![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Electron carries of the respiratory chain are located where? |
Mitochondrial inner membrane |
|
|
Electron flow through the respiratory chain drives what? |
H+ transport out of the matrix |
|
|
ATP synthase is activated by what? |
H+ concentration gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane |
|
|
Where does the respiratory chain and ATP synthase occur? |
In the inner membrane of the mitochondria |
|
|
In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from NADH and FADH2 are used to do what? |
To reduce molecular oxygen to water |
|
|
The electron-transfer potential of NADH or FADH2 is converted into what? |
The phosphoryl-transfer potential of ATP |
|
|
Is NADH a strong or weak reducing agent? Does it have a positive or negative reduction potential? |
NADH is a STRONG reducing agent (wants to DONATE electrons) and it has a NEGATIVE reduction potential |
|
|
Is O2 a strong or weak oxidizing agent? Does it have positive or negative reduction potential? |
O2 is a STRONG oxidizing agent (wants to ACCEPT electrons) and it has a POSITIVE reduction potential. |
|
|
What is an oxidant (oxidizing agent)? |
An acceptor of electrons in a redox reaction |
|
|
What is a reductant (reducing agent)? |
A donator of electrons in an redox reaction |
|
|
What is DeltaE'o? |
Change in reduction potential (reduction minus oxidation) |
|
|
What is Coenzyme Q? |
CoQ is a hydrophobic molecule that shuttles protons and electrons about the inner mitochondrial membrane. |
|
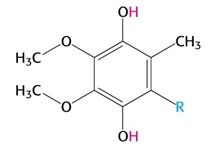
|
Reduced form of CoQ (QH2) |
|
|
ATP synthesis requires what uptake? |
H+ uptake |
|
|
Electrons are transferred from NADH to O2 through a chain of what 3 protein complexes? |
1. NADH-Q oxidoreductase 2. Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase 3. Cytochrome c oxidase |
|
|
Electron flow within NADH-Q oxidoreductase, Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase, and Cytochrome c oxidase leads to what? |
To the transport of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane |
|
|
Electrons from FADH2 enter the electron-transport chain where? |
At the Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase |
|
|
What is the purpose of Succinate-Q Reductase? |
Protein complex that contains succinate dehydrogenase that generates FADH2 in the citric acid cycle. |
|
|
Of the four protein complexes in the electron-transport chain, which do not transport protons? |
Succinate-Q Reductase |
|
|
Of the four protein complexes in the electron transport chain, which are proton pumps? |
1. NADH-Q oxidoreductase 2. Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase 3. Cytochrome c oxidase |
|
|
The high-potential electrons of NADH enter the respiratory chain where? |
At the NADH-Q oxidoreductase (complex I) |
|
|
What are the 7 basic components of the electron transport chain? |
1. NADH 2.NADH-Q Oxidoreductase 3. Q (Coenzyme Q) 4. Q-Cytochrome c oxidoreductase 5. Cyt c 6. Cytochrome c oxidase 7. O2 |
|
|
In the electron-transport chain, the electron transfer steps are in order of what? |
Reduction potential, i.e., electron affinity of the components INCREASES as electrons move down the chain. |
|
|
The flow of 2 electrons from NADH to CoQ through NADH-Q oxidoreductase leads to what? |
To the pumping of FOUR hydrogen ions out of the matrix of mitochondrion. |
|
|
What is the function of Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase? |
Catalyze the transfer of electrons from QH2 produced by NADH-Q oxidoreductase and the succinate-Q reductase complex to oxidized cytochrome c |
|
|
How many protons are pumped out of the matrix per NADH? |
10 |
|
|
NADH-Q Oxidoreductase pumps out of the matrix how many protons? |
4
|
|
|
Q-Cytochrome c oxidoreductase pumps out of the matrix how many protons? |
4 |
|
|
Cytochrome c oxidase pumps out of the matrix how many protons? |
2 |
|
|
How does Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase pump out 4 H+ but only take in 2+? |
The 2 extra H+ that are being released are from QH2 in the membrane |
|
|
How does cytochrome c oxidase pump out 2 H+ even though it takes in 4 H+? |
Because 2 H+ go to 1/2O2 to form water in the membrane |
|
|
How many protons are pumped out of the matrix per FADH2? |
6 |
|
|
The inner mitochondrial membrane has low permeability for H+ except for what? |
ATP synthase |
|
|
What is the Proton-Motive Force? |
