![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2 3 diphosphoglycerate |
Decreases affinity for oxygen
(Binds to deoxygenated Hb to help it release the last of its oxygen and unload' |
|
|
How is 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate made in RBCs? |
Bisphosphoglycerate mutase, which bypassed phosphoglycerate kinase in glycolysis and doesn't produce ATP |
|
|
Location of mRNA post processing such as intron splicing, 5' methyl guanine capping, 3' poly A tail, |
All in nucleus |
|
|
P bodies |
MRNA Related, cytosol |
|
|
Bilateral lens subluxation (dislocated), massive stroke (thrombosis), marfanoid habitus, osteoporosis |
Deficiency of cystathione synthetase, requires B6 (pyridoxine) cofactor
Homocystinuria, supplement with B6 |
|
|
N-acetyglutamate |
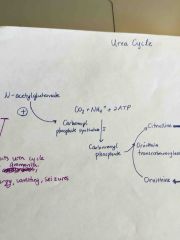
Activates carbamoyl phosphate synthase I, which makes carbamoyl phosphate (from CO2, ammonia, ATP) in the first step of urea cycle
Defect leads to ammonia build up, seizures, lethargy
|
|
|
Rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis (most specific) |
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP)
Tissue inflammation causes arginine residues in proteins such as vimentin to be converted into citrulline |
|
|
5' to 3' exonuclease activity |
DNA polymerase I
Exonuclease is excision of RNA primer and proofreading |
|
|
ApoE3 and ApoE4 defect |
Chylomicrons and VLDL, bind to hepatic Apo receptors
Defect is chylomicron accumulation (type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia) |
|
|
ApoB-100 |
LDL |
|
|
ApoC-II defect |
Lipoprotein lipase defect Type I: increased chylomicrons, TG, cholesterol
Pancreatitis, eruptive xanthomas, creamy supernatant layer |
|
|
ApoA-I defect |
Low HDL, increased free circulating cholesterol
ApoA-I needed for cholesterol esterification (decreases water solubility) by lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) |
|
|
ApoB-48 |
Chylomicron assembly and secretion by intestines |
|
|
ApoB100 |
LDL particle uptake by extra hepatic cells |
|
|
Pantothenic acid |
coenzyme A
Need for oxaloacetate to citrate in TCA cycle |
|
|
Glucokinase |
Only in beta cell of pancreas |
|
|
Glucokinase |
Only in beta cell of pancreas |
|
|
Hexokinase |
Glucose to G6P, all cells except pancreas |
|
|
Beta thalassemia |
Transcription, processing and translation (NOT PROTEIN FOLDING) of mRNA |
|
|
Supplement for orotic aciduria with megaloblastic anemia |
Uridine |
|
|
Dry skin, hepatosplenomegaly, liver tox, hair loss, visual changes, hair loss |
Vitamin A OVERDOSE |
|
|
Cheilosis (cracked lips), stomatitis (inflamed mouth mucosal), glossitis (smooth tongue) , dermatitis, corneal revascularization |
Vitamin B2 riboflavin deficiency |
|
|
Collagen processing OUTSIDE OF osteoblasts cell (after Golgi transport) |
Procollagen peptidases cleave terminal N and C
Concert procollagen into tropocollagen (way less soluble now)
Self assemble into fibrils
Lysyl oxidase form crosslinks |
|
|
NEUTRAL amino acids in urine, skin rash, ataxia (neuro) |
Hartnup disease
Loss of tryptophan leads to niacin deficiency (dermatitis, dementia, diarrhea)
Give niacin (B3) |
|
|
Homeobox |
Morphogenesis, segmental organization, limb locations |
|
|
High glucose |
Depleted cAMP
Inhibit lac operon |
|
|
Low glucose effect on lac |
Increase cAMP (glucagon also increase cAMP)
High cAMP makes cAMP-CAP, positive regulator of lac operon |
|
|
Receptor tyrosine kinases with INTRINSIC enzyme activity (they are themselves an enzyme that phosphorylates) |
MAP-kinase (autophosphoryation, then phosphorylates Ras)
Growth factor receptors: EGF, PDGF, FGF |
|
|
Receptor tyrosine kinases with INTRINSIC enzyme activity (they are themselves an enzyme that phosphorylates) |
Ras MAP-kinase (autophosphoryation, then phosphorylates Ras)
Growth factor receptors: EGF, PDGF, FGF, insulin |
|
|
Tyrosine kinase associated receptor (not an enzyme themselves), use JAK/STAT |
Receptor activated JAK, JAK phosphorylates STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription)
Cytokines receptors, growth hormone, prolactin, IL-2 |
|
|
JAK STAT |
Tyrosine kinase ASSOCIATED receptor |
|
|
JAK STAT |
Tyrosine kinase ASSOCIATED receptor |
|
|
MAP-Ras kinase |
Intrinsic enzyme activity, receptor tyrosine kinase |
|
|
Indirect bilirubin uptake by liver is |
Passive : organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) |
|
|
Indirect bilirubin uptake by liver is |
Passive : organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) |
|
|
Direct bilirubin secretion by liver |
ATP binding cassette protein (MRP2)
Active secretion
Defective in Rotor syndrome and Dubin Johnson, excess conjugated bilirubin in urine (flows back through passive diffusion through OATP) |
|
|
Gs path |
Increased cAMP leads to active Protein kinase A, leads to increase intracellular calcium and to inhibited myosin life chain kinase |

