![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the distribution of water in the body |
Intracellular: 25L Extracellular: 15L -> 10L in intersisital fluid -> 5L in blood |
|
|
What is the polarity of water? |
Water is polar, oxygen has a partial negative charge and hydrogen has a partial negative charge |
|
|
What are some functions of water in the body |
Thermal regulation, regulating osmolality |
|
|
Define Osmolality |
The sum of all dissolved solutes in the blood |
|
|
Define an Acid |
A substance which donates a proton |
|
|
Define a Base |
A substance which accepts a proton |
|
|
Describe the dissociation of acids |
Weak acids only dissolve partially, strong acids dissociate fully |
|
|
What is Ka? What does Ka mean? |
Ka is the tendency of an acid to dissociate, a larger Ka the greater tendency to dissociate and therefore the stronger the acid |
|
|
At what point is a buffer most effective? |
When the pH=pKa the buffer is most useful because it is 50% dissociated, meaning there is equal concentration of acid and conjugate base |
|
|
What range are buffers most effective in? |
When the pH=pKa but also within +/-1 pH unit pf the pKa |
|
|
Describe the Carbonic Acid/Bicarbonate Buffer system |
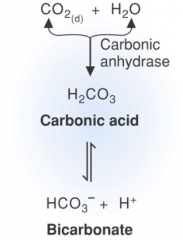
|
|
|
Causes of Metabolic Acidosis |
Diarrhea, production of acids (ex. lactic acid) |
|
|
Causes of Metabolic Alkalosis |
Vomiting, retaining bicarbonate |
|
|
Causes of Respiratory Acidosis |
CO2 retention (ex. emphysema) |
|
|
Causes of Respiratory Alkalosis |
Hyperventilation, drug overdoses, fever |

