![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a solvent? What is the most versatile solvent known? |
The dissolving agent of a solution. Water is the most versatile solvent known. |
|
|
What is a molecule? |
Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds. |
|
|
What is a nucleus (what is it a plural of)?
HINT: 2 definitions |
Nucleus is the plural of nuclei, and it is an atoms central core, containing protons and neutrons.
AND
The organelle of a eukaryotic cell that contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes, made of chromatin |
|
|
What is cohesion vs adhesion vs surface tension, and what are all of these properties of (what molecule? |
Cohesion - The sticking together of molecules of the same kind, often by hydrogen bonds.
Adhesion - the attraction between different kinds of molecules
Surface Tension - a measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid.
These are all properties of water (b/c of cohesion, water has high surface tension) |
|
|
Define temperature in terms of atoms |
A measure in degrees of the average thermal energy of the atoms and molecules in a body of matter. |
|
|
What is an atom? |
The simplest unit of matter, that retains properties of an element. |
|
|
What is atomic mass? |
The TOTAL mass of an atom (also called atomic weight). e.g. AMU
It is the weighted average of the elements isotopes. It approximately equals the mass number (b/c that is the one with the largest relative abundance) |
|
|
What is a compound? |
A substance containing two or more elements in a fixed ratio. For example, table salt (NaCl) consists of one atom of the element sodium (Na) for every atom of chlorine (Cl). |
|
|
Define a chemical reaction |
The making and breaking of chemical bonds, leading to changes in the composition of matter. |
|
|
Define population |
A group of individuals belonging to one species and living in the same geographic area. |
|
|
Define biology vs systems biology |
Biology is the scientific study of life
Systems Biology - is an approach to studying biology that aims to model the dynamic behavior of whole biological systems based on a study of the interactions among the systems parts. |
|
|
What is a covalent bond |
A type of STRONG chemical bond in which two atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons |
|
|
What does a pH scale measure, and what is its range
BONUS: what does pH stand for? |
A pH scale measures the acidity of a solution, ranging in value from 0 (most acidic) to 14 (most basic).
BONUS: The letters pH stand for potential hydrogen and refer to the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)
Something that is more acidic increases the hydrogen ion (H+) in a solution |
|
|
Define emergent properties |
New properties that arise with each step upward in the hierarchy of life, owing to the arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases. |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical substance that resists changes in pH by accepting hydrogen ions from or donating hydrogen ions to solutions |
|
|
What is a prokaryotic cell? What domains are these cells found in? |
A type of cell lacking a membrane enclosed nucleus and other membrane enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea |
|
|
Define evolution |
Descent with modification; the idea that living species are descendants of ancestral species that were different from present-day ones; also, the genetic changes in a population from generation to generation. |
|
|
What is the difference between a nonpolar and polar covalent bond |
A nonpolar covalent bond shares electrons EQUALLY.
A polar covlaent bond between atoms that differ in electronegativity. The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it slightly negative, and the other atom slightly positive. |
|
|
Define an ion, cation and anion |
An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has gains or lost one ore more electrons, thus acquiring a charge
Cation- have a positive charge (lost electrons)
Anions - have a negative charge (gained electrons) |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions. |
|
|
What is an aqueous solution? |
A solution in which water is the solvent |
|
|
What is a tissue? |
An integrated group of cells with a common function, structure, or both. |
|
|
Describe a controlled experiment |
An experiment in which an experimental group is compared with a control group that varies only in the factor being tested (e.g. other than IV everything is controlled) |
|
|
Define reactant vs product in a chemical reaction |
A reactant is the starting material in a chemical reaction
A product is the material resulting from a chemical reaction |
|
|
What are the two prokaryotic domains of life? |
1. Bacteria 2. Archaea |
|
|
What is a genome |
The complete set of genetic material in an organism or virus |
|
|
Define community |
An assemblage of all the populations of organisms living close enough together for potential interactions |
|
|
What is a radioactive isotope? |
An isotope whose nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy |
|
|
Define a chemical bond |
An attraction between two atoms resulting from a sharing of outer-shell electrons or the presence of opposite charges on the atoms. The bonded atoms gain complete outer electron shells. |
|
|
What is ocean acidification? |
Decreasing pH of ocean waters due to absorption of excess atmospheric CO2 from the burning of fossil fuels. |
|
|
Define natural selection |
A process in which individuals with certain inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce than are individuals that do not have those traits. |
|
|
Define element |
A substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical means |
|
|
Define hydrogen bond |
A type of weak chemical bond formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of a polar covalent bond in one molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom of a polar covalent bond in another molecule (or in another region of the same molecule). |
|
|
Define electron shell |
A level of electrons at a characteristic average distance from the nucleus of an atom. |
|
|
What is artificial selection vs natural selection |
Artificial Selection - The selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to promote the occurence of desirable traits.
