticle d) Chromatids |
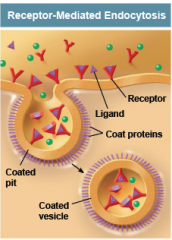
b) Ligands
Neurotransmitters are a type of ligand. |
|
|
What is the process, or ability that differentiates living things from non-living matter?
|
The ability to produce more of its own kind, or cell division.
|
|
|
While cell division produces entire new organism when performed by unicellular organisms, multicellular organisms depend on this process for 3 important processes. What are they?
|
1. Development from a fertilized egg.
2. Growth 3. Repair |
|
|
The moment a cell is created to the moment it divides is called the _____.
|
Cell cycle.
|
|
|
There is a name given to define all the DNA inside a cell?
|
The genome.
|
|
|
When DNA is bound to proteins in into an organized X structure, it is called a _____.
|
Chromosome.
|
|
|
Species do not all have the same number of chromosomes in their nucleus. How many chromosomes are found in human nuclei?
|
46.
2n=46 2(23)=46 |
|
|
Cell which are designed for the purpose of reproduction in multicellular organisms are known as _____.
|
Gametes
(Sperm and eggs) |
|
|
All cells other than those designed for reproduction are known as _____.
|
Somatic cells.
|
|
|
Before cell separation can occur, a cell needs to duplicate all of it's genetic information. Chromosomes contain two segments of identical genetic information. What are these segments called?
|
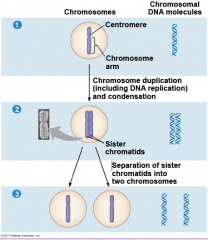
They are called sister chromatids.
Each chromatid has the genetic information required to be a chromosome, and will become it upon separation. |
|
What is the name of the region displayed in the chromosome above?
|
The centromere.
This is where the sister chromatids are the most closely attack. Later, the spindle microtubules will attach to this section. |
|
|
There are two types of cell division. They may be represented as follows:
1. 2n -> 2n or n -> n and 2. 2n -> n What are these known as? |
1. Mitosis
2. Meiosis "n" is the amount of chromosome found within the nucleus. |
|
|
Cell spend most of their life in the interphase stage of the cell cycle. This stage has 3 different phases, what are they known as?
|
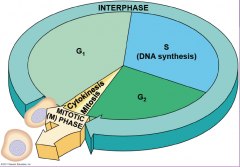
G1 (First gap)
S (Synthesis, of DNA) G2 (Second gap) |
|
|
A structure of microtubules responsible for the separation of chromosomes during mitosis is known as?
1. Centrosome 2. Centrioles 3. Mitotic spindle 4. Centromere |
3. Mitotic spindle
Centrosomes are found in animal cells and are responsible for the assembly of the spindle microtubules. |
|
|
Where can centrosomes be found during the final stages of cell separation?
|
At opposing extremities of the cell.
|
|
|
Mitotic spindles are made up of which of the cytoskeleton's fibers?
1. Microtubules 2. Microfilaments 3. Intermediate filaments 4. Cellulose |
1. Microtubules
|
|
|
There are 5 phases in mitosis. At which stage is Anaphase?
|
Fourth. During anaphase chromatids break free and become chromosomes while pulled to the cell's poles by the spindles.
|
|
|
What is the name and # of the phase where the nuclear envelope breaks apart?
|
Prometaphase, the second phase.
Tip: By remembering Prometa- (1.Pro-, 2.Prometa-, 3.Meta-) and Telo- (Greek for "end") you should better remember the order of the 5 stages. |
|
|
The final stage of cell separation is known as:
1. Telekinesis 2. Cytokinesis 3. Phagokinesis 4. Mitokinesis |
2. Cytokenesis. The cytoplasm separates.
|
|
|
Cytokenesis, the actual division of the cell occurs differently in animal and plant cells. How does it differ?
|
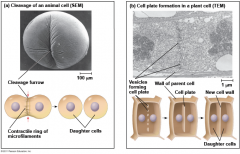
Animal cell: Cleavage furrow forms and daughter cells pinch off
Plant cells: Cell plate forms in the center of the cell and grows outwardly. "To cleave" is to separate. A furrow is a deep wrinkle like those on some people's foreheads. |
|
|
Children inherit ____ from the parents that reflect similar traits.
|
Genes.
|
|
|
Genes are passed on from one generation to the next via cells called_____.
|
Gametes
|
|
|
Each pair of ______ include one chromosome from each parent.
1. Chromatids 2. Sex chromosomes 3. Homologous chromosomes 4. Tetrad |
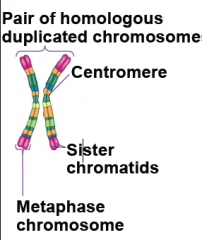
3. Homologous chromosomes
) ( Each of the ) are individual chromosomes. Each contain information for the same function but have different details. |
|
|
Humans have 23 pairs of, similar, homologous chromosomes. How many unique chromosomes do humans have?
|
46.
|
|
|
2n is used to describe a diploid cell.
n would be used to describe a _____ cell. |
Haploid cells.
These are gametes, or sexual cells. |
|
|
Of the 23 chromosomes found in human gametes (sex cells), one of these is called a 1.____ chromosome and come in two types. These two types are known as 2.___ and 3.___ chromosomes.
