![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Contains cellulose fibrils
|
Cell Wall
Function: Protect and Support |
|
|
Phospholipid Bilayer with embedded proteins
-fluid mosaic |
Plasma Membrane
Function: Defines cell boundary; regulates molecule passage into and out of cells *In animals contains cholesterol |
|
|
Nuclear envelope, nucleoplasm chromatin and nucleoli
"control centre of cell", usually largest organelle |
Nucleus
Function:Storage of genetic info; synthesis of DNA and RNA *DNA-wound=chromosomes -unwound=chromatin *Surrounded by selectively permeable nuclear membrane |
|
|
Concentrated area of chromatin, RNA and proteins
|
Nucleolus:
Function: Ribosomal sub unit formation |
|
|
Series of interconnected, folded membranes, connected to nuclear envelope
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Function: Produces all components of cell membrane -aids in transport of protein & lipids throughout cell |
|
|
Contains cellulose fibrils
|
Cell Wall
Function: Protect and Support |
|
|
Phospholipid Bilayer with embedded proteins
|
Plasma Membrane
Function: Defines cell boundary; regulates molecule passage into and out of cells |
|
|
Nuclear envelope, nucleoplasm chromatin and nucleoli
|
Nucleus
Function:Storage of genetic info; synthesis of DNA and RNA |
|
|
Concentrated area of chromatin, RNA and proteins
|
Nucleolus:
Function: Ribosomal sub unit formation |
|
|
Membranous flattened channels and tubular canals
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Function: Synthesis and/or modification of proteins and other substances, distributed by vesicle formation |
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
Ribosomes
Protein Synthesis Proteins transported in vesicles "Network of folded membranes studded with ribosomes |
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
-No Ribosomes
-Synthesis of various substances for transport depending on cell type -Peroxisomes aid in detox |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
"Post Office"-acts as a transfer station for substances being transported through cell
-Sometimes called "dictycomes" in plants -Vesicles arrive on the ER on one face and leave the golgi on opposite face -stack of membranous saccules |
|
|
Lysosome
|
*only in animal cells*
"Digestive system of cell" -formed by golgi -can break down proteins, fats, carbs, excess call membrane, defective organelles -"suicide sacs" use enzymes to destroy cell -Contains digestive enzymes |
|
|
Vacuole
|
*Usually only in plant cells*
Large fluid filled sacs surrounded by single membrane -Plant:may contain only 1 central vacuole that stores& supports the cell -stores substances, salt, sugar, prot -may aid in motility (micro orgs) by contracting vacuole |
|
|
Peroxisome
|
Surrounded by single membrane
-synthesize bile acids & metabolizes toxic compunds -Liver and kidney contain lots! |
|
|
Mitochondria
|
"Power house"
-Cellular respiration, produce ATP (energy) -Inner membrane (cristae) bounded by an outer membrane. -Double membrane |
|
|
Chloroplast
|
*Plants Only*
-Photosynthesis -Green pigment -Membranous grana bounded by 2 membranes *Plastid* |
|
|
Leucoplast
|
-Storage
-convert glucose to starch -Colorless *Plastid* |
|
|
Chromoplast
|
Color fruits & flower petals
-red, blue, yellow, orange pigments *Plastids* |
|
|
Cytoskeleton
|
Helps cell maintain shape
-aids in movement -framework for organelles to move w/i cell -guides transport vesicles -essential for cell division -Components:Microtubules,Intermediate &Microfilaments |
|
|
Microtubules
|
Thick, hollow, cylindrical tubes
-13 rows of tubulin (protein) |
|
|
Microfilaments (Actin)
|
-thin, can assemble and disassemble
-in muscle cells, interact with myosin to contract muscles |
|
|
Intermediate Filaments
|
-medium sized, between actin and microtubules
-keratin in epithelial cells -desmin in muscle -neurofilaments in axins *Prom in cells subject to mechanical stress |
|
|
Cilia & flagella
|
-Movement of cell
-9+2 pattern of microtubules |
|
|
Centriole
|
*Animal cells only*
-Important in cell division -made up of 9 microtubule "triplets" -Found in pairs |
|
|
Prokaryotic
|
*No nucleus*
+ cell membrane -no complex organelles -small -DNA/RNA floats freely in cell -cell division by binary fission |
|
|
Eukaryotic
|
*Plant and animal cells*
+nucleus +cell membrane +complex organelles -larger and more complex -DNA/RNA contained in nucleus -cell division by mitosis |
|
|
Has Plastids (Chloroplasts, leucoplasts, chromoplasts)
|
Plant
|
|
|
No centrioles. Have Phragmoplasts to aid in cell division
|
Plant
|
|
|
Has Centrioles to aid in cell division
|
Animal
|
|
|
Surrounded by rigid cell wall
|
Plant
|
|
|
No cell wall
|
Animal
|
|
|
Larger vacuoles
|
Plant
|
|
|
Smaller or no vacuoles
|
Animal
|
|
|
Lysosomal enzymes contained in central vacuole
|
Plant
|
|
|
Have Lysosomes
|
Animal
|
|
|
Larger vacuoles
|
Plant
|
|
|
Smaller or no vacuoles
|
Animal
|
|
|
Lysosomal enzymes contained in central vacuole
|
Plant
|
|
|
Have Lysosomes
|
Animal
|
|
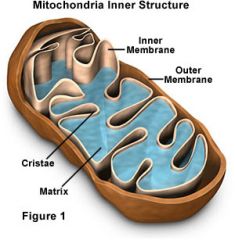
|
Cristae
Matrix Outer membrane Inner membrane "Double membrane" |
|
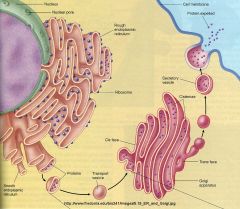
|
Golgi
|
|
|
DNA
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid
|
|
|
RNA
|
ribonucleic acid
|
|
|
3 Types of protein components that make up cytoskeleton
|
Actin filaments
Intermediate filaments Microtubules |
|
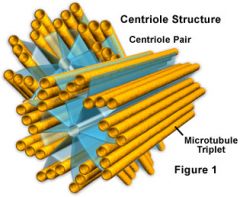
|
Centrioles
|
|
|
Endomembrane system
|
Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes and transport vesicles
|
|
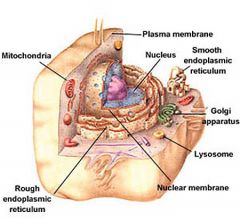
|
Animal cell
|
|
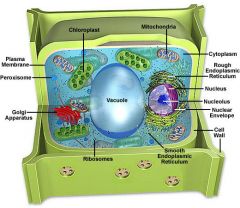
|
Plant cell
|

