![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Protein digestion |

3- intestinal phase: Intestinal peptidase (tripeptedase, dipeptedase) to amino acids |
|
|
|
Absorption of amino acids |

|

|
|
|
Sources of amino acid ? Amino acid pool can biosynthesis? |
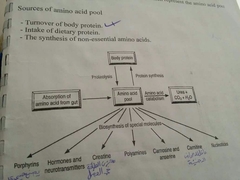
|
|
|
|
Transamination |
The transfer of an amino (-NH2) group from an amino acid to a keto acid. Interconversion of amino acids which Catalyzed by a group of enzymes called transaminases ( aminotransferase ) |
|
|
|
The salient features of transamination |
1- Require pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) vitamin B6 2- no free NH3 3- reversible reaction 4- both catabolic and anabolic of amino acids 5- finally concentrate nitrogen in glutamate 6- all amino acid except lysine, threonine and proline 7- serum transaminases are important for diagnosis and prognosis purpose 8- only two namely aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminases |
|
|
|
Diseases of increasing transamination |
-In liver diseases Increase SGPT - ALT -In myocardial infarction Increase SGOT - AST
|
|
|
|
Deamination |
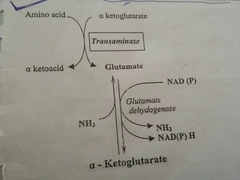
|
|
|
|
Urea cycle |

|
|
|
|
Hyperammonemia treatment |
Higher than 50 mg/dl ... Oral administration of antibiotics (neomycin) |
|