The remaining chromosomes in the gamete are known as 4.___ . |
1. Sex chromosomes
2. X 3. Y 4. Autosomes |
|
|
When two haploid (n) cells fuse (n+n=2n) the resulting cell is called a:
1. Zygote 2. Gamete 3. Somatic cell 4. Sperm |
A Zygote. The zygote will now develop into a multicellular organism through mitosis.
|
|
|
During the prophase of meiosis 1, homologous and replicated chromosomes loosely pair up. This is known as:
1. Equational division 2. Synthesis 3. Gametogenesis 4. Synapsis |
4. Synapsis
From the ancient greek Sunapsis - conjunction. |
|
|
Chromatids from homologous pairs exchange DNA segments during meiosis 1. What is this phenomenon known as?
|
Crossing over.
|
|
|
Homologous pairs that have crossed over eachother are attached at this level. This is known as what? (1.)
The resulting group of 4 attached chromatids is know as a ___(2.). |
1. Chiasmata
2. Tetrad |
|
|
Anaphase 1 and anaphase 2 differentiate in a very important way. How do they differentiate?
|
In anaphase 1 homologous pairs of replicated chromosomes which aligned during the synapsis process of prophase 1 are pulled apart while their chromatids remain attached. The nuclei result in have half as many chromosomes, or "2n -> n".
In anaphase 2 the chromatids which had previously remained attached are now seperated. The nuclei result in equivalent amounts of chromosomes, or "n -> n". |
|
|
During metaphase, chromosomes align in a regain called the (1.).
1. a) Metaphase furrow b) Middle lamella c) Metaphase plate d) Metaphase wall |
c) the metaphase plate.
This is just a region, not an actual structure. |
|
|
The process of producing gametes (sex cells) differs in males and females. What is this process called?
|
Gametogenesis.
|
|
|
The development of these gametes is continuous. What are they? What is the process called?
|
They are sperm cells, and the process is called gametogenesis.
|
|
|
The production of eggs is a process known as:
1. Oocytosis 2. Ovagenesis 3. Oogenesis 4. Embryocytosis |
3. Oogenesis.
[oh-uh-jen-uh-sis] -Dictionary.com |
|
|
The resulting haploid cells from meiosis in males and females differs in what way?
|
All four haploids in male cell will be functional gametes, while only one in females.
|
|
|
What is required for secondary oocytes to complete meiosis 2?
|
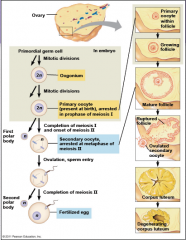
They require to be fertilized by a sperm cell.
|
|
|
Spermatogonial stem cell that have gone through 2 mitotic divisions and are ready for meiosis 1 are known as:
1. Spermatogonium 2. Primary spermatocytes 3. Secondary spermatocytes 4. Spermatids |
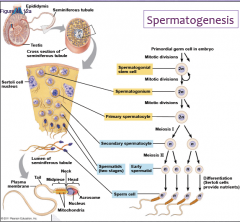
2. Primary spermatocytes
|
|
|
Plants which produce offsprings of the same variety are known as what?
|
True-breeding plants
|
|
|
A gene is to a character as an allele is to a_____?
|
Trait.
The trait is the phenotypical expression of the gene at a specific locus. |
|
|
The process of breeding two true-breeding plants is known as?
|
It is known as hybridization.
|
|
|
The initial plants used in the process of hybridization are known as the __ generation.
The generations following this are the __ and __ generations. |
P
F1 F2 |
|
|
In the F1 generation as certain trait is present while the other is not. What is the present trait known as?
|
It is known as a dominant trait, while the other is the recessive trait.
|
|
|
Alternative versions of a gene at a specific locus are known as a _____?
|
Alleles.
The locus is a specific location on a chromosome responsible for a particular trait, or aspect, of the organism. |
|
|
A pair of homologous chromosomes have genetic information for the same characters. Therefore, how many alleles do (diploid organisms) have per locus?
|
2.
If the genetic information at particular locus is the same in each homologous chromosome, then the character is homozygous. |
|
|
What is the advantage of meiosis in the reproduction of organisms?
|
Genetic variability.
Organisms inherit alleles which are potentially different from each parent. If the expressed allele (or alleles) is beneficial to the organism in its given environment then its chances of reproducing are enhanced and the specie may proliferate. |
|
|
When two alleles are both phenotypically expressed, then we can assume that there is ____ of the alleles
1. Codominance 2. Complete dominance 3. Incomplete dominance |
1. codominance.
|
|
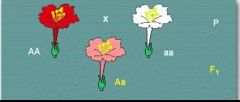
This is an example of which degree of dominance?
|
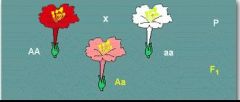
incomplete dominance
|
|
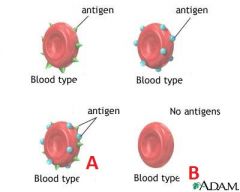
Identify the blood types for A and B and their respective alleles.
A is displaying what degree dominance? |
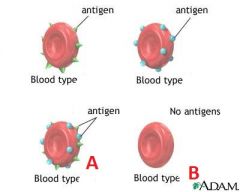
A- Blood type AB, the alleles are I^A and I^B
B- Blood type O and the alleles are i and i. A is displaying codominance. |
|
|
What is a gene pool?
|
A gene pool consist of all the alleles in all the loci in a group of individuals capable of interbreeding within a localized area.
|
|
|
Are dominant alleles more numerous than non-dominant alleles?
|
No
|
|
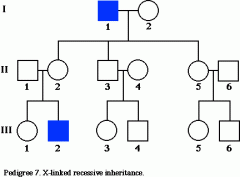
What type of chart is this?
And what purpose does it serve? |
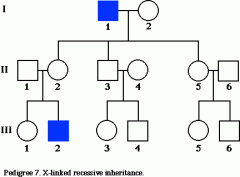
It is a pedigree chart.
