![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the biochemical background of the Sanger sequencing?
|
The dideoxy nucleotides act as terminator for DNA replication of that specific strand due to its lack of 3’OH group. Making 4 in vitro systems, each having a different dideoxy nucleotide, we can determine the sequence by knowing which nucleotide was last in each case. Then electrophoresis is used to determine the sequence.
|
|
|
What is the main difference between Sanger sequencing and cyclic-array sequencing?
|
Cyclic array: multiple dna fragments can be sequenced at once, in vitro dna cloning is used. Sanger: modified bacteria and cloning vectors to amplify dna. Only use target gene of interest or whole genome. |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of cyclic-array sequencing compared to Sangersequencing?
|
Advantages for Cyclic array: Faster and no Modified E. coli are used
Disadvantages for Cyclic array: 10x Less accurate and only short sequences can be processed |
|
|
What is the most important gene of a helper virus used in gene therapy? Why don’t the recombinant viruses contain it?
|
Helper virus contains the genes for: gag, pol, env viral proteins. Recombinant viruses don’t contain it to ensure that the gene therapy is not infective
|
|
|
What is the role of virulence gen (vir) in producing genetic modified plants?
|
transfer and activation of Ti (tumor inducing) DNA into the host cell.
|
|
|
What is DNA fingerprinting? Give a question/problem that can be answered/solved by using this technique!
|
Using Common Characteristics of the genome that vary in individuals like a fingerprint to distinguish and identify, (via southern blot or PCR.) Used in paternity testing and Forensics.
|
|
|
What phenomenon can be detected by the yeast two-hybrid technique?
|
identification of protein-protein interactions. Two types of yeast cells, which contain two parts of a protein of interest, transfect ->the mutant yeast cells will have both proteins in one cell. |
|
|
What kind of molecular biology techniques are used to detect RFLP and STR?
|
RFLP: Southern Blot or PCR ,
STR: PCR |
|
|
What is the genetic background of the RFLP phenomenon?
|
Refers to a difference between samples of homologous DNA Molecules with different locations for restriction Enzymes, giving different lengths of DNA fragments when exposed to these enzymes
|
|
|
What supplementary technique is needed for confirming the findings and making the results of DNA-chip analysis quantitative?
|
quantitative PCR or modern blotting
|
|
|
What kind of macromolecule will be bound to the DNA chip and which cellular macromolecule can we determine in a gene expression study?
|
. cDNA will be bound to the DNA Chip and will hybridize with Oligo DNA fragments.
|
|
|
What is the most important advantage of DNA fingerprinting based on STR markers over DNA fingerprinting based on RFLP?
|
SNP have frequent occurrences, are relatively simple to locate
RFLP: need more sample to perform test |
|
|
What is the difference between transfection and transformation?
|
Transformation: Introduction of genes into yeast and bacterial cells (Prokaryotic),
Transfection: Introduction of genes into eukaryotic cells. |
|
|
What properties enable type 2 restriction endonucleases for creating recombinant constructs?
|
cleave the DNA at the recognition sequence, making it very predictable. Also, no ATP needed.
|
|
|
List the enzymes that are necessary for inserting a DNA sequence into the polylinker region of a mammalian expression plasmid.
|
DNA Ligase, Restriction Endonucleases, (Plasmid/cloning vector itself)
|
|
|
What is the main difference between Southern and Western blot techniques?
|
Southern blot: DNA identification, (use capillary force for blotting. , )
Western blot: Proteins identification,( use electrocution for blotting, no readioactivity for detection.) |
|
|
What does the expression ‘recombinant DNA’ mean?
|
DNA in which one or more segments or genes have been inserted, either naturally or by laboratory manipulation, from a different molecule or from another part of the same molecule, resulting in a new genetic combination
|
|
|
What problems may emerge if we insert into a vector a DNA fragment that is blunt at both ends?
|
the cloning is less efficient
fewer colonies are made it takes longer time |
|
|
What is the fundamental difference between conventional and real-time PCR?
|
conventional: end-point detection/result result in band gel time consuming, less presise RT-PCR display data after each cycle spesial dye, signal strencht increased quality and quantity is shown exact measurement |
|
|
Can we perform PCR amplification by using temperature-sensitive (i.e. not taq) DNA polymerase? If yes, how; if not, why?
|
Yes; Every cycle the sample would have to be heated to 90Co to denature the Double stranded DNA, but the Enzyme would also be denatured and would need to be reintroduced after cooling the sample back to 37Co.
|
|
|
How can DNA fragments be visualised during agarose gel electrophoresis?
|
. Ethidium bromide Most commonly used to dye
fragments are separated because of a charge. |
|
|
List the most important components of a plasmid type mammalian expression vector.
|
. ORI (Origin of replication),
Site of insertion promotor ribosomal binding site start and stop codon Poly A sequence, Gene of interest.
|
|
|
List the most important components of a cloning vector.
|
EcoRI site, Two genes coding for selective resistance, Ori and the gene of interest.
|
|
|
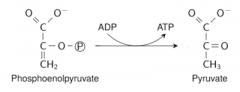
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate kinase -
|
|

