![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nuclesome
|
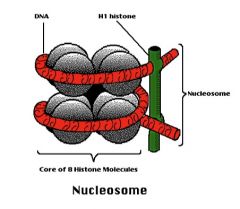
histone octamer and ~150 DNA base pairs + H1 bundled at the side to maintain stability and bind bundles together
|
|
|
Histone
|
- acts as a docking/coiling site for the DNA
- rich in positively charged amino acids (lysine and arginine) |
|
|
Histone Modification
|
Enzymes can act on histone to alter Histones
- acetylation - most important, acts on histone tails - methylation - ubuiquination - phosphorylation |
|
|
Histone Acetyltransferase (HAT)
|
Histone acetylation acts on histone tails, bonds to them and makes them slightly more negative which in turn opens up nucleosome to allow DNA to be accessible for transcription
|
|
|
Histone deacetyltransferase (HAT)
|
subtracts acetyl group from histone tails, makes the nucleosome tighter and more compact
|
|
|
Ploidy
|
The number of sets of chromosomes in a biological cell
|
|
|
Diploid
|
Two complete sets of chromosomes in every somatic cell (not sex cell)
|
|
|
Centromere
|
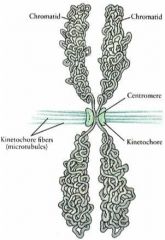
Constricted region of chromosome that links the sister chromatids
|
|
|
Kinetochore
|
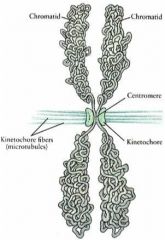
Tightly packed region where spindle fibers attach on chromosome
|
|
|
Metacentric
Subcentric Acrocentric |

|
|
|
Genetic location
|
Use of 3 key features to identify chromosome recognition
- size tells you which chromosome it is - arm P - petite, Q -long - position - banding pattern can give types of disease and location on the chromosome |
|
|
Telomere
|
repeated elements of heterochromatin DNA sequence placed at the ends of chromosomes. The sequence is repeated thousands of times to protect from recombination, degradation, and fusing with other chromatids.
Sequence IS: 5' - TTAGGG - 3' |
|
|
End of replication problem
|
Where RNA primer was on DNA chain during replicaiton there is no -OH to add onto so space is left empty => Enter telomerase
|
|
|
Telomerase
|
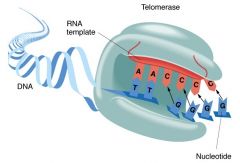
Ribonucleoprotein that uses its own RNA template to extend the 3' end of DNA to fill in the gap left behind by RNA primer. Uses repeat after repeat after repeat 5' - TTAGGG - 3'
|
|
|
Senescence
|
If a cell goes through to many cellular divisions it will eventually reach its limit of division (Hayflick limit) and the cell will shut off - it does not respond to its environment and basically experiences cell death. Referred to as biological aging. Telomerase is said to be turned on in cancer cells, effectively allowing for the continuation of cellular replication.
|