It displays the interelationships of parents children across generations and provides information about their phenotypes. |
|
|
The phenomenon that explains how the quantity of certain alleles may fluctuate from one generation to the next is known as what?
|
A genetic drift.
|
|
|
Macromolecules are ___ composed of ___.
|
Macromolecules are polymers composed of monomers.
|
|
|
What is the macromolecule of DNA?
And what is the monomer of this? |
Nucleic acid, which has nucleotides as monomers.
|
|
|
What is a dehydration reaction?
|
It is the process of binding monomers by the removal of a water molecule.
|
|
|
What is hydrolysis?
|
It is the process of "splitting" a polymer by adding a water molecule to the chain.
Hydro- means water Lysis- means splitting |
|
|
The polymer composed of amino acids is known as what?
|
Polypetide.
These are the composites of proteins. |
|
|
What is a nucleoside?
|
A nucleoside is the combination of nitrogenous base and a molecule of pentose sugar (deoxyribose or ribose).
Combined with a phosphate group they make up a nucleotide. |
|
|
Nucleotides are bound together by ______ bonds at the _' carbon of one molecule and the _' phosphate of the next nucleotide.
|
Nucleotides are bound together by covalent bonds at the 3' carbon of one molecule and the 5' phosphate of the next nucleotide.
|
|
|
1. Pyrimidines are composed of
2. Purines are composed of a) Adenine b) Thymine c) Uracile d) Cytosine e) Guanine |
1. Pyrimidines are composed of Cytosine, Uracile, Thymine
2. Purines are composed of Adenine, Guanine. Pyrimidines CUT Purines and purines go "AAAGGG!!" |
|
|
The backbone of DNA is composed of two molecules. What are they?
|
Pentose sugar (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA)
with a phosphate group. |
|
|
The shape of a DNA molecule is a _____.
The arrangement of both DNA backbones running opposite of one another relative to the positioning of their 5' and 3' extremities is known as _____. |
The shape of a DNA molecule is a HELIX.
The arrangement of both DNA backbones running opposite of one another relative to the positioning of their 5' and 3' extremities is known as ANTIPARALLEL. |
|
|
How many genes are present in a single DNA molecule?
|
A whole bunch.
|
|
|
Guaninne ALWAYS binds with _______.
While Adenine bines with ____ in DNA and ___ in RNA. |
Guaninne ALWAYS binds with Cytosine.
While Adenine binds with Thymine in DNA and Uracile in RNA. |
|
|
CTGCAGA
What would the RNA segment look like? |
CTGCAGA --RNA--> GACGUCU
|
|
|
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific DNA sequences called ______ and form many _______.
|
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific DNA sequences called RESTRICTION SITES and form many RESTRICTION FRAGMENTS.
Useful restriction enzymes produce restriction fragments with sticky ends that may be bonded using DNA ligase. Ligase means to bind. (Like in receptor-induced endocytosis) Or in ligaments which bind bones to bones. |
|
|
What does RFLP stand for?
What does this cause? |
RFLP - Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
It causes change in the location of restriction sites. |
|
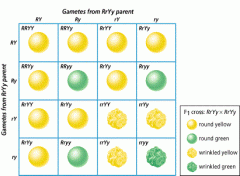
What is this called?
And what is it useful for? |
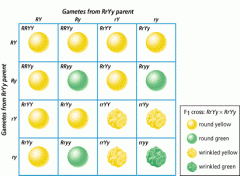
Punett squares are useful for characterizing the potential outcomes of a dihybrid cross and also gives us the probability that a certain trait will be expressed as a result.
|
|
|
Name 2 characteristics of non-vascular plants.
|
1. They do not have true roots or stems.
2. They are often small in size 3. They depend on water for reproduction 4. They lack vascular tissue Moss, liverwort and bryophyta are examples. |
|
|
Vascular plants can be classified into two main categories. What are they?
|
Seedless and seed-bearing.
|
|
|
Seedbearing plants can be classified into two groups. What are they?
|
Angiosperms - fruit-bearing plants
Gymnosperms - "naked" seed plants such as in conifers. Gymno means naked. Gymnasiums were places the ancient greeks when to go do sports and hang out naked. |
|
|
Angiosperms (covered seed plants) can be classified into two main groups.
What are they? And where do they get their name from? |
Dicot - presence of 1 cotyledon
Monocots - presence of 2 cotyledons |
|
|
The lateral meristem tissue responsible for replacing the epidermis with periderm in woody plants is known as what?
|
Cork cambium.
The other type of lateral meristem is vascular cambium. |
|
|
The pores responsible for gas exchange in leaves are known as what?
What type and how many cells guards them? |
Stomata, they are guarded by two guard cells each.
|
|
|
There are two types of vascular tissues in plants. What are they known as?
|
Phloem and Xylem
|
|
|
What purpose does xylem tissue serve and what is it composed of?
|
It transports water from the roots to the shoots of plants and it is composed of long dead cells.
|
|
|
Photosynthetic cells in plants are part of which tissue system?
|
The ground tissue system.
|
|
|
What plant tissue system is pith part of? And where it found?
|
Pith is part of the ground tissue sysetm and it is found within vascular tissue.
Cortex is found outside of the vascular tissue. |
|
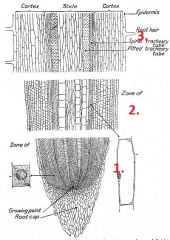
Behind the root cap are three zones of cells.
