![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
Glucose uses what type of transport? |
|
|
|
Symport |
Na + Glucose Transport uses what type of tranport |
|
|
|
ECF |
1/3 fluid of cell |
|
|
|
Phospholipids, glycoshingolipids, cholesterol |
Major lipids in mamalian membranes |
|
|
|
Lipds, CHONS, CHO-containing molecules |
Membranes composed of |
|
|
|
Myelin (0.23) Mouse of liver cells (0.85 ratio) |
Membrane where lipid exceeds protein content |
|
|
|
Phosphatidic Acid |
Simplest form of PHOSPHOGLYCERIDE |
|
|
|
Phosphatidyl-choline |
Major Phosphoglyceride by mass in membranes |
|
|
|
Phosphoglyceride, Sphingomyelin |
2 Phospholipids |
|
|
|
GSL |
Sugar containing lipids built on backbone ceramide |
|
|
|
More kinks |
More double bonds means (in cell membranes) |
|
|
|
Straight tails |
Saturated fatty acids (CM component) |
|
|
|
02, C02 and N2 |
Substances that readily diffuse into the cell |
|
|
|
H2O |
Substance; very High permeability coefficient but impermeable to cell membrane |
High permeability = High Diffusion across |
|
|
1. Inner 2. Outer |
(inner/outer leaflet) 1. Phosphatidyl serine? 2. Phosphatidyl choline? |
Choline containing PL: OUTER AminoPL: inner |
|
|
1. Outer 2. Inner |
(inner/outer leaflet) 1. Sphingomyelin? 2. Phosphatidyl ethanolamine |
|
|
|
1. Direct contact 2. Transport from ER in vesicles 3. Phospholipid exchange CHON's |
How lipids enter membranes? (3) |
|
|
|
Integral CHON |
Membrane CHON that require detergents |
|
|
|
Integral |
Most membrane CHON's are: Integral? Peripheral? |
|
|
|
Integral CHON |
Membrane CHON with hydrophillic ends and inner hydrophobic region |
|
|
|
⬆unsaturared FA= ⬆Fluidity |
⬆fluidity = ⬆Permeability |
|
|
|
Lipid rafts |
Sp feature in CM; Involved in signal transduction |
|
|
|
Caveolae |
Sp feature in CM; derived from lipid rafts; flasked shaped facing cytosol |
Chons: Insulin receptor, Gprotein, folate receptor, endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
|
|
Tight jx's |
Sp feature in CM; loc below apical surfaces in epithelial cells; prevent diffusion of macromolec between cells |
Eg occludins, claudins, juctional adhesions molec's |
|
|
Thermal agitation Conc gradient Solubility of solute |
Simple diffusions is limited by certain factors (3) |
|
|
|
Only passive |
(Ion channels) Passive? Active? |
|
|
|
Either |
(transporters) Active? Passive? |
|
|
|
Na |
Which has higher charge density? Na or K? |
⬆charge density = larger shell of hydration= more difficult to diffuse |
|
|
Conc gradient Electrical potential Permeability coef Hydrostatic pressure gradient Temperature |
Factors affecting net diffusion (5) |
|
|
|
Conc gradient Amt of carriers avail Affinity of solute + carrier interaction Rapidity of conformational change for loaded/unloaded carriers |
Factors affecting rate of facilitated diffusion (4) |
|
|
|
Insulin |
⬆'s glucose transpo to fat and muscles ⬆'s AA transpo into liver |
Hormone, same with Glucocorticoid Hormones |
|
|
Growth hormones |
⬆'s AA transpo in all cells |
Hormone |
|
|
Ionophores |
Shuttles for the mov't of ions |
Eg valinomycin for k+ ions |
|
|
Ionophores |
Hydrophillic center and Hydrophobic periphery |
|
|
|
Aquaporin |
Form water channels that improve simple diffusion; permit passage of H20; Exlude (02 binding in lining) proton and (narrow) ion passage |
There are 10 aquaporin Ap2: nephrogenic diabetes inspidus |
|
|
Hydrolysis of ATP Electron movt Light |
Sources of energy for Active transpo (3) |
|
|
|
30% |
Maintenance of concentration gradient is what (%) of total energy expenditure |
|
|
|
ATPase |
Integral CHON activated by Na, K |
|
|
|
Calcium |
What stimulates both endocytosis and exocytosis |
|
|
|
1. Non selective 2. Selective |
(Selective/nonselective) 1. Fluid phase pinocytosis? 2. Absortptive:Receptor mediated? |
|
|
|
PIP2 (Phosphatidylinositol 4,5 biphosphate) |
Impt role in vesicle assembly |
|
|
|
GAP junx |
Permit direct transfer of small molecule; |
|
|
|
Gap junx |
Composed of connexins |
|
|
|
12, 2 |
How many connexins in connexon? How many hemiconnexon in " ? |
|
|
|
CV abnorm 1 type of deafness Xlinked charcot marie tooth disease |
Mutations in gene encoding connexins (3) |
|
|
|
Receptors Enzymes Transporters Ion channels Structural components |
CHONS in Plasma memrabe (5) |
|
|

