![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why measure biodiversity? |
Enables comparisons to be made:
Between different areas In the same area at different times |
|
|
Biodiversity |
The variety of living organisms in an are |
|
|
Species |
A group of similar organisms able to reproduce to give fertile offspring |
|
|
Genetic Biodiversity |
The variation of alleles within a species |
|
|
Species richness |
Is the number of different species in an area |
|
|
Species evenness |
The measure of the relative abundance of each species in an area |
|
|
How is diversity measured? |
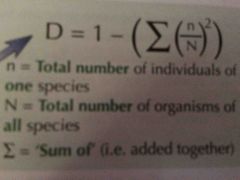
Simpson's index of biodiversity |
|
|
Factors affecting Global Biodiversity |
1)Human Population Growth 2)Increased use of Monoculture in Agriculture 3)Climate change |
|
|
Climate change |
The variation of the earth's climate |
|
|
Rio Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) |
Aims to develop international strategies on the conservation of biodiversity
1) How to use animal and plant resources in sustainable way 2) made it international law that conserving biodiversity is everyone's responsibility 3) Provides guidance to governments on how to conserve biodiversity |
|
|
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) |
An agreement designed to increase international cooperation in regulating trade in wild animal and plant specimens.
1) Making it illegal to kill endangered species 2) Limiting trade through licensing and making it illegal to trade 3) Raise awareness of threats to biodiversity-education
|