What are they known as? |
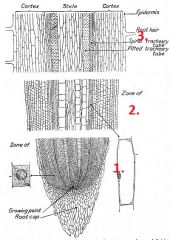
1. Zone of cell division
2. Zone of elongation 3. Zone of maturation |
|
|
Where is mesophyl found in plants? What tissue system is it part of?
|
Mesophyl, part of the ground tissue system, is found in leaves.
|
|
|
A matured ovary in plants is known as what?
|
A fruit.
|
|
|
A group of cells carrying out similar functions in unison is known as what? (in animals)
|
Tissue.
|
|
|
What are the four types of tissue in animals?
|
1. Epithelial
2. Muscle 3. Connective 4. Nervous |
|
|
Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and cemented onto a _____.
|
Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and cemented onto a BASAL LAMELA.
|
|
|
What is the different between simple and stratified epithelial tissue?
|
Stratified epithelial tissue is composed of many layers while simple epithelial tissue has but one layer.
|
|
|
What are the characteristic of squamous, cuboidal, and columnar epithelial cells?
|
Squamous - are flat
cuboidal - are cube shaped columnar - are elongated Squamous means scale. Squamata, or lizards, have scales, which are flat. |
|
|
Chondrocytes are part of which animal tissue?
|
Cartilage. Which is part of the connective tissue system.
|
|
|
Name two types of leukocytes.
|
Name two types of leukocytes.
Could have been two of the following: 1. Monocytes 2. Netrophils 3. Basophils 4. Eosinphils 5. Lymphocytes |
|
|
How do leukocytes function in defense?
What are leukocytes? |
Leukocytes eliminate bacteria and debris through phagocytosis.
Leukocytes are white blood cells, which are bigger but less numerous than RBCs. |
|
|
The encasing of chondrocytes and osteocytes are known as what?
|
Lacunae.
|
|
|
Muscle cells are made of a membrane called _____ and an internal fluid called _____.
|
Muscle cells are made of a membrane called SARCOLEMMA and an internal fluid called SARCOPLASM.
|
|
|
What is a characteristic shared by both skeletal muscle cells and heart muscle cells?
|
They are both striated.
They are both multinucleated. |
|
|
What is a characteristic unique to heart muscle cells?
|
Each cell is branched.
|
|
|
Name 6 of the 10 main organ systems found in humans.
|
1. Respiratory
2. Circulatory 3. Digestive 4. Excretory 5. Neural 6. Skeletal 7. Endocrine 8. Integidimentary 9. Reproductive 10. Muscular |
|
|
Organize the following terms in the appropriate order.
1.Trachea 2. Nares 3. Alveoli 4. Larynx 5. bronchioles 6. pharynx 7. glottis |
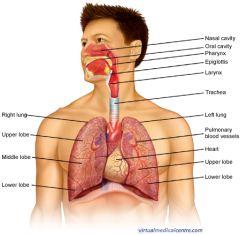
2. Nares
6. Pharynx 7. Glottis 4. Larynx 1. Trachea 5. Bronchioles 3. Alveoli |
|
|
The set of muscles that separate the abdominal cavity from the thoratic cavity is known as what?
|
The diaphragm
|
|
|
The mammalian four chambered heart is composed of two ___ and two ____.
|
The mammalian four chambered heart is composed of two ATRIA and two VENTRICLES.
Atria --> Atrium Atrium means entrance, like the atrium of a building. Blood always enters in the atria. |
|
|
The esophagus is part of which organ system?
|
The digestive system.
Pharynx -> Esophagus -> stomach |
|
|
Starting from the bronchioles, what is the flow of blood through the mammalian circulatory system?
|
Pulmonary vein -> left atrium -> left ventricle -> aorta -> Right atrium -> Right ventricle -> pulmonary artery
|
|
|
Order these
1. Urinary bladder 2. ureters 3. urethra |
2. ureters 1. urinary bladder 3. urethra
|
|
|
Name the two elements of a name in biology's binominal nomenclature system.
|
1 Genus 2. Species
|
|
|
The two domains of prokaryotes are known as what?
|
Bacteria and archea.
|
|
|
Bacterial cells walls are composed of which two types of molecules?
|
Bacterial cell walls are composed of peptidoglycans embedded in polypetides.
|
|
|
What colour might we expect to find a Gram-positive bacteria stained as?
Why? |
Purple. The purple crystals in the Gram stain remains stuck in bacteria with thicker cell walls.
|
|
|
The ability for bacteria to move towards or away from a stimulus is known as what?
What if the stimulus is of chemical nature? |
Taxis.
Chemotaxis. |
|
|
Name two characteristics of cyanobacteria.
|
They are photoautrophic, form filaments, and some fix nitrogen from the environment.
|
|
|
Diatoms are bacteria or eukaryotes?
|
They are eukaryotic
|
|
|
The two divisions in a diatom's silica skeleton are known as what?
|
Epitheca and hypotheca.
|
|
|
What is the organism responsible for PSP (paralytic shellfish poisoning)
|
Dinoflagellates.
|
|
|
Does brown algae have chloroplasts present in its cells?
|
~Yes~
|
|
|
What colour is the algae found in the kingdom rhodophyta? Where can these be found?
|
Red. They can be found in deep oceans.
Rhodo- means rose. |
|
|
Chlorophyta algae are usually which colour?
|
Green.
|
|
|
Unicellular organism with pseudopodias are known as what?
|
Amoebas.
|
|
|
Name two characteristic typical of parameciums.
|
They ingest food via the gullet and they have two nuclei.
A diploid macronucleus and a haploid micronucleus. |
|
|
Explain the process of conjugation in parameciums.
