![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Source of Acetyl-CoA (Oxidation of what?) |
Oxidation of FA, glucose, amino acids, acetate and ketone bodies |
|
|
alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (E1,E2,E3) |
E1: Oxoglutarate decarbxylase E2: Dihydrolipoyl succinyltransferase E3: Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase |
|
|
Cofactors of alpha-ketoglutarate complex and their functions |
1) Thiamine - pyrophosphate (helps to activate biological activity of enzyme) 2) FAD (catalyze redox reaction) 3) Lipoate |
|
|
Pyruvate dehyrogenase complex (E1,E2,E3) |
E1: Pyruvate dehyrogenase E2: Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase E3: Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase |
|
|
What's the function pyruvate dehydrogenase complex? |
It's linking the Glycolysis to Citric acid cycle |
|
|
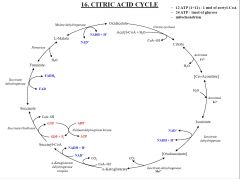
What's the first step in CAC? |
1) formation and oxidation of Isocitrate - Hydroxyl group of isocitrate is moved and oxidized to keto-group - Cleavage of carboxyl group => release of CO2 by oxidative decarboxylation |
|
|
What's the second step in CAC? |
2) alpha-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA - oxidative decarboxylation by alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex -energy in reduction stage of NADH |
|
|
What's the third step in CAC? |
3) Generation of GTP by substrate level phosphorylation - Succinyl-CoA => Succinate |
|
|
What's the last fourth step in CAC?
|
4) Oxidation of succinate to oxalacetate - Oxidation of succinate to Fumarate and formation of FADH2 out of FAD (succinate donates methylene group) - Dehydration of Fumarate to Malate -Alcohol group of malate is oxidized to keto-group => NaAD-NADH+H |
|
|
What's the Amphibolic? |
Anabolic + Catabolic |
|
|
Anabolic? |
*build up - acetyl-coa + oxalacetate = citrate |
|
|
Anabolic feature of CAC provides intermediates for biosynthesis? |
-Oxalacetate => Phosphoenolpyruvate => Glucose -Oxalacetate => aspartate, asparagine => pyrimidines -Malate => pyruvate-Succinyl-CoA => Haem, Porphyrins -Alpha-ketoglutarate => Glutamate, Glutamine => arginine, proline, histidine -Citrate => FA, steroids |
|
|
Catabolic? |
*break down- not only acetyl-coa is oxidized in the cycle - also other compounds, which are metabolized to the cycle intermediates, can also serve as substrate of the cycle |
|
|
Catabolic feature of CAC |
- Asparate, Aspargine can enter as Oxalacetate -Tyrosine, phenylalanine can enter as fumarate -isoleucine, methionine, valine, threonine -> propinoyl-coa => Succinyl-CoA-proline, histidine, arginine as alpha-ketoglutarate |
|
|
CAC |
|

