![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Light reaction
|
takes place in photosystems in thylaakoid membrane
generates ATP and increases potential energ of electrons by moving them from H[2]O to NADPH |
|
|
Electrons excitation produces energy
|
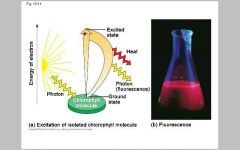
|
|
|
Photosystem
|
reaction-center complex surrounded by light-harvesting complexes
|
|
|
Reaction-Center
|
where primary electron acceptor accepts excited electron from chlorophyll a
|
|
|
Light-Harvesting complexes
|
funnel energy of photons to reaction center
|
|
|
Photosystem II
|
best at absorbing wavelengths of 680nm (functions first)
|
|
|
P680
|
reaction-center chlorophyll a of PSII
|
|
|
Photosystem I
|
best at absorbing wavelength of 700nm
|
|
|
P700
|
reaction-center chlorophyll a of PSI
|
|
|
2 Routes of Electron flow?
|
1. Linear electron flow
2. Cyclic Electron flow |
|
|
Linear electron flow
|
primary pathway that involves both photosystems to produce ATP and NADPH using light energy
|
|
|
Linear Electron Flow Steps
|
(look at set)
|
|
|
Cyclic Electron Flow
|
Only uses PSI and produces only ATP; no NADPH
believed to have evolved before linear electron flow (some organisms only have PSI) |
|
|
Cyclic Electron Flow steps
|
1. electron flow generates surplus ATP, satisfying higher demand in Calvin cycle
picture |
|
|
Chloroplast vs. Mitochondria: Chemiosmosis
|
• Generates ATP from different sources
Mitochondria = food Chloroplasts = light • Proton travel Mitochondria = into intermembrane space and drive ATP synthesis as diffues back into mitcohondrial matrix Chloroplast = into thylakoid space and drives ATP synthesis as the diffuse back into stroma |