What purpose does this serve? |
It is the process of two cells exchanging their haploid micronuclei.
It provides genetic diversity. |
|
|
A special photorecptor is present in euglena.
What is it called? where is it located? |
The stigma, or eyespot. It is located near the flagella. It serves the purpose of taking the cell towards or away from light.
|
|
|
Fungal cell walls are made out of the same stuff as the exoskeletons of arthropods.
What is this stuff called? |
Chitin.
|
|
|
Fungi are made of mycelium, which are networks of _______.
|
Hyphae
|
|
|
Sometimes fungi have separations in their hyphae.
What is this called? |
A septa.
|
|
|
Ascomycota can reproduce asexually by producing spores called ______ found at the ends of specialized hyphae called ______.
|
Ascomycota can reproduce asexually by producing spores called CONIDIA found at the ends of specialized hyphae called CONODIOPHORES.
|
|
|
The sac like structure containing the sexual spores in ascomycota are called _____ and are found on fruiting bodies called _____.
|
The sac like structures containing the sexual spores in ascomycota are called ASCI and are found on fruiting bodies called ASCOCARPS.
|
|
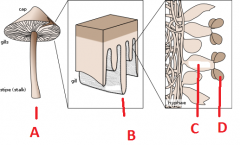
Name these structures using the following terms.
1. Basidium 2. Basidiospore 3. Basidiocarp 4. Basidia |
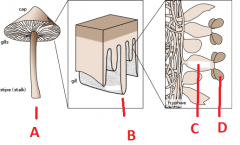
A 1. Basidium
B 3. Basidiocarp C 4. Basidia D 2. Basidiospore |
|
|
There is a type of unicellular fungi.
What is it known as? What is its mean of reproduction? |
Yeast.
Asexually -Binary and budding. Sexually - mating and meiosis |
|
|
The mutual endosymbiont involving fungus and green algea is known as what?
|
Lichen
|
|
|
Are animals:
1. Chemotrophs 2. Photoautotrophs 3. Homotrophs 4. Heterotrophs |

4. Heterotrophs.
They obtain organic nutrients form their environment |
|
|
Are there unicellular animals?
|
No all animals are multicellular
|
|
|
How can we easily differentiate animal cells from plant cells?
|
The lack of a cell wall
|
|
|
After an egg is fertilized with a sperm, a zygote is formed.
The zygote then develops into a spherical _____ which folds into itself to become a ______. Grastulla / Blastulla. |
The zygote then develops into a spherical BLASTULLA which folds into itself to become a GASTRULA.
|
|
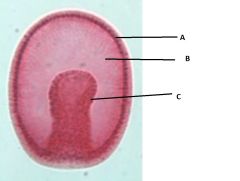
Here is a gastrula.
Label it appropriatly. 1. Mesoderm 2. Endoderm 3. Ectoderm |
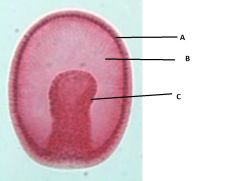
1. Ectoderm
2. Mesoderm 3. Endoderm |
|
|
Some animals have true body cavities 1., some have false cavities 2., and some have no cavity 3.
What are they called? 1. 2. 3. Pseudocoelomates / coelomates / Acocoelomates |
1. Coelomates
2. Pseudocoelomates 3. Acoleomates |
|
|
Two tissues are unique to animals.
Which are they? |
Nervous tissue and muscle tissue.
|
|
|
What is the difference in the arrangement in the nervous tissue in radial animals and in bilateral animals?
|
Bilateral animals have a centralized nervous system.
Radial animal have non-centralized nervous systems. |
|
|
What does sessile mean?
|
It means that it does not move on its own.
|
|
|
There are two types of digestive systems. What are they called, and what are their characteristics?
|
Incomplete digestive system - mouth and anus are the same hole
Complete digestive system - mouth and anus have their own holes. |
|
|
There are two types of complete digestive systems.
What are they known as, and what are their characteristics? |
Undifferentiated digestive system- a simple alimentary canal through which food passes.
Differentiated digestive systems - have specialized organs within it's passage. Porifera have no digestive system. |
|
|
What types of circulatory systems do mammals, ants, and sponges have?
|
Mammals - closed circulatory system
Ants - open circulatory system Sponges- have no circulatory system |
|
|
The system important for osmoregulation and and the removal of certain waste products is known as what?
|
The excretory system.
|
|
|
What type of excretory system do insects have?
1. Nephridia 2. Metanephridia 3. Protonephridia 4. Malphigian Tubules |
Insects have malphigian tubules.
|
|
|
Give an example of an appendage found in the animal kingdom.
|
A leg, wing, tentacle, fin, etc.
|
|
|
Porifera (sponges) are suspension feeders.
What does this mean? |
It means they get their food from particles 'suspended', or floating in water.
|
|
|
Sponges feed by pulling water into their _____ and ejecting it out of their ____.
|
Sponges feed by pulling water into their SPONGOCOEL and ejecting it out of their OSCULUM.
|
|
|
Sponges pull in food particles using flagellated collar cells named ____.
a) Chondrocyte b) Choanocyte c) Ameobocytes d) Cnidocytes |
Sponges pull in food particles using flagellated collar cells named CHOANOCYTES.
|
|
|
Sponges are made of a gelatinous matrix called _____1. within this matrix are____2. cells which aid in digestion.
a) scollex b) mesohyl c) geloderm d) ameobocytes e) echinocytes |
Sponges are made of a gelatinous matrix called MESOHYL 1. within this matrix are AMEOBOCYTES, cells which aid in digestion.
|
|
|
Cnidarians come in two forms. What are they?
|
Polyp \|/ and medusa /|\
|
|
|
A key feature of cnidarians is a specialized cell that aids in defense and attack. They are the cells that cause the "stinging" of jellyfish.