The energy-rich, unequal distribution of protons between the matrix and cytoplasm of a mitochondrion. |
|
|
The electron transport chain and ATP synthase are biochemically separate systems linked by what? |
Proton-motive force |
|
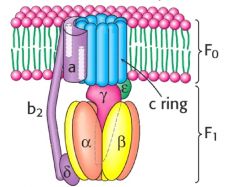
Label each part |
a = proton channel b2 = stator c ring = proton rotor gamma = cam shaft Beta = ATP synthesis site |
|
|
The F1 subunit of ATP sythase is composed of how many alpha and beta subunits? |
3 alpha 3 beta (active sites) |
|
|
What drives the ATP synthase motor? |
H+ |
|
|
ATP synthase catalyzes what? |
The formation of ATP from ADP and orthophosphate (HPO4-2) |
|
|
The moving unit, or rotor, of ATP synthase consists of what? |
C ring, and the gamma-epsilon stalk |
|
|
The stationary unit, or stator, of ATP synthase consists of what? |
Everything EXCEPT the c ring and the gamma-epsilon stalk |
|
|
What are the 3 steps of the beta subunit in the process of ATP synthesis? |
1. Trapping of ADP and Pi 2. ATP synthesis 3. ATP release and ADP and Pi building |
|
|
At any given moment, one of the three beta subunits will be in what 3 conformations? |
1. L - loose (ADP and Pi binding) 2. T - tight (ATP synthesis) 3. O - open (ATP release) |
|
|
What drives ATP synthesis in ATP synthase? |
The rotation of the gamma cam shaft |
|
|
The gamma cam shaft rotates how many degrees and in what direction? |
120 degrees counter clock wise |
|
|
Transport of ATP from mitochrondria to cytosol in exchange for ADP and pi costs what? |
1 H+ |
|
|
Cytosolic NADH from glycolsis can do what? |
Can enter the mitochondrial electron-transport chain by reducing dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glycerol 3-phosphate via glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
|
|
Glycerol 3-phosphate goes on to do what in the glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle? |
It is reoxidized to dihydroxyacetone phosphate on the inner mitochondrial membrane and its electrons go to FAD to form FADH2 which enters the respiratory chain as QH2. |
|
|
When cytoplasmic NADH transported by the glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle is oxidized by the respiratory chain, how many ATP are formed? Why? |
1.5 instead of 2.5 because the electrons from NADH are carried to the respiratory chain via FAD against its concentration gradient hence uses 1 ATP |
|
|
How many H+ are needed to make 1 ATP? |
3 H+ are needed to turn gamma 1/3 to make 1 ATP |
|
|
What is the yield of ATP from NADH? |
10 H+ pumped out/4 return per ATP made = 2.5 ATP made per NADH |
|
|
What is the yield of ATP from FADH2? |
6 H+ pumped out/4 return per ATP made = 1.5 ATP made per FADH2 |
|
|
The complete oxidation of glucose yields how many molecules of ATP? |
30! |
|
|
What is the net yield of ATP from glycolysis? |
2 ATP |
|
|
What is the net yield of ATP from the citric acid cycle? |
2 ATP |
|
|
What is the net yield of ATP from oxidative phosphorylation? |
26 ATP |
|
|
2 NADH are formed in glycolysis. Assuming what, how many ATPs are formed? |
Assuming transport of NADH by the glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle, 1.5 ATP are formed per NADH |
|
|
2 NADH are formed in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate. How many ATP molecules are formed? |
2 NADH forms 5 ATP |
|
|
2 FADH2 formed in the citric acid cycle yields how much ATP? |
3 ATP |
|
|
6 NADH formed in the citric acid cycle yield how much ATP? |
15 ATP |
|
|
Electrons do not usually flow through the electron-transport chain to O2 unless what is true? |
Unless ADP is simultaneously phosphorylated to ATP |
|
|
The level of ADP determines what? |
The rate of oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
If [ADP] is high, what happens to oxidative phosphorylation? |
Oxidative phosphorylation increases |
|
|
At rest, low concentrations of ADP, means what for NADH and FADH2 produced by the citric acid cycle? |
They are not oxidized back into NAD+ and FAD by the electron-transport chain and thus the citric acid cycle SLOWS. |
|
|
Some organisms possess the ability to do what? |
Uncouple oxidative phosphorylation from ATP synthesis to generate heat! |
|
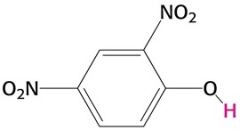
What does it do? |
2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an uncoupler that is TOXIC to eat and inhibits ATP sythesis.
|
|
|
What is uncoupling protein 1? |
Uncoupling protein that generates heat by permitting the influx of protons into the mitochondria without the ATP synthesis. |

