![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
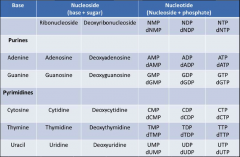
Nucleoside
|
base + sugar
|
|
|
Nucleotide
|
Nucleoside (base+sugar) + phosphate group
|
|
|
Nucleoside and Nucleotide
|
|
|
|
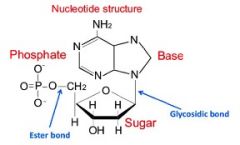
Nucleotide Structure
|
|
|
|
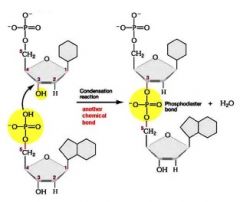
Phospho diester bond requires energy, derived from cleaving other two phosphate groups off
New nucleotides always added at 3' end! |
|
|
|
Base stacking
|
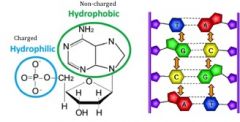
Hydrophobic interactions between adjacent bases in a single nucleic acid strand - hydrophilic pushed to outside and hydrophobic stays on inside
|
|
|
DNA structure - Complementarity
|
2 strands that run anti-parallel to each other, held together by hydrogen bonds between bases on opposite chains - creates a minor and major groove in the structure. Major groove is where most interactions take place
|
|
|
Structurally relevant forms of DNA
|
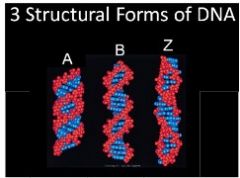
A and B turn to the right – B happens in Nature
Z turns to the left and only occurs in lab |
|
|
Organizational structure of DNA
|
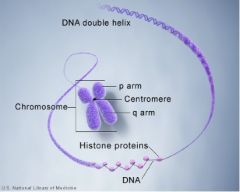
DNA strands wrap around histones => histones bind closely together => make up chromosome
|
|
|
Cell Cycle G1 Phase
|
Biosynthetic activities are at a high rate
Synthesis of millions of proteins required in S-Phase for DNA replication |
|
|
Cell Cycle S Phase
|
DNA replication phase, ends when DNA has "effectively doubled"
Fastest phase of the cell cycle |
|
|
Cell Cycle G2 Phase
|
Synthesis of millions of proteins required in mitosis
Creation of microtubules and centrosomes necessary for mitosis |
|
|
Cell Cycle Mitosis phase
|
cell separates chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets in two nuclei - the daughter cells
|
|
|
Cell cycle regulation - Cyclins
|
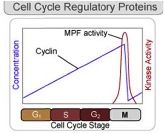
Cyclins - proteins that control cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) enzymes (Cdk stay at constant level)
Cyclins build up to certain points before moving cell cycle to next phase |
|
|
Cell cycle regulation - Cyclin dependent kinases
|
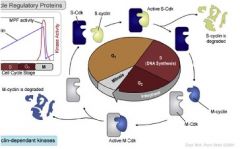
Enzymes that are normally off unless activated by cyclins, they activate other proteins via phosphorylation - continue in cell cycle regulation
|
|
|
Maturation promoting factor
S-phase promoting factor |
Must be bound by cyclins and complex subsequently can activate the machinery to keep the process going
|
|
|
Helicase
|
Hydrolyzes (breaks down with water) H bonds and unwinds DNA - works best in major groove
|
|
|
Topoisomerase
|
Relieves supercoiling/stress ahead of the helicase molecule, cuts through phosphodiester bond
|
|
|
Single Strand Binding Protein (SSBP)
|
- Binds to single strands and protects them from destruction by cell
- Prevents strands from re-annealing - Tells replicating factors where to bind |
|
|
Origin of replication complex
|
multi sub-unit complex that binds chromatin to DNA strand, at origin of replication - necessary for DNA replication to occur
|
|
|
Primase (aka RNA polymerase)
|
adds a 10-15 nucleotide primer to unwound DNA strand, this triggers DNA polymerase to attach and begin DNA synthesis
|
|
|
DNA polymerase alpha (α)
|
Begins synthesizing new DNA
- has low processivity (does not stay bound to DNA well) - needs RNA primer to begin - can only build in the 5'-->3' direction |
|
|
DNA polymerase Delta (δ) and Epsilon (ε)
|
Take over replication after DNA polymerase alpha
- have better processivity due to Proliferating Cell Nuclear Agent (PCNA) |
|
|
Proliferating Cell Nuclear Agent (PCNA)
|
Protein that acts to increase processivity for polymerase delta and epsilon
|
|
|
Geminin
|
Stops newly synthesized DNA from re-replicating into new strands
|
|
|
Flap endonuclease 1 and RNAase H
|
removes RNA primers
|
|
|
DNA polymerase Delta (δ)
|
Adds in new DNA bases to missing gaps on lagging strand
|
|
|
DNA Ligase
|
Comes in after DNA polymerase Delta (δ) and seals the new bases in place
|
|
|
Semi-conservative replication
|
During DNA replication each new daughter strand will have an original parent strand and a newly created daughter strand
|
|
|
Process of DNA replication (quick)
|
helicase unwinds -> ssbp binds -> topisomerase releases tension -> origin of replication complex binds -> RNA primase forms primer -> DNA poly alpha starts replication -> DNA poly delta/epsilon take over -> geminin binds -> RNA primers removed -> gaps filled in/sealed -> histones bind and wrap
|
|
|
Okazaki fragment
|
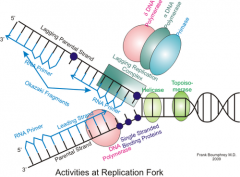
Short, newly synthesized DNA fragments that are formed on the lagging template strand
|
|
|
Fidelity
|
How accurate DNA polymerases can copy the DNA - held high due to exonuclease proofreading
|
|
|
3'-5' Exonuclease proofreading
|
Enzymatic activity that goes back and essentially removes and replaces mismatched nucleotides
|
|
|
S Phase promoting factor (SPF)
|
S-CDK-protein that initiates the start of the S-phase
|
|
|
Mitosis promoting factor (MPF)
|
M-CDK-protein that initiates the start of the mitosis-phase
|