What are these called? 1. Namatocytes 2. Phagocytes 3. Stingatocytes 4. Cnidocytes |
4. Cnidocytes
|
|
|
Which of these is not a class of the cnidarian phylum?
1. Hydrozoan 2. Anthozoan 3. Cubozoan 4. Scyphozoan |
None. They are all classes of the cnidarian phylum.
|
|
|
Cnidocytes are special cells found in animals of the cnidarian phylum. They have a special organelle that ejects a stinging thread into preys and predators.
What are these known as? 1. Nematocysts 2. Scyphocysts 3. Heterocysts 4. Echinocysts |
1. Nematocysts
|
|
|
Hydrozoans, a cnidaria, can be found as which shapes in nature?
|
They can be found as both polyp and medusa shapes.
|
|
|
Give an example of an echinoderm.
What sort of symmetry do they exhibit as adults? As youth? |
Sea stars.
The are radially symmetrical as adults and bilaterally symmetrical as larvae. |
|
|
A special system allows echinoderms to move about. What is it know as?
|
A water vascular system.
|
|
|
What are the structures bellow the arms of echinoderms that are resonsible for locomotion?
1. Muscular feet 2. Locomotor Appedanges 3. Microtubules 4. Tube feet |
4. tube feet
They are moved by the water vascular system. |
|
|
Sea daisies, a recently discovered class of echinoderm live on what type of surface?
|
Sea diaisies live on submerged wood.
|
|
|
Chordates are:
1. Coleomates 2. pseudocoleomates 3. Acoleomates |
1. Coleomates
|
|
|
Tunicates belong to which phyla?
1. Echinoderms 2. Cnidaria 3. Chordata 4. Porifera |
3. Chordata
|
|
|
Name two important groups of parasitic platyhelminthes.
|
Tapeworms and trematodes.
|
|
|
Trematodes, a parasitic platyhelminthes, have a very interesting ability. What is it?
|
They can produce proteins that mimic their hosts and use it to manipulate the hosts immune system.
|
|
|
Where do tapeworms live? How do they remain here?
|
Tapeworms live in the intestines of vertebrates, and they remain attached there thanks to the scolex, a sctructure containing hooks and suckers.
|
|
|
Tapeworms have organs called proglottids.
What does it contain? |
Proglottids contains the tapeworms sex organs.
|
|
|
Give 3 elements that are typical of molluscs.
|
1. Muscular foot
2. Visceral mass 3. Mantle |
|
|
What is a radulla?
|
It is a teeth-like structure found in many molluscs which they use for feeding.
|
|
|
Chitons are plated molluscs that feed on algae using their radulla. What class of mollusc are they in?
|
Polyplacophora.
|
|
|
What is the most distinctive feature gastropods?
|
Torsion. Torsion is what causes gastropods anus and mantle to end up above their head.
Torsion means twisting. |
|
|
Cepha- meaning head and -pod meaning feet make up the word cephalopod.
Give an example of a cephalopod. |
A squid.
|
|
|
Give three important characteristics of cephalopods.
|
1. Closed circulatory system
2. modified muscular foot worms tentacles 3. beak-like mouths at the center of their tentacles 4. complex brains 5. bilateral symmetry 6. well developed sensory organs |
|
|
An animal with a shell divided into two halves that is drawn together by muscles is known as a what?
|
Bivalve.
|
|
|
What is an annelid?
|
An annelid an organisms whose body is composed of fused rings.
|
|
|
Annelids are
1. Coleomates 2. Pseudocoleomates 3. Acoleomates |
Coleomates
|
|
|
University student require a special type of substance to study all night long.
What is this substance known as? |
It is known as coffee.
|
|
|
Annelids are divided into two groups.
What are these groups? |
Polychaetes - Have parapodias
Oligochaetes - earthworms and leeches |
|
|
Leeches produce a special chemical that prevents the blood from coagulating. It is known as:
1. Hirudin 2. Chitin 3. Syphonin 4. Super saiyan |
1. Hirudin
|
|
|
What is the key feature of polychaetes?
What purpose does this server? |
They have paddle-like parapodia that aids in locomotion and serves as gills.
|
|
|
How do earthworms eat?
|
Soil travels through the alimentary canal and they get their nutrition from this.
|
|
|
How do olichaetes reproduce?
|
Though they are hermaphrodites, they do crossbreed and some may reproduce via segmentation.
|
|
|
Two out of every three known animal is an _____.
|
Two out of every three known animal is an ARTHROPOD.
|
|

What is this called?
|

This is a cat.
|
|
|
Ecdysozoans are covered in a thick coat known as a what?
|
A cuticle
|
|
|
The cuticle of ecdysozoans is molted or shed through a process know as___?
1. Ecdytomorphism 2. Ecdysis 3. Cuticlulation 4. Ecdysozoan cuticle cycle |
2. Ecdysis
|
|
|
Where can nematodes be found?
|
In aquatic and moist environments.
|
|
|
The arthropod body plan consists of what?
|
A hard exoskeleton, jointed appendages, and a segmented body.
|
|
|
What material is the exoskeleton of arthropods made of?
It is the same material that makes up the walls of mycelium. |
Chitin.
|
|
|
What type of circulatory system do arthropods have?
|
They have an open circulatory system.
|
|
|
What is the type of arthropod that can be found mostly in aquatic environments?
|

Crustacea
|
|
|
Millipedes and centipedes are part of which group of arthropods?
|
Myriapods.