Natural Selection - a process in which individuals with certain inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce than are individuals that do not have those traits. |
|
|
Define molecule |
Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
|
|
|
What is a biosphere |
The entire portion of Earth inhabited by life; the sum of all the planet's ecosystems. |
|
|
Define organelle |
A membrane enclosed structure with a specialized function within a cell. |
|
|
Define an organ |
A specialized structure composed of several different types of tissues that together perform specific functions. |
|
|
Define technology |
The application of scientific knowledge for a specific purpose, often involving industry or commerce but also including uses in basic research. |
|
|
Define heat in terms of energy |
Thermal energy in transfer from one body of matter to another. |
|
|
What is a cell |
The basic unit of living matter separated from its environment by a plasma membrane; the fundamental structural unit of life |
|
|
What is a solution? |
A liquid that is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances |
|
|
What is a base? |
A substance that DECREASES the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration in a solution |
|
|
What is a theory? |
A theory is a widely accepted explanatory idea that is broader ins cope than a hypothesis, generates a new hypotheses and is supported by a large body of evidence |
|
|
What is thermal energy? |
Thermal energy is kinetic energy due to the random motion of atoms and molecules; energy in its most random form. |
|
|
What is a domain and what are the three domains of life? |
A taxonomic category above the kingdom level. The three domains of life are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya |
|
|
What is electronegativity? |
The attraction of a given atom for the electrons of a covalent bond. |
|
|
What is an ecosystem? |
All the organisms in a given area, along with the nonliving (abiotic) factors with which they interact; a biological community and its physical environment. |
|
|
What is evaporative cooling |
The process in which the surface of an object becomes cooler during evaporation |
|
|
Define organ system |
A group of organs that work together in performing vital body functions. |
|
|
Define organism |
An individual living thing, such as bacterium, fungus, protist, plant or animal |
|
|
Define trace element |
An element that is essential for life but required in extremely minute amounts |
|
|
What is Eukarya? |
It is the domain of life that includes all eukaryotic organisms |
|
|
What is a prokaryotic cell? |
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and other membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea |
|
|
What is a hypothesis? |
A testable explanation for a set of observations based on the available data and guided by inductive reasoning |
|
|
What is a eukaryotic cell? |
A type of cell that has a membrane enclosed nucleus and membrane enclosed organelles. All organisms except bacteria and archaea are composed of eukaryotic cells. |
|
|
What is matter? |
Anything that occupies space and has mass |
|
|
Atomic Mass vs Mass Number (define) |
Atomic Number of an element, equates to the number of protons that element has
Atomic Mass of an element is the sum of the proton and neutrons in the atoms nucleus. |
|
|
Whats life's hierarchy of organization? |
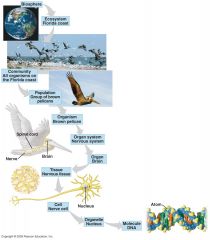
|
|
|
What are the three domains of life, and the 4 kingdoms of one of them? |

|
|
|
Inductive vs deductive reasoning |
Deductive reasoning is a basic form of valid reasoning. Deductive reasoning, or deduction, starts out with a general statement, or hypothesis, and examines the possibilities to reach a specific, logical conclusion. The scientific method uses deduction to test hypotheses and theories.
Inductive reasoning is the opposite of deductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning makes broad generalizations from specific observations. Even if all of the premises are true in a statement, inductive reasoning allows for the conclusion to be false. Here’s an example: "Harold is a grandfather. Harold is bald. Therefore, all grandfathers are bald." The conclusion does not follow logically from the statements. |

