![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the equation for ΔG?
|
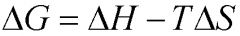
|
|
|
What are the "biochemist's" standard state concentrations of [H+], [H2O], and [Mg2+]?
|
[H+] = 10 ^ -7 M (or pH = 7)
[H2O] = 55.5 M [Mg2+] = 1 mM |
|
|
What is the "standard transformed free energy change"?
|
It's ΔG'°, or the transformed ΔG° for use in biochemistry with the adjusted standard states for concentrations of H+, H2O and Mg2+.
|
|
|
Why aren't [H+], [H2O] or [Mg2+] included in reactant or product equilibrium formulas?
|
it's a convention to include them in the calculation of K'eq.
|
|
|
What's the relationship between the standard free energy change and equilibrium constant?
|
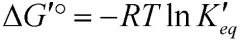
|
|
|
What is the equation relating the equilibrium constant to molar concentrations and stoichiometric proportions?
|
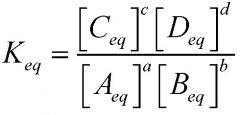
Notice that the concentrations are the EQUILIBRIUM concentrations.
|
|
|
What's the relationship between ΔG and ΔG'°?
|
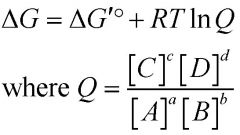
|
|
|
Why is it said the enzymes affect the rates of reactions rather than the thermodynamic constants (equilibrium, free energy change, etc)?
|
Enzymes lower the activation energy of a particular reaction, which is kinetic related. The change in free energy from reactants to products doesn't change, just the energy wall to get there, therefore making it easier for the reaction to proceed quickly.
|
|
|
By combining reactions, ΔG is additive, what is K'eq?
|
Multiplicative.
|