Myria- means many |
|
|
Millipedes have ___ pair(s) of appendages per trunk segment and eat ___.
|
Millipedes have 2 pair(s) of appendages per trunk segment and eat decaying wood and leaves.
|
|
|
Centipedes have ___ pair(s) of appendages per trunk segment and eat ___.
|
Centipedes have 1 pair(s) of appendages per trunk segment are carnivorous.
|
|
|
Myriapedes have jaw-like ______ and are terrestial.
1. Beaks 2. Gullets 3. Mandibles 4. Radula |
Myriapedes have jaw-like MANDIBLES and are terrestial.
|
|
|
What is a key characteristic responsible for the success of hexapods?
|
Flight!
|
|
|
What distinguishes insects with complete metamorphis?
|

They begin their lives as larvae, grub, or caterpillars
but look completely different as adults. |
|
|
While larger crustacean exchange gas via gills, smaller crustacean exchange gas via ____.
|
While larger crustacean exchange gas via gills, smaller crustacean exchange gas via THE CUTICLE.
|
|
|
What are the four key characteristics of chordates? (You should really know this one)
|
1. Notochord
2. Pharyngeal slits 3. Dorsal, hollow nerve cord 4. Muscular post-anal tail |
|
|
A long, flexible rod between the digestive tract and the nerve cord in chordates is known as a ____.
|
Notochord
|
|
|
A plate of ectoderm develops into a cord dorsal to the notocord in certain chordates. This cord is important for relaying signals throughout the organism's body.
What is this called? |
Dorsal, Hollow Nerve Cord
|
|
|
Chordates can be divided into 3 subphyla.
What are they!? |
Tunicates
Lancelets And Vertabrates |
|
|
Okay so Tunicates only ressemble chordates for the first few minutes of their life. But it doesn't change that they are chordates. ok?
They have this special organ that they use for drawing in water to feed on suspended particles and also for defending against predators. What is this organ called? |
It's called a syphon, ok?
|
|
|
There's a type of chordate that looks like little like little knives. What are these called?
|
Lancelets.
|
|
|
Chordates with heads.
What are they called? |
Craniates.
|
|
|
Craniates share certain features.
Name some. (They are all related to features of the head) |
Eyes.
A skull. And other sensory organs. |
|
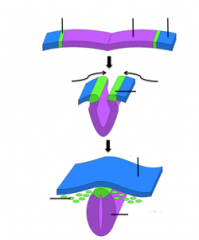
What is a feature unique to craniates?
It develops into many important features such as the bones and cartilage of the skull |
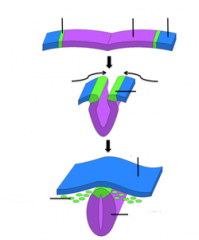
The neural crest
|
|
|
Chordates with a backbone are known as:
|
Vertebrates
|
|
|
Aquatic vertbrates differ from non-vertabrate fishies in what way?
|
They have rays in their fins.
|
|
|
What living class of animals represent the oldest vertebrates?
|

Lampreys.
They have no jaws. Still are scary though |
|
|
Poikiloderm!
What does this mean? |
Body temperature is same as outside.
|
|
|
Vertebrates with jaws are known as:
1. Gnathostomes 2. Jawthostomes 3. Tetrapods 4. Craniates |
Gnathostomes
Jaws are for gnawing. |
|
|
Chondrichthyans.
Give an example of an animal in this group. What is their skeleton mostly made of? |
Sharks.
Mostly made of cartilage. |
|
|
The hole out of which waste and reproduction happens in chrondrichthyans is called what?
(Birds also have this) |
Cloaca
|
|
|
There are 3 ways that animals give birth to other animals.
What are they and what differs them? |
Oviparous - lay eggs outside
Viviparous - give birth like humans Ovoviviparous - lay eggs internally |
|
|
What is a key characteristic of aquatic osteichthyans?
|
The presence of a swim bladder.
|
|
|
Tetrapods.
What are they? |
Chordates with limbs.
|
|
|
Order these in terms of the appearance in the chain of evolution.
Craniates, gnathostomes, tetrapods, vertebrates, amniotes. |
Vertebrates, Craniates, Gnathostomes, Tetrapods, amniotes
|
|
|
Tetrapods have some specific adaptations.
Name 2 |
1. Four limbs with digits
2. A neck 3. Absence of gills 4. Ears |
|
|
Tiktalik.
What was this? |
Theoretically, the first tetrapod-like creature.
|
|
|
What are tetrapods that have adapted to give birth on land?
|
Amniotes.
|
|
|
Give 2 examples of amniotes.
|
birds
reptiles mammals |
|
|
Why are amphibians called amphibians?
|
Amphibians means "both ways of life"
They are born in water but are land animals as adults. |
|
|
Where do some amphibians keep their eggs?
|
Back, mouth, stomach.
|
|
|
What is a key characteristic of reptiles?
|
The presence of scales.
|
|
|
What is a key characteristic of turtles?
|
The shell which is fused to their ribs and vertebra
|
|
|
Birds are archosaurs, reptiles.
What are key features of birds? Name 4. |
Scales have evolved into feathers
Lack of a urinary bladder A single ovary teeth are replaced by beaks bones are porous |
|
|
3 defining features of mammals.
|
Large brains.
Hair. Mammary glands. Differentiated teeth. (different types of teeth) |
|
|
There are 3 lineages of mammals.
Can you name them? |
Monotremes (platopus)
Marsupial (With pouches) Eutherians (the rest) |
|
|
The pouch of marsupials is known as what?