Diseases/ pathologic states |
Abnormalities of membranes |
|
|

A. Fluid B. Absorptive |
Two types of pinocytosis |
|
|

Transporters aka carriers/permeases
Active transporters aka pumps |
Conparison of transporter and Ion channel |
|
|
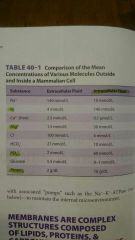
ICF = K, Mg, PO4, CHON ECF= Na, Ca, Cl, HCO, gluc |
Molecule concentrations in ECF, ICF |
|
|
|
Oligosaccharide chainsbof membrane glycoCHON |
Membrane abnormality: For metastasis of cancer cell |
|
|
|
PNH |
Membrane abno: Mutation resulting in ⬇ attachment of the GPI anchor |
|
|
|
Heriditary spherocytosis |
Mutations in the gene encodig spectrin |
|
|
|
Sphingomyelin |
2nd major class of Phospholipids |
|
|
|
a. Phosphoglyceride b. Sphingomyelin c. GSL |
Glycerol backbone is to ___a____ Sphingosine backbone is to ____b____ Ceramide backbone is to ___c____ |
|
|
|
A. Plasma membrane B. Mitochondria, golgi, nuclear membrane |
A. Main locations of cholesterol? B. Other minor locations? |
|
|

Enzymatic markers for diff membranes |
What is the enzamtic marker for plasma membrane? (3) Er? Golgi app? |
|
|
|
1. Small size molecule 2. Relatively lack of charge |
Why does H2O have a ⬆ permeability coefficient? |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic |
Many drugs are __________ (hydrophobic or hydrophillic?) |
To readily traverse the membrane |
|
|
Membrane Phospholipids |
Used as solvent for membrane CHON's to have it functional |
|
|
|
A. Negative B. Positive |
A. Polar AA's have ( pos/neg) hydrophobicities? B. Hydrophobic AA? |
|
|
|
Glycophosphatidylinositol structure (GPI) |
A number of cell surface CHON's are linked to the plasma membrane via |
|
|
|
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis SDS-PAGE |
A technique that separates membrane CHON's based on their molecular mass |
|
|
|
Translocases |
Transfer certain PL's (phosphatidylcholine) from the inner leaflet to the outer |
|
|
|
Globular |
Shape of integral CHON's |
|
|
|
Glycophorin A |
Simple membrane proteins eg span the membrane only once |
Everything else, many times |
|
|
SALT Solutions of high ionic strength |
Peripheral CHON's can be released or treated using? |
Eg. ankyrin (bound in band 3) Spectrin (cytoskeletal structure in RBC) |
|
|
Dont interact directly with the hydrophobic cores of the PL's in the bilayer |
Why do peripheral CHON's do not require detergents? |
|
|

Lipid membranes |
Formation of lipid membranes |
|
|
|
Mild sonication: treated to PL's eiyher natural or synthetic to form vesicles in which lipids form a bilayer |
How are liposomes formed? |
|
|
|
1. Lipid content can be varied 2. Purified membrane CHON's or enz can be incorporated 3. The environment can be controlled 4. Liposomes madee can be used to entrap certain compounds inside themselves (eg drugs and isolated genes) |
Advantages of using artificial membrane systems (4) |
|
|
|
Phospholipid |
Rapid during lateral diffusion |
|
|
|
True |
Cholesterol modifies fluidity of membranes? T/F |
|
|
|
Limiting fluidity |
Normal: ⬆ Tm = ⬆fluidity But with Cholesterol, ⬆Tm = ❓ |
|