(The name ressembles "marsupial") |
Marsupium.
|
|
|
What is the defining factor of euthrenians?
|
They have a complex placenta in which the young complete crucial steps development.
|
|
|
Which primate group are humans a part of?
|

We are apes.
|
|
|
3 key characteristics of primates.
|
Oposable thumbs
Large brain Short jaws complex social behaviour |
|
|
Two key characteristics of humans.
|
Bipedalism
Higher cognitive functioning |
|
|
Small circular fragments of DNA that replicate separately from chromosomes in bacteria are known as...
1. Plasmosomes 2. Plastioles 3. Pseudosomes 4. Plasmids |
4. Plasmids
|
|
|
What is a cloning vector?
1. The chemical used for isolating your DNA fragments 2. The original plasmids before the selected DNA is added 3. The plasmids after the selected DNA has been added 4. An enzyme used to seal DNA bonds between restriction fragments |
2. The original plasmids
|
|
|
A clone carying a gene of interest can be found using a ____.
|
A clone carrying a gene of interest can be found using a NUCLEIC ACID PROBE.
|
|
|
What is a stemcell?
|
It is a nonspecialized cell that can reproduce indefinetly and eventually differentiate into a specialized cell.
|
|
|
What is special about embryonic stem cells?
|
They can differentiate into any cell type.
|
|
|
What purpose does the polymerase chain reaction serve?
|
With it, we can produce many copies of a specific DNA fragment.
|
|
|
PCR - Polymerase Chain Reaction has three important steps to its cycle.
What are they? |
heating, cooling, and replicating
|
|
|
A variation in a DNA sequence is known as a ____.
|
A variation in a DNA sequence is known as a POLYMORPHISM.
|
|
|
What are problems attributed to cloning animals?
|
Many of the clones are unhealthy and exhibit defects.
|
|
|
Anura is part of..?
Give an example of one |
Anura is an amphibian.
And example would be a frog |
|
|
Parapodia belong to?
What does it server? |
Parapodia belongs to polychaetes.
They serve in motility and breathing (gills) |
|
|
Chelicerates are..?
An example of one? A feature typical of them? |
Chelicerates are arthropods.
Horseshoe crabs and spiders would be example. Their pincer-like appendages are typical of them |
|
|
Hexapods are part of...?
Give an example. What is typical of them? |
Part of Arthoropods
A fly. Wings are typical of them. |
|
|
Oligocaetes are part of...?
Give an example. How do they feed? |
They are part of the annelids group.
An earthworm s an oligochaete. Soil travels through their alimentary canal with which their absorb nutrients. |
|
|
Apoda are part of?
Give an example Where do they get their name from? |
Apodas are amphibians
Caecilians (big ugly worm-like creatures) The name A - poda simply means that they have no legs |
|
|
The 4 types of excretory systems are?
|
Protonephridia
Metanephridia Malphigian tubules Nephridia |
|
|
What are chondrichtyans?
They are part of which phylum? Where do they get their name from? |
Sharks and stuff.
Chordates. Chondrichthyans, like in chondrocytes and chondrium, implies that they are cartilaginous beings. |
|
|
Taq polymerase is essential for..?
|
Taq polymerase is essential for the PCR, or polymerase chain reaction.
|
|
|
What are mandibles?
Where are they found? |
Mandibles are jaw-like structures found in myriapods.
|
|
|
What is "Alveoli"?
To which kingdom do they belong? |
Alveoli are sac-like structures found inside the membrane of organism in the alveolata kingdom.
|
|
|
_____ is a chemical used by leeches to prevent blood clotting.
|
hirudin
|
|
|
What are peptidoglycans?
And where are they found? |
Peptidoglycans are sugar polymers and they are found in bacterial cell walls.
|
|
|
What is an operculum?
|
It is a scruture found in osteichthyan fishes that protects the gills.
|
|
|
Chondrichtchyans have a cartilaginous skeleton.
Osteichtchyans have a ____ skeleton. |
Osteichtchyans have a bony skeleton.
|
|
|
Name the 4 families of cnidarians
|
Cubozoan
Scyphozoan Hydrozoan Anthozoan |
|
|
Cnidarians use the organelle called ____ found in ____ cells to eject their stinging threads.
|
The organelles called nematocysts are found in cnidocytes.
|
|
|
What are proglottids?
Give and example of an organism which bares them. |
Tapeworms have proglottids which is the location of their sexual organs.
|
|
|
Give an example of a gastropod.
What is a feature typical of them? |
A slug.
They have torsion. |
|
|
ears are a feature of _____
|
Ears are a feature of tetrapods
|
|
|
Platypus is in which order of mammals?
|
Monotremes.
|
|
|
In sponges, water goes into the ____ and exits out of the ____.
|
Waters enters via the spongocoel and exits via the osculum.
|
|
|
What are eosinophils?
|
Leukocytes.
(White blood cells) |
|
|
Calcium carbonate is a component of which structure found in mollusks?
|
The shell.
|
|
|
What is the matrix of neural tissue?
|
Neuroglia
|
|
|
What is another term for polypeptide?
|
Protein.
|
|
|
Cellulose fibers embedded in polysachrides and polypepitdes is a typical feature of which structure found in some eukaryotic cells?
|
Plant cell walls.
|
|
|
In sponges ___ cells take in nutrients, pass them on to ____ which help digest them, and are fixed in a matrix called ____.
|
In sponges choanocytes cells take in nutrients, pass them on to amoebocytes which help digest them, and are fixed in a matrix called mesohyl.
|

